- Network access point
-
A Network Access Point (NAP) was a public network exchange facility where Internet Service Providers (ISPs) connected with one another in peering arrangements. The NAPs were a key component in the transition from the NSFNET era when many networks were government sponsored and commercial traffic was prohibited to the commercial Internet providers of today. They were often points of considerable Internet congestion.
History
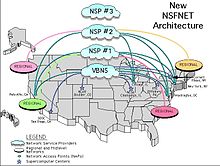
The four Network Access Points (NAPs) were defined under the U.S. National Information Infrastructure (NII) document as transitional data communications facilities at which Network Service Providers (NSPs) would exchange traffic, in replacement of the publicly-financed NSFNET Internet backbone.[1] The National Science Foundation let contracts supporting the four NAPs, one to MFS Datanet for the preexisting MAE in Washington, D.C., and three others to Sprint, Ameritech, and Pacific Bell, for new facilities of various designs and technologies, in New York (actually Pennsauken, New Jersey), Chicago, and California, respectively.[2] As a transitional strategy, they were effective, giving commercial network operators a bridge from the Internet's beginnings as a government-funded academic experiment, to the modern Internet of many private-sector competitors collaborating to form a network-of-networks, anchored around the Internet Exchange Points we know today.
This was particularly timely, coming hard on the heels of the ANS CO+RE controversy,[3][4] which had disturbed the nascent industry, led to congressional hearings,[5] resulted in a law allowing NSF to promote and use networks that carry commercial traffic,[6] prompted a review of the administration of NSFNET by the NSF's Inspector General (no serious problems were found),[7] and caused commercial operators to realize that they needed to be able to communicate with each other independent of third parties or at neutral exchange points.
Today, the phrase "Network Access Point" is of historical interest only, since the four transitional NAPs disappeared long ago, replaced by modern IXPs, though in Spanish-speaking Latin America, the phrase lives on to a small degree, among those who conflate the NAPs with IXPs.
See also
- Commercial Internet eXchange (CIX)
- Federal Internet Exchange (FIX)
- Internet exchange point (IXP)
- very high speed Backbone Network Service (vBNS)
- Commercial traffic and Controversy sections of the NSFNET article
References
- ^ NSF Solicitation 93-52 - Network Access Point Manager, Routing Arbiter, Regional Network Providers, and Very High Speed Backbone Network Services Provider for NSFNET and the NREN(SM) Program, May 6, 1993
- ^ E-mail regarding Network Access Points from Steve Wolff (NSF) to the com-priv list, sent 13:51 EST 2 March 1994
- ^ The Cook Report on the Internet
- ^ "A Critical Look at the University of Michigan's Role in the 1987 Merit Agreement", Chetly Zarko in The Cook Report on the Internet, January 1995, pp. 9-17
- ^ Management of NSFNET, a transcript of the March 12, 1992 hearing before the Subcommittee on Science of the Committee on Science, Space, and Technology, U.S. House of Representatives, One Hundred Second Congress, Second Session, Hon. Rick Boucher, subcommittee chairman, presiding
- ^ Scientific and Advanced-Technology Act of 1992, Public Law No: 102-476, 43 U.S.C. 1862(g)
- ^ Review of NSFNET, Office of the Inspector General, National Science Foundation, 23 March 1993

This computer networking article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.