- Myos Hormos
-
Myos Hormos was located in the Red Sea coast of Roman Egypt

Myos Hormos was a Red Sea port constructed by the Ptolemies around the 3rd century BC. Following excavations carried out recently by David Peacock and Lucy Blue of the University of Southampton, it is thought to have been located on the present-day site of Quseir al-Quadim (old Quseir), eight kilometres north of the modern town of Quseir in Egypt.[1]
Contents
History
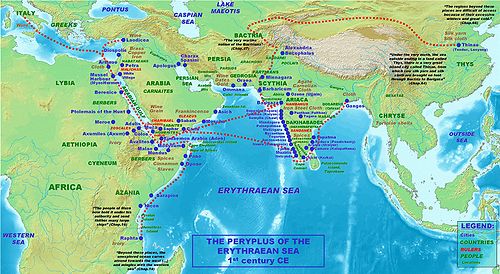
Myos Hormos, after the Ptolemies, was with Berenice one of the two main ports in Roman Egypt for trade with India, Africa and probably China.[2]
Some of its main destinations were the Indus delta, Muziris and the Kathiawar peninsula in India. The coastal trade from Myos Hormos and Berenice along the coast of the Indian Ocean is described in the anonymous 1st century AD handbook Periplus of the Erythraean Sea.
According to Strabo (II.5.12), by the time of Augustus, up to 120 ships were setting sail every year from Myos Hormos to India:
"At any rate, when Gallus was prefect of Egypt, I accompanied him and ascended the Nile as far as Syene and the frontiers of Ethiopia, and I learned that as many as one hundred and twenty vessels were sailing from Myos Hormos to India, whereas formerly, under the Ptolemies, only a very few ventured to undertake the voyage and to carry on traffic in Indian merchandise."—Strabo II.5.12. [1]The port of Myos Hormos was connected to the Nile valley and Memphis by a Roman road, built in the 1st century.
After the 4th century the port was abandoned, because of the Roman Empire crisis and the end of the trade between Rome and India.
Only in the 17th century the port started to get again some importance, mainly because of holy travel from Cairo to Mecca. The city of old Qusair is the actual Myos Hormos.[3]
References
- ^ "Cane (Qana')". Maritime Incense Route. http://nabataea.net/myoshormos1.html. Retrieved 7 Dec 2008.
- ^ http://nabataea.net/isearoute.html Roman sea routes in the Indian Ocean
- ^ Articles and photos of Myos Hormos and actual Old Qusair (in Italian)
Bobliography
- G.W.B. Huntingford. The Ethnology and History of the Area Covered by the Periplus in Huntingford ed., "Periplus of the Erythraean Sea" (London, 1980).
External links
See also
- Roman trade with India
- Qusair
- Berenice
- Roman Egypt
Coordinates: 26°9′23.58″N 34°14′29.70″E / 26.15655°N 34.241583°E
Categories:- Former populated places in Egypt
- History of Rome
- History of Egypt
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.