- Sisoridae
Taxobox
name = Sisoridae
fossil_range =Pliocene - Recenet
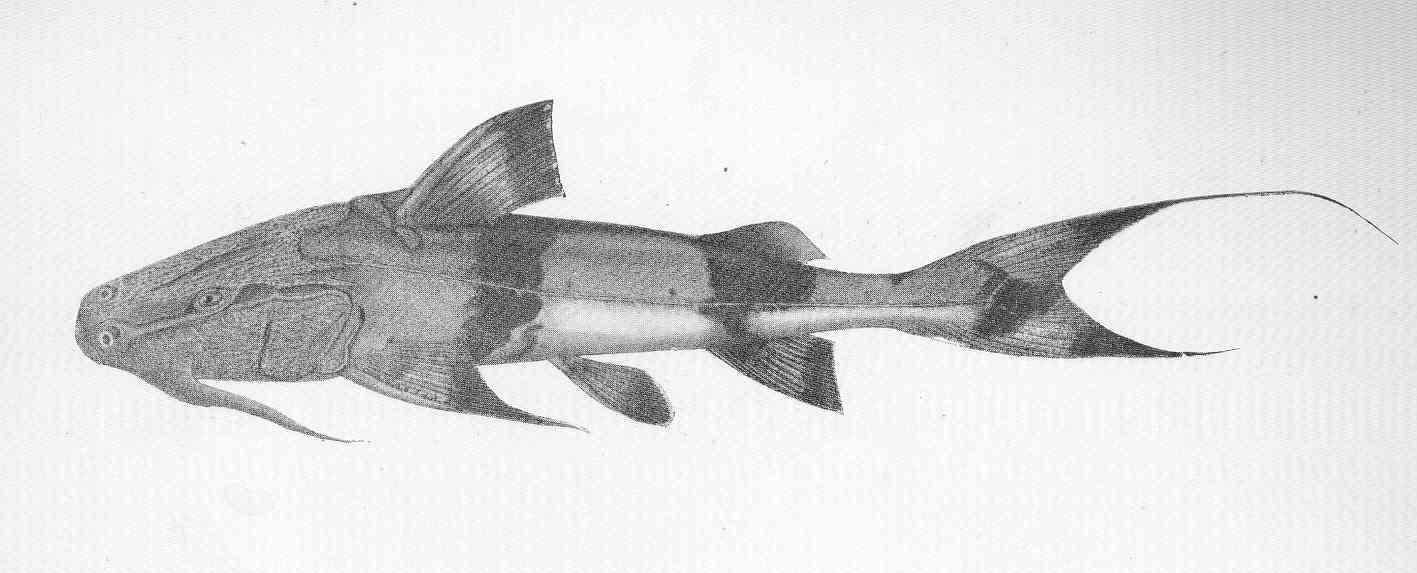
image_width = 250px
image_caption = "Bagarius yarrelli "
regnum =Animalia
phylum =Chordata
classis =Actinopterygii
ordo =Siluriformes
superfamilia =Sisoroidea
familia = Sisoridae
familia_authority =Bleeker ,1858
subdivision_ranks = Generacite journal|url=http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2006f/zt01345p096.pdf|title=Genera of the Asian Catfish Families Sisoridae and Erethistidae (Teleostei: Siluriformes)|first=Alfred W.|last=Thomson|coauthors=Page, Lawrence M.|journal=Zootaxa |volume=1345|pages=1–96|year=2006|format=PDF ]
subdivision = Subfamily Sisorinae
"Bagarius "
"Gagata "
"Gogangra "
"Nangra "
"Sisor "
Subfamily Glyptosterninae
Tribe Glyptothoracini
"Glyptothorax "
Tribe Glyptosternina
"Euchiloglanis "
"Exostoma "
"Glaridoglanis "
"Glyptosternon "
"Myersglanis "
"Oreoglanis "
"Parachiloglanis "
"Pareuchiloglanis "
"Pseudexostoma "
Tribe Pseudecheneidina
"Pseudecheneis "Sisoridae is a family of
catfish es (order Siluriformes). These Asian catfish live in fast-moving waters and often have adaptations that allow them to adhere to objects in their habitat.Taxonomy
Sisoridae is recognized as a natural, monophyletic group based on morphological and molecular evidence. Sisoridae is divided into two subfamilies, Sisorinae and Glyptosterninae (glyptosternoids). Sisorinae contains the five genera "
Bagarius ", "Gagata ", "Gogangra ", "Nangra ", and "Sisor ". Glyptosterninae contains three tribes. Glyptothoracini contains only the genus "Glyptothorax " and Pseudecheneidina contains only the genus "Pseudecheneis ". The remaining genera, "Euchiloglanis ", "Exostoma ", "Glaridoglanis ", "Glyptosternon ", "Myersglanis ", "Oreoglanis ", "Parachiloglanis ", "Pareuchiloglanis ", and "Pseudexostoma ", are contained in the tribe Glyptosternina. Themonophyly of the entire family and the tribe Glyptosterninae are well supported by osteological morphology and molecular data.In the genera "Glyptothorax" (tribe Glyptothoracini) and "Pseudecheneis" (tribe Pseudecheneidina), the species have a thoracic adhesive apparatus to attach to objects in the stream bed; in "Glyptothorax", grooves of this apparatus run parallel or oblique to the axis of the body, while in "Pseudecheneis" groovs run transverse to the axis of the body. The thoracic adhesive apparatus is not present in the other sisorid genera. The paired fins may be
plait ed to form an adhesive apparatus in "Pseudecheneis", glyptosternoids, and variably in "Glyptothorax". Thus, glyptosternoids lack a thoracic adhesive apparatus but do have plaited paired fins, and members of the subfamily Sisorinae lack either a thoracic adhesive apparatus or plaited paired fins.The monophyly of certain glyptosternoid genera is doubtful. The
paraphyly of "Pareuchiloglanis", "Oreoglanis", and "Pseudexostoma" (with the possible inclusion of "Myersglanis" and "Parachiloglanis") has been demonstrated and a rediagnosis of glyptosternine genera is needed.cite journal|url=http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2004f/zt00428.pdf|title=Two glyptosternine catfish (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from Vietnam and China|first=Heok Hee|last=Ng|journal=Zootaxa |volume=428|pages1-12|format=PDF ]Evidence from a 2007 molecular analysis supports polyphyly of "Pareuchiloglanis". "Glaridoglanis" might be a basal member of the tribe Glyptosternina. "Pseudecheneis" may be placed in the tribe Glyptosternina, but its sister-group relationship between it and the monophyletic glyptosternoids cannot be rejected.cite journal|title=Phylogenetic relationships of the Chinese sisorid catfishes: a nuclear intron versus mitochondrial gene approach|first=Xianguang|last=Guo|coauthors=He, Shunping; Zhang, Yaoguang|journal=Hydrobiologia|year=2007|volume=579|pages=55–68|doi=10.1007/s10750-006-0369-8]
It has been proposed to move the genera of
Erethistidae into Sisoridae. [cite journal|url=http://silurus.acnatsci.org/ACSI/library/biblios/2007_Ferraris_Catfish_Checklist.pdf|title=Checklist of catfishes, recent and fossil (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes), and catalogue of siluriform primary types|first=Carl J., Jr.|last=Ferraris|journal=Zootaxa |volume=1418|pages=1–628|year=2007|format=PDF ]Distribution
Sisorids inhabit freshwater and originate from southern
Asia , fromTurkey andSyria to SouthChina andBorneo , primarily in the Oriental region.cite book|title=Fishes of the World |last=Nelson|first=Joseph S.|publisher=John Wiley & Sons , Inc|year=2006|isbn=0-471-25031-7] Glyptosterninae is distributed from theCaucasus to China.cite journal|url=http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2005f/zt01047p019.pdf|title=Two new species of "Pseudecheneis", rheophilic catfishes (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from Nepal|first=Heok Hee|last=Ng|coauthors=Edds, David R.|journal=Zootaxa |volume=1047|pages=1–19|year=2005|format=PDF ] Most glyptosternine genera are found in China, with the exception of "Myersglanis". Glyptosternoid catfish species have restricted distributions, and many apparently wide-ranging species have been shown to consist of more than one species, each with restricted distributions.cite journal|url=http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2006f/zt01254p068.pdf|title=The identity of "Pseudecheneis sulcata" (M’Clelland, 1842), with descriptions of two new species of rheophilic catfish (Teleostei: Sisoridae) from Nepal and China|first=Heok Hee|last=Ng|journal=Zootaxa |volume=1254|pages=45–68|year=2006|format=PDF ] Sisorids are mostly small forms inhabit mountain streams.Fossil record and biogeography
The oldest known sisorid fossil is "B. bagarius" found in Sumatra and India of the
Pliocene . The origin of glyptosternoid fishes could be in the later Pliocene. Another study proposes glyptosternoids possibly originated in theOligocene -Miocene boundary (19–24 Mya) and radiated from the Miocene toPleistocene along with several rapid speciation events in a relatively short time. The three great uplifts of theQinghai /Tibet Plateau destroyed the pattern of river systems in the late Pliocene to the early Pleistocene. The ancestor of "Euchiloglanis" originated from the allied "Glyptosternon" in the second uplift and "Pareuchiloglanis", "Pseudexostoma", "Oreoglanis", "Exostoma", and "Glaridoglanis" originated with the third uplift. The "Exostoma" group ("Exostoma", "Pseudexostoma", and "Oreoglanis") originated after the outline of the Qinghai/Tibet Plateau was formed. The speciation of this group was not strong and the distribution limited.cite journal|url=http://rmbr.nus.edu.sg/rbz/biblio/55/55rbz147-155.pdf|title=A Review of the Catfish Genus "Pseudexostoma" (Siluriformes: Sisoridae) with Description of a New Species from the Upper Salween (Nujiang) Basin of China|first=Wei|last=Zhou|coauthors=Yang, Ying; Li, Xu; Li, Ming-Hui|journal=The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology|year=2007|volume=55|issue=1|pages=147–155|format=PDF ]Description
Most of these fish have four pairs of
barbels and a largeadipose fin . The maximum size is 2metre s. In all fish except those of the subfamily Sisorinae, some sort of adhesive apparatus, either in the form of a thoracic adhesive apparatus or inplait ed paired fins, allow the fish to adhere to objects.References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
