- Mastodon (steam locomotive)
-
Mastodon 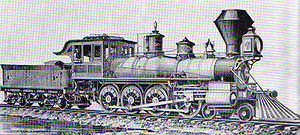
Artist drawing of CPR #229, "Mastodon." Power type Steam Builder Central Pacific's Sacramento, California, shops Serial number 20 Build date April 1882 Configuration 4-8-0 Gauge 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) (standard gauge) Driver diameter 55 in dia Weight on drivers 81,000 lb Locomotive weight 105,850 lb Fuel capacity 10,700 lb (4,900 kg) Water capacity 2,500 USgal (9,500 l; 2,100 imp gal) Boiler pressure 135 psi Heating surface:
Total1,355.3 sq ft (125.91 m2) Cylinder size 19 in dia × 30 in stroke Tractive effort 22,595 lbf Career Central Pacific,
Southern PacificNumber 229; renum. 1950 in 1891; renum. 2800 in 1901; renum. 2925 in 1906 Nicknames Mastodon First run April 1882 Scrapped June 29, 1935, Brooklyn shops, Portland, Oregon Mastodon was the unofficial name of the Central Pacific Railroad's number 229, the world's first successful 4-8-0 steam locomotive.
History and career
The engine was designed and built by the road's master mechanic, Andrew Jackson "A.J" Stevens at Sacramento Locomotive Works in 1882. The locomotive had two highly unusual features: the firebox shape and the steam distribution.
The rear end of the firebox was depressed so that the outer shell was below the water level, leaving no clear steam space. The roof was sloped down towards the back so that steam bubbles would flow forward till they reached the upper vertical part of the backplate which was in two pieces. The fire-hole door was in the lower backplate. The firebox was very long, 13ft 4 3/4in to the tubeplate, the grate being 9ft in length. It is not clear what object Stevens had in mind when having this abnormal construction, which must have costly to build and maintain: it did give more room in the cab. The special valve gear operated four slide valves for each cylinder, two, one for each end, [other locomotives had a single slide valve in the centre] being worked by Stephenson valve gear, but used for reversing only, and two more, on top of the first two, for controlling the cutoff, these being operated by a third eccentric through a rocking lever with a sliding block on one arm. The use of a double valve gear is reminiscent of Centipede, but separate valves for each end of the cylinder were novel on a locomotive. This valve gear gave very good steam distribution even at short cut-offs; short as understood for a saturated-steam engine with a boiler pressure low by modern standards. At long cut-off and a speed of 8mph the indicated mean effective pressure was 124lb/sq in, which is over 91 per cent of the boiler pressure of 135lb/sq in, that is to say more than the 85 per cent normally used to calculate the tractive effort at starting.—Carling, 4-8-0 Tender LocomotivesThe only other locomotives to use such a valve gear were the 20 copies of Mastodon (see below) and CPR #237 El Gobernador. After being readied for its initial shakedown run, the engine met with a minor mishap in which its large "balloon" stack was knocked away from the boiler. During all the careful preparations, apparently nobody noticed that the stack was nearly a foot taller than the doors to the roundhouse. The problem was fixed and an impressive series of trials on the steep grades of the Sierra Nevada Mountains soon followed, in which it easily outperformed the smaller 4-4-0 and 4-6-0 engines used by the railroad in those days. Later, Mastodon was sent east to the Cooke Locomotive Works, along with blueprints and men who had built the engine, where more than 20 copies were produced; these were identical except for having their cylinder bore increased to 20-inches (from Mastodon's 19). The success of this engine inspired railroad president Leland Stanford to instruct Stevens to build an even larger locomotive, which would be the largest the world had ever seen up until that time. This engine, a 4-10-0 named El Gobernador (CPRR #237), looked virtually identical to Mastodon, with the exception of being longer and having an additional pair of driving wheels. Unfortunately, this engine, unlike its predecessor, was doomed to failure.
Sometime in the early 20th century, No. 229 (now renumbered as Southern Pacific 2925) was converted from wood to oil-firing and was later assigned to the Oregon lines. Despite its historical significance, the engine was broken up for scrap at the Brooklyn Shops in Portland, Oregon, in the mid-1930s.
References
- Diebert, Timothy S. and Strapac, Joseph A. (1987). Southern Pacific Company Steam Locomotive Conpendium. Shade Tree Books. p. 48. ISBN 0-930742-12-5.
- Dunscomb, Guy L. (1963). A Century of Southern Pacific Steam Locomotives 1862 - 1962. Guy L. Dunscomb & Son.
- Carling, D. Rock (1972). 4-8-0 Tender Locomotives. Drake Publishers Inc.. ISBN 0-87749-150-X.
Categories:- Southern Pacific Railroad locomotives
- 4-8-0 locomotives
- Steam locomotives of the United States
- Railway locomotives introduced in 1882
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
