- Shifting dullness
-
"Dullness" redirects here. For the goddess in The Dunciad, see Dulness.
In medicine, shifting dullness refers to a sign, elicited on physical examination, for ascites[1].
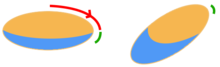
To perform the test, first the midline is percussed eliciting a resonant note due to gas in the bowel. If there is no area of resonance then the test cannot be performed. Percussion is then moved progressively more lateral (away from the examiner) - this is depicted as the red section in the diagram on the right - until the note becomes dull, as depicted by the green section. The examiner's index finger is left on the resonant side, and the middle finger is left on the dull side; thus straddling a fluid-air level. The patient is then asked to lean on their right lateral side (assuming the examiner used the traditional right sided approach). This sandwiches the patient between the examiner's hands and body, stabilising the patient. It is imperative that the finger positions aren't lost. After waiting sufficient time for any fluid to shift (up to 30 seconds), the dull position is then percussed. It may now be resonant. The percussion may now be performed down the anterior side until a new dullness is found. To confirm a positive result it is recommended that the now resonant area become dull again when the patient is back in the supine position.
If the borders between tympanic (resonant) and dullness remain the same, the person probably does not have ascites, or has less than 2 litres of free fluid present[citation needed]. If the fluid causing the dullness was not free, then the air-fluid level would not move. Shifting dullness is usually present if the volume of ascitic fluid is greater than 1500 ml[citation needed]. If low volume ascites is suspected, then an attempt to elicit the puddle sign may be performed.
References
- ^ Murray Longmore, Ian B. Wilinson, Edward H. Dawvidson, Alexander Foulkes and Ahmad R. Mafi Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine 8thEdition Oxford University Press 2010 ISBN 978-0-19-923217-8
See also
Accessory Abdominopelvic Abdominal – general Categories:- Medical signs
- Medical sign stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.