- Santa Barbara Municipal Airport
Infobox Airport
name = Santa Barbara Airport
nativename =
nativename-a =
nativename-r =
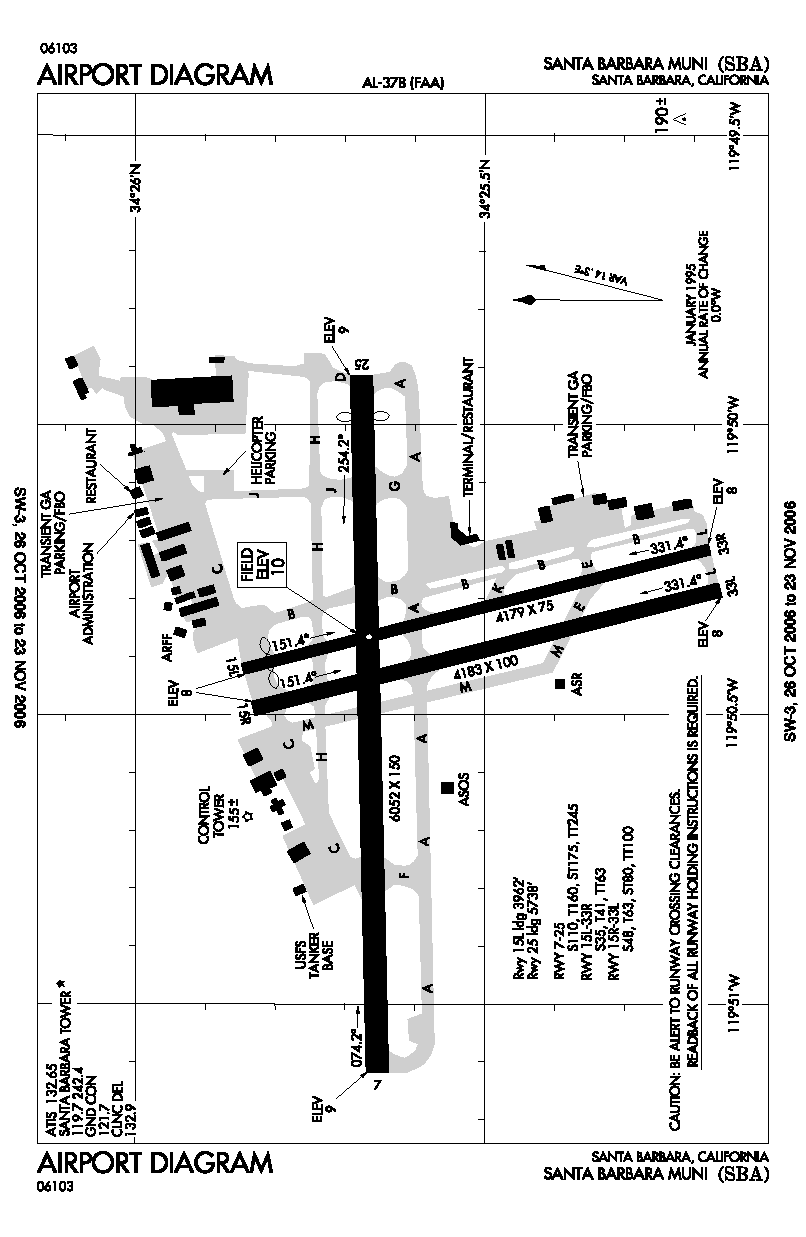
image-width =
caption =
IATA = SBA
ICAO = KSBA
FAA = SBA
type = Public
owner =
operator = City of Santa Barbara
city-served = Santa Barbara, California
location =
elevation-f = 10
elevation-m = 3
coordinates = Coord|34|25|34|N|119|50|25|W|type:airport_region:US
website =
metric-elev =
metric-rwy =
r1-number = 7/25
r1-length-f = 6,052
r1-length-m = 1,845
r1-surface =Asphalt
r2-number = 15L/33R
r2-length-f = 4,179
r2-length-m = 1,274
r2-surface = Asphalt
r3-number = 15R/33L
r3-length-f = 4,183
r3-length-m = 1,275
r3-surface = Asphalt
stat-year =
stat1-header =
stat1-data =
stat2-header =
stat2-data =
footnotes =Santa Barbara Airport Airport codes|SBA|KSBA|SBA, also known as Santa Barbara Municipal Airport, is a public
airport located convert|7|mi|km|0 west of downtown Santa Barbara,California in Santa Barbara County, USA.The airport is adjacent to the
University of California, Santa Barbara and the city of Goleta. However, the land that the airport sits on was annexed to the city of Santa Barbara by a convert|7|mi|km|0 long, convert|300|ft|m|-1 wide corridor, most of which lies under the Pacific Ocean. Much of the airport is between 10 and 15 feet above sea level, and it is bordered by thewetland area known as the Goleta Slough.Many airlines serve the Airport as of early 2005 with 45 daily departures to ten U.S. cities (see below). In 2005, an estimated 900,000 passengers used the airport.
History
Santa Barbara's aviation history began in 1914 when Lincoln Beachey flew an airplane across Goleta Valley. Two years later the Loughead Brothers, who later changed their name to Lockheed, established a seaplane factory on State Street and constructed a wooden ramp on West Beach to launch their planes. In 1928, Gordon Sackett and Royce Stetson landed a Hisso-powered airplane in a cow pasture near the corner of Hollister and Fairview Avenues and set up a flight school on the spot. That first airstrip marked the beginning of what was to become the Santa Barbara Municipal Airport.
As airplane manufacturing grew in the late 1930s that simple airstrip developed into an airfield. Western General set up shop and began producing Meteor airplanes, while Santa Barbara Airways' founder Frederick Stearns II built two additional runways and two large hangars. Stearns also installed the first radio equipment at the airfield. [1] http://www.flysba.com/?pageID=99]
Commercial service began in 1932 with
Pacific Seaboard Airlines , andUnited Airlines inaugurated service from Santa Barbara/Goleta in 1936.As the prospect of war escalated the United States Government established a defense program to construct 250 airports across the country on a cost-sharing basis with local governments. T.M. Storke secured Santa Barbara's enrollment in the program, and in 1941 groundbreaking ceremonies were held for the Santa Barbara Municipal Airport. The Spanish-style terminal building, commissioned by United Airlines in 1942 was designed by William Edwards and Joseph Plunkett, an architectural team whose work, including the Arlington Theatre and the National Armory, helped shape the Mediterranean style of the city.
In 1947, the Santa Barbara Flying Club was formed to promote general aviation in the region. The club is still going strong as a registered non-profit meeting monthly at the [http://www.flysba.com/?pageID=51 Visitor Center] , and working with other groups and businesses to continue making Santa Barbara a great place to fly.
In the 1951 war film
Flying Leathernecks ,John Wayne 's character was stationed in Goleta. The movie references the airbase as being in Goleta because, during War World II, the airbase had not yet been annexed by Santa Barbara. There is a short clip of the airport and surrounding area in the movie.Three runways are currently used: 7/25 and two parallel runways 15/33. In addition to these runways, the airport originally had an additional strip: runway 3/21. The development of the
University of California, Santa Barbara (to the southwest) and the construction of hangars in support of production of theAero Spacelines Super Guppy (to the northeast) were factors in the abandonment and eventual removal of this runway.Future expansion
In early 2007, Santa Barbara executives tentatively approved a $60 million project to expand the terminal, while keeping the "Santa Barbara Airport Experience” by building around the original 1942 terminal. Some of the features of the redesign are passenger loading bridges, making it so everything is contained in one building including car rentals, security, gates and the baggage tents [2] http://flysba.com/pdf/terminal_project.pdf] [http://www.flysba.com/pdf/Council%20Terminal%20Pres%205-17-05.pdf Aviation Facilities Plan ] ]
Airlines and destinations
*
Alaska Airlines
**Horizon Air (Portland (OR), Sacramento [begins November 9] , Seattle/Tacoma)
*Allegiant Air (Las Vegas)
*American Airlines
** American Eagle (Dallas/Fort Worth, Los Angeles)
*Delta Air Lines
**Delta Connection operated bySkyWest Airlines (Salt Lake City)
*United Airlines
**United Express operated by SkyWest (Denver, Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Jose)
*US Airways
**US Airways Express operated byMesa Airlines (Las Vegas, Phoenix)References
* [http://www.flysba.com/ Santa Barbara Airport] (official site)
*FAA-airport|ID=SBA|use=PU|own=PU|site=02235.*AExternal links
*Webcams at [http://www.bookstore.ucsb.edu/home/webcams.html UCSB Bookstore] offer live views of the airport environment.
*The [http://santabarbaraflyingclub.org/ Santa Barbara Flying Club] is a registered non-profit organization founded in 1947.
*FAA-diagram|00378
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
