- XB-42 Mixmaster
infobox Aircraft
name =XB-42 Mixmaster
type =Medium Bomber
manufacturer =Douglas Aircraft Company 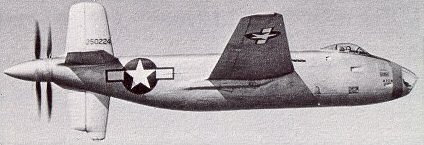
caption =XB-42
designer = Edward F. Burton
first flight =6 May avyear|1944
introduction =
retired =
status =Cancelled in 1948
primary user =United States Army Air Forces (intended)
more users =United States Air Force (intended)
produced =
number built =2
unit cost =US$13.7 million for the program, including B-43Knaack, Marcelle Size. "Post-World War II bombers, 1945-1973". Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History, 1988. ISBN 0-16-002260-6.]
variants with their own articles =The Douglas XB-42 Mixmaster was an experimental
bomber aircraft , designed for a high top speed. The unconventional approach was to mount the two engines within thefuselage driving a pair of contra-rotating propellers mounted at the tail, leaving the wing and fuselage clean and free of aerodynamics-reducing protrusions. Two prototype aircraft were built, but the end ofWorld War II changed priorities and the advent of the jet engine gave an alternative way toward achieving high speed.Design and development
Developed initially as a private venture, an unsolicited proposal was presented to the
United States Army Air Forces in May1943 . This resulted in an Air Force contract for two prototypes and one static test airframe, the USAAF seeing an intriguing possibility of finding a bomber capable of theB-29 Superfortress ' range without its size or cost.The aircraft mounted a pair of Allison V-1710-125 liquid-cooled V-12 engines behind the crew's cabin, each driving one of the twin propellors. Air intakes were in the wing leading edge. The undercarriage was tricycle and there was a long fin under the tail to prevent the propellers from striking the ground. The pilot and co-pilot sat under twin bubble canopies, and the bombardier sat in the extreme front behind a glass nose. Defensive armament was two 0.50 calibre machine guns each side in the trailing edge of the wing, which retracted into the wing when not in use. These guns were aimed by the copilot through a sighting station at the rear of his cockpit, The guns had a limited field of fire and could only cover the rear, but with the plane's high speed it was thought unlikely that intercepting fighters would be attacking from any other angle. Two more guns were fitted to fire directly forward. A proposed attack variant would have been armed with 16 machine guns or a 75 mm cannon and two machine guns. Winchester 2005, p. 27.]
Testing
The first XB-42 prototype flew on
6 May 1944. Performance was excellent, being basically as described in the original proposal; as fast or faster than thede Havilland Mosquito but with defensive armament and twice the bombload. The twin bubble canopies proved a bad idea as communications were adversely affected and a single bubble canopy was substituted after the first flight. Testing revealed the XB-42 suffered from some instability as excessive yaw was encountered, [ Winchester 2005, p. 26.] vibrations and poor engine cooling - all problems that could probably have been dealt with.The end of
World War II , though, allowed the Air Force to consider possibilities in a little more leisure and it was decided to wait for the development of better jet bombers rather than continue with the B-42 program.The XB-42 set a speed record of 433.6 mph from
Long Beach, California toWashington DC in December 1944.One of the XB-42 aircraft had been destroyed in a crash, but the other was used in flight test programs, including fitting uprated engines and underwing
turbojet s (1600 lb/7.1kN thrust), making it the XB-42A. In this configuration, it reached 488 mph (785 km/h). Damaged in a hard landing in1947 after 22 flights, it was repaired but never flew again.urvivors
The prototype was struck off charge in
1949 and was given to theNational Air and Space Museum , in whose care it remains although it has never been placed on display. The wings were removed for transport but have since been inadvertently lost.Specifications (XB-42)
aircraft specifications
plane or copter?=plane
jet or prop?=prop
crew=
length main=53 ft 8 in
length alt=16.4 m
span main=70 ft 6 in
span alt=21.5 m
height main=18 ft 10 in
height alt=5.7 m
area main=555 ft²
area alt=51.6 m²
empty weight main=20,888 lb
empty weight alt=9,475 kg
loaded weight main=33,200 lb
loaded weight alt=15,060 kg
max takeoff weight main=35,702 lb
max takeoff weight alt=16,194 kgengine (prop)=
Allison V-1710 -125
type of prop=V12 engine s
number of props=2
power main=1,800 hp
power alt=1,300 kW eachmax speed main=410 mph
max speed alt=660 km/h
range main=
* Combat range: 1,800 mi
range alt=2,900 km)
* Ferry range: 5,400 mi (8,700 km
ceiling main=29,400 ft
ceiling alt=8,960 m
climb rate main= ft/min
climb rate alt= m/s
loading main=59.8 lb/ft²
loading alt=292 kg/m²
power/mass main=0.11 hp/lb
power/mass alt=0.18 kW/kgguns=4× .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns
bombs=8,000 lb (3,600 kg)ee also
aircontent
related=
*XB-43 Jetmaster sequence=
* "B-" sequence: XB-39 - YB-40 - XB-41 - XB-42 - XB-43 - XB-44 - B-45
* "A-" sequence: A-39 - A-40 - A-41 - XA-42 - XA-43 - A-44 - XA-45lists=
*List of attack aircraft
*List of bomber aircraft
*List of military aircraft of the United States see also=
*Pusher configuration References
Notes
Bibliography
* Winchester, Jim. "The World's Worst Aircraft: From Pioneering Failures to Multimillion Dollar Disasters". London: Amber Books Ltd., 2005. ISBN 1-904687-34-2.
External links
* [http://www.nationalmuseum.af.mil/factsheets/factsheet.asp?id=2653 XB-42]
* [http://www.nationalmuseum.af.mil/factsheets/factsheet.asp?id=2654 XB-42A]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
