- Israel Defense Forces ranks
-
Israel Defense Forces _ 

The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) have a unique rank structure. Because the IDF is an integrated force, ranks are the same in all services (there is no differentiation between army, navy, air force, etc.) The ranks are derived from those of the paramilitary Haganah developed in the Mandate period to protect the Yishuv. This origin is reflected in the slightly-compacted rank structure; for instance, the Chief of Staff (Ramatkal) is seemingly only equivalent to a Lieutenant General in other militaries.
Contents
Current ranks
Category Rank name[1] , rank equivalent and Nato code Insignia קצינים ראשים
Supreme Officers
or
General Officers(רב-אלוף (רא"ל
Rav aluf (Ra'al)
(Chief of Staff, Command of the Army or Army Group)
(Lieutenant General, NATO OF-9–OF-10)
(Rav Aluf means 'Arch-General', which would be equal to a Field Marshal or Five Star General in other armies and equivalent to NATO OF-10.)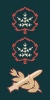
אלוף
Aluf
(Commanding General, Command of the Branch of Arms, Corps)
(Major General, equivalent to NATO OF-8–OF-9)
(Aluf, meaning "General", translates as "High Commander".)
(תת-אלוף (תא"ל
Tat aluf (Ta'al)
(Commanding General, Command of the Service of Arms, Corps, Division, Brigade)
(Brigadier General, equivalent to NATO OF-7–OF-8)
(Tat aluf translates as "Subordinate-General")
קצינים בכירים
Senior Officers
or
Field Grade Officers(אלוף משנה (אל"מ
Aluf mishne (Alam)
(Regiment or Brigade Commander)
(Colonel or Brigadier, equivalent to NATO OF-6)
(Aluf mishne translates as "Junior General")
(סגן-אלוף (סא"ל
Sgan aluf (Sa'al)
(Battalion Commander)
(Lieutenant Colonel, equivalent to NATO OF-5)
(Sgan Aluf translates as "Deputy-General")
(רב סרן (רס"ן
Rav seren (Rasan)
(Executive Officer of a Battalion; Company or Battery Commander)
(Major, equivalent to NATO OF-4)
(Rav Seren means "Arch-Captain")
קצינים זוטרים
Ktzinim
Junior Officers
or
Company Grade Officersסרן
Seren
(Company Commander)
(Captain, equivalent to NATO OF-3)
(Seren, meaning "Captain", translates as "Captain" or "Commander")
סגן
Segen — since 1951
((סגן ראשון (סג"ר
Segen rishon (Sagar) — 1948–51
(Company Executive Officer; Platoon Commander)
(Lieutenant, equivalent to NATO OF-2)
(Segen rishon means "Lieutenant First Class"; Segen literally translates as "Assistant")
(סגן-משנה (סג"מ
Segen mishne (Sagam) — since 1951
(סגן
Segen — 1948–51
(Platoon Commander)
(Second Lieutenant, equivalent to NATO OF-1)
(Segen mishne, means "Junior Lieutenant"; Segen literally translates as "Assistant")
קצינים אקדמאים
Ktzinim Akademaim
Academic Officers(קצין אקדמאי בכיר (קא"ב
Katsín akademai bakhír (Ka'ab)
(Professional Officer of the First Class in the Reserve — equivalent to Captain.)
(officer of medical service, officer of dental medical service, officer of veterinary service, officer of justice, officer of religion.)
(Chief Academic Officer)
(קצין מקצועי אקדמאי (קמ"א
Katsín miktsoí akademai (Kama)
(Professional Officer of the Second Class in the Reserve — equivalent to First Lieutenant.)
(officer of medical service, officer of dental medical service, officer of veterinary service, officer of justice, officer of religion.)
(Professional Academic Officer)
נגדים
Nagadim
Non-Commissioned Officers(רב-נגד (רנ"ג
Rav nagad (Ranag)
(Chief Warrant Officer, most senior specialist professional, equivalent to NATO WO-3–WO-5)
(it translates as "Warrant Officer" or "Arch-NCO")
[2](רב-נגד משנה (רנ"מ
Rav nagad mishne (Ranam)
(Warrant Officer, senior specialist professional, equivalent to NATO WO-2)
(it translates as "Junior Warrant Officer" or "Junior Arch-NCO")
[Since 2011]
(רב-סמל בכיר (רס"ב
Rav samal bakhír (Rasab)
(Command Sergeant Major, the most senior NCO rank, equivalent to NATO OR-9; it translates as "Chief Master-Sergeant")

(רב-סמל מתקדם (רס"מ
Rav samal mitkadem (Rasam)
(Sergeant Major, NATO OR-9, senior soldier of a company, battery, battalion or regiment; it translates as "Advanced Master-Sergeant")

(רב-סמל ראשון (רס"ר
Rav samal rishon (Rasar)
(Master Sergeant, senior non-commissioned officer, equivalent to NATO OR-8–OR-9; it translates as "Master-Sergeant First Class")

(רב-סמל (רס"ל
Rav samal (Rasal)
(Sergeant First Class, equivalent to Nato OR-7; it translates as "Master-Sergeant")

חוגרים
Hogrim
Enlisted( סמל ראשון (סמ"ר
Samal rishon (Samar)
(Staff Sergeant, a Squad Leader, Nato OR-6; it translates as "Sergeant First Class")

סמל
Samal[3]
(Sergeant, a Squad Leader, Nato OR-5; it translates as "Sergeant".)

(רב טוראי (רב"ט
Rav turai (Rabat)
(Corporal, Nato OR-3 - OR-4; it traslates as "Arch-Private")

טוראי
Turai
(Private E-2 or Private, Nato OR-2; it translates as "Private")
(none) Tiron
Recruit
(Not an actual rank)טירון
Tirón
(Private E1 or Recruit, NATO OR-1)
[Formally not a rank. (See comments in notes in the bottom)](none) No longer in use (ממלא מקום קצין (ממ"ק
Memale makom katsín (Mamak)
(Lowest officer posts)
(Acting Officer or Aspirant; A brevet officer ranking below a Junior Lieutenant)
(Memale makom translates as "successor" or "placeholder", and katsin means "officer")
[Existed until 1994 and no longer in use]
(רב טוראי ראשון (רט"ר
Rav turái rishón (Ratár)
(First Corporal)
[Existed from 1972 to 1982 and no longer in use. (See comments in notes in the bottom)]
(טוראי ראשון (טר"ש
Turai rishon (Tarash)
(Private E-3 or Private First Class, Nato OR-3)
[Existed until 1999 and no longer in use. (See comments in notes in the bottom)]
History
When the IDF were created in 1948, there were 7 enlisted and NCO ranks, and 8 officer ranks. The ranks were as follows:[4]
Enlisted Officer Rav-Aluf ("Chief Leader", Lieutenant General) Rav Samal Rishon ("Chief Sergeant First Class", Master Sergeant) Aluf ("Leader", Major General) Rav Samal Yehidati ("Chief Sergeant Second Class", First Sergeant) Aluf-Mishneh ("Second Leader", Colonel) Samal Rishon ("Sergeant First Class", Staff Sergeant) Sgan Aluf ("Vice-Leader", Lieutenant Colonel) Samal (Sergeant) Rav Seren ("Chief Captain", Major) Rav Turai ("Chief Private", Corporal) Seren (Captain) Turai Rishon (Private First Class) Segen (Lieutenant) Turai (Private) Segen Mishneh (Second Lieutenant) Ranks and their insignia were influenced by the British / Commonwealth model. This was later reformed when the IDF started to adopt a rank system similar to the United States armed forces in the 1990s.
The Rav Samal Yehidati was equal to a Warrant Officer II (Company Sergeant Major) and Rav Samal Rishon was equivalent to a Warrant Officer I (Regimental Sergeant Major). They wore their insignia on the lower sleeve of their shirt or jacket or on a leather wrist strap when wearing short-sleeve order.
Notes
- In the IDF, the same ranks are used throughout the military, including the Israeli Air Force and Israeli Navy. This contrasts with many other armed forces that have a separate rank system for different branches. [1]
- As the ranks of the Israel Defence Forces (IDF) are traditionally translated one-to-one to Western ranks then the rank of Aluf (אלוף) is translated as Major General, and Rav Aluf (רב אלוף) is translated as Lieutenant General. However, a more proper translation (in terms of both language and organizational role) of Aluf would be to full General (OF-9 in NATO terms). Similarly, as the Hebrew prefix Rav is equivalent to the English prefix arch- (as in archangel), a more fitting translation for the rank of Rav-Aluf would be Arch-General, or, more conventionally, Field Marshal (NATO OF-10).
- Enlisted insignia are worn on the arm sleeves whereas NCO and officer insignia are worn on the shoulders.
- Officer insignia are silver with a dark blue background in the air force and gold with a black background in the navy. In the army, both lieutenant ranks usually have the blackish-gold ranks (shown above) with an olive-green background until promoted to the rank of captain. Enlisted ranks are green in the army, blue in the air force, and golden in the navy. Subaltern officers wear rank bars embossed with a laurel branch (aronot). Senior and General officers wear "pips" that look like an oak-leaf (alim).
- The rank of Memale makom katsín (ממלא מקום קצין) or "Acting Officer in the Reserves" was one of the Academic Officer ranks. It indicated a cadet in the Israeli army who had finished the basic preparation for an officer rank (קורס קצינים בסיסי), but for some reason abandoned or failed to complete the professional officer preparation (השלמה חיילית). They occupied the lowest officer posts, which are not concerning with command, and were considered below a 2nd Lieutenant (Sagam) in rank. It was discontinued in 1994.
- The rank of Master Corporal was used from 1972 to 1982. There was a shortage of staff during this period and the higher rank was offered to convince soldiers to sign an army contract[citation needed].
- The rank of Private First Class was discontinued in 1999. Privates now retain their rank until promoted to Corporal, usually after 10 months of peacetime service (6 months for support roles and 4 months for combatants). Combat units traditionally do not take the rank of corporal, remaining without insignia until they are promoted to the rank of sergeant.
- Non-commissioned officer ranks listed on this page correspond to the Hebrew Nagad ranks, a word that translates as 'non-commissioned officer'. Corporals and sergeants however who are commanders are called Mashak, an abbreviation that also translates into English as 'non-commissioned officer' (or, literally, 'a commander who is not an officer').
- Academic Officers: These are special ranks, given to soldiers who are of academic education, but for some reason have not completed officers' training (since the draft age is 18, only few soldiers complete academic education before being drafted, most commonly by postponing draft for this reason). "Kama" is equivalent to 1st Lieutenant, and "Ka'ab" is equivalent to Captain. Officers of these ranks are considered professional manpower (mostly engineering), and rarely take posts of command. Upon completing officers' training, an academic officer is awarded the corresponding "real" rank. Their insignia bars are embossed with a scroll (?) rather than a laurel branch (aronot).
- Upon enlistment to military service in Israel, all soldiers begin a basic training course, undergo several days or weeks of 'integration' from citizens to soldiers. This course is called recruit training or Tironut and the soldier being trained on this course is called a recruit (Private E-1 or Tiron), which is often erroneously interpreted as a rank, similar to the American Private E-1. There is no such rank and Tironim (recruits) are ranked Turai (Private).
- In the IDF enlisted ranks are earned by means of time in service (pazam), rather than by a particular post or assignment. Higher NCO and officer ranks require assignment to an awarding post. It usually takes between 24 to 32 months to achieve the rank of Staff Sergeant. Ranks of 1st lieutenant and captain also take only time, but much longer (a full year as 2nd lieutenant, and 3 years as first, respectively).
See also
References
- ^ "IDF Ranks". IDF 2011. http://dover.idf.il/IDF/English/about/insignia/ranks.htm. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ Y Net, IL, http://www.ynet.co.il/articles/0,7340,L-4085389,00.html.
- ^ The word "samal" originated as an acronym for Hebrew: סגן מחוץ למנין "segen mi-khutz la-minyan" (inspired by NCO abbreviation), but nowadays is no longer treated as an acronym or an abbreviation: see e.g., Avraham Akavia, "Milon le-munkhey tzava" (1951), p. 220, 270; Avraham Even-Shoshan, "Ha-milon ha-khadash" (1967), vol. 4., p. 1814 ; Yaakov Kna'ani, "Otzar ha-lashon ha-ivrit" (1972), p. 4078; Zeev Shiff, Eitan Habber, "Leksikon le-bitkhon Yisrael" (1976), p. 114; "Milon Sapir" (ed. Eitan Avnian) (1998), vol. 5, p. 2019; Avraham Even-Shoshan, "Milon Even-Shoshan be-shisha krakhim" (2003), ISBN 965-517-059-4, vol. 4, p. 1302; "Entziklopedya Karta" (5th edition, 2004), ISBN 965-220-534-6, p. 409; "Milon Ariel" (ed. prof. Daniel Sivan and prof. Maya Fruchtman) (2007), ISBN 978-965-515-009-4, p. 765. (Hebrew)
- ^ Wallach, Jeuda; Lorekh, Netanel; Yitzhaki, Aryeh (1978). "Battles of the Jordan Valley". In Evyatar Nur. Carta's Atlas of Israel. Volume 2 - The First Years 1948–1961. Jerusalem, Israel: Carta. p. 91. (Hebrew)
External links
Israel Defense Forces Arms · Commands · Directorates · Attachés ArmsCommandsDirectoratesCorps Ground forcesInfantry brigadesCombat support
and rear-frontOrdnance · Medical · Intelligence · C4I · Education · Adjutant · Logistics · Military Police · Rabbinate · GeneralDivisions TerritorialRegularInsignia Other topics History · Wars · Military operations · Ministry of Defense · Military equipment · Checkpoints · Military prisons · Security Forces · Mossad · Shabak · Police · Border Police · Intelligence Community · Security Council · Foreign Affairs and Defense CommitteeMilitary ranks and insignia by country Africa Egypt (Army · Air Force · Navy) · South Africa · Tanzania
Americas Asia Burma · People's Republic of China (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Republic of China · India (Army · Air Force · Navy) · Indonesia · Iran (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Iraq · Israel · Japan · Jordan · Korea · Lebanon · Pakistan · Saudi Arabia · Singapore · Sri Lanka (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Thailand · Vietnam
Former: Imperial Japan (Army · Navy)Europe Albania · Austria · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Denmark (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Estonia · Finland · France (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland (Land Forces · Coast Guard) · Ireland (Army · Naval Service · Air Corps) · Italy (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Macedonia · Monaco · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Serbia · Slovenia · Spain (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey · Ukraine · United Kingdom (Navy · Army · Air Force) · Vatican
Former: Austria–Hungary · East Germany · Nazi Germany (Volkssturm · SA · SS) · Kingdom of Greece (Army · Navy) · Soviet Union · Yugoslavia · Serbia and MontenegroOceania Categories:- Military ranks of Israel
- Military insignia
- Israel Defense Forces
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
