- Miles and Misra method
-
The Miles and Misra Method (or surface viable count) is a technique used in Microbiology to determine the number of colony forming units in a bacterial suspension or homogenate. The technique was first described in 1938 by Miles, Misra and Irwin who at the time were working at the LSHTM[1]. The Miles and Misra method has been shown to be precise[2].
Materials
- A calibrated dropping pipette, or automatic pipette, delivering drops of 20μl.
- Petri dishes containing nutrient agar or other appropriate medium.
- Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) or other appropriate diluent.
- Bacterial suspension or homogenate.
Method
- The inoculum / suspension is serially diluted by adding 1x of suspension to 9x of diluent. When the quantity of bacteria is unknown, dilutions should be made to at least 10-8.
- Three plates are needed for each dilution series, for statistical reasons an average of at least 3 counts are needed.
- The surface of the plates need to be sufficiently dry to allow a 20μl drop to be absorbed in 15-20 minutes.
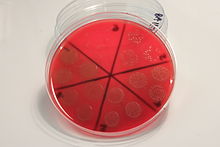
- Plates are divided into equal sectors (it is possible to use up to 8 per plate). The sectors are labelled with the dilutions.
- In each sector, 1 x 20 μl of the appropriate dilution is dropped onto the surface of the agar and the drop allowed to spread naturally. In the original description of the method a drop from a height of 2.5 cm spread over an area of 1.5-2.0 cm. It is important to avoid touching the surface of the agar with the pipette.
- The plates are left upright on the bench to dry before inversion and incubation at 37°C for 18 – 24 hours (or appropriate incubation conditions considering the organism and agar used).
- Each sector is observed for growth, high concentrations will give a confluent growth over the area of the drop, or a large number of small/merged colonies. Colonies are counted in the sector where the highest number of full-size discrete colonies can be seen (usually sectors containing between 2-20 colonies are counted).
- The following equation is used to calculate the number of colony forming units (CFU) per ml from the original aliquot / sample:
-
- CFU per ml = Average number of colonies for a dilution x 50 x dilution factor.
See also
References
- ^ Miles, AA; Misra, SS, Irwin, JO (1938 Nov). "The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood.". The Journal of hygiene 38 (6): 732–49. PMID 20475467.
- ^ Hedges, AJ (2002 Jun 25). "Estimating the precision of serial dilutions and viable bacterial counts.". International journal of food microbiology 76 (3): 207–14. PMID 12051477.
Categories:- Microbiology techniques
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.