- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Infobox_Disease
Name = PAGENAME
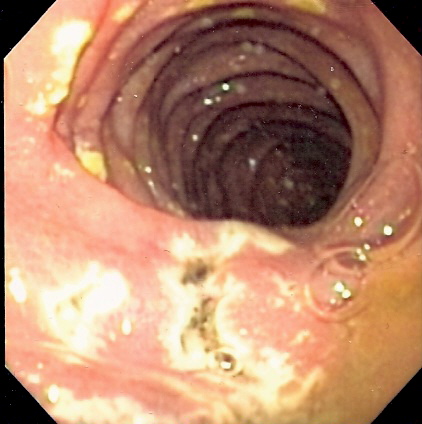
Caption = Endoscopy image of multiple smallulcer s in the distalduodenum in a patient with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
DiseasesDB =
ICD10 = ICD10|E|16|4|e|15
ICD9 = ICD9|251.5
ICDO =
OMIM =
MedlinePlus = 000325
eMedicineSubj = med
eMedicineTopic = 2437
eMedicine_mult = eMedicine2|ped|2472 | MeshID = D015043Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a disorder where increased levels of the hormone
gastrin are produced, causing thestomach to produce excesshydrochloric acid . Often the cause is a tumor (gastrinoma ) of theduodenum orpancreas producing the hormonegastrin . Gastrin then causes an excessive production of acid which can lead to peptic ulcers (in almost 95% of patients)Gastrin works on stomach
parietal cell s causing them to secrete morehydrogen ion s into the stomach lumen. In addition, gastrin acts as a trophic factor for parietal cells, causing parietal cell hyperplasia. Thus there is an increase in the number of acid-secreting cells, and each of these cells produces acid at a higher rate. The increase in acidity contributes to the development ofpeptic ulcer s in the stomach and duodenum.High acid levels lead to multipleulcer s in the stomach and small bowel.Patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome may experience abdominal pain and
diarrhea . The diagnosis is also suspected in patients without symptoms who have severe ulceration of the stomach and small bowel, especially if they fail to respond to treatment.Gastrinomas may occur as single tumors or as multiple, small tumors. About one-half to two-thirds of single gastrinomas are
malignant tumors that most commonly spread to theliver andlymph node s near the pancreas and small bowel. Nearly 25 percent of patients with gastrinomas have multiple tumors as part of a condition calledmultiple endocrine neoplasia type I (MEN I). MEN I patients have tumors in theirpituitary gland andparathyroid gland s in addition to tumors of the pancreas.ymptoms
*
epigastric pain (stomachache)
*vomiting blood (hematemesis ) (occasional)
*difficulty in eating
*diarrhea
*steatorrhea Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is made by several laboratory tests and imaging studies.
Laboratory tests:
*secretin stimulation test, which measuresgastrin levels in response to secretin
* fasting gastrin levels
* antral acidityTherapy
Proton pump inhibitor s (such asomeprazole andlansoprazole ) and histamineH2-receptor antagonist s (such asfamotidine andranitidine ) are used to slow down acid secretion. If possible the tumours should be surgically removed, or treated withchemotherapy .Octreotide can be used to slow down acid secretion.History
This syndrome was first described in
1955 by R Zollinger and E Ellison.cite journal |author=Zollinger RM, Ellison EH |title=Primary peptic ulcerations of the jejunum associated with islet cell tumors of the pancreas |journal=Ann. Surg. |volume=142 |issue=4 |pages=709–23; discussion, 724–8 |year=1955 |pmid=13259432|doi=10.1097/00000658-195510000-00015]Footnotes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
