- Battle of Magnesia
-
Battle of Magnesia Part of War against Antiochus III Date December 190 BC Location Near Magnesia ad Sipylum, Lydia (modern Turkey) Result Decisive Roman victory Belligerents Roman Republic Seleucid Empire Commanders and leaders Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus,
Scipio Africanus,
Eumenes II of PergamumAntiochus III the Great,
Zeuxis ,
Seleucus [1]Strength 30,000
(ancient sources)[2]
50,000
(Grainger)[3]70,000
(ancient sources)[2]
50,000
(Grainger)[4]Casualties and losses at least 349
(ancient sources)[5]
5,000
(Grainger)[6]up to 50.000 dead and captured
(ancient sources)[2][5]
10,000
(Grainger)[6]- Thermopylae
- Eurymedon
- Myonessus
- Magnesia
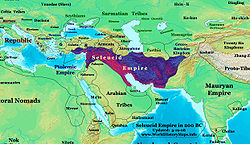
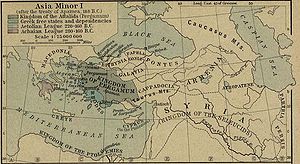
The Battle of Magnesia was fought in 190 BC near Magnesia ad Sipylum, on the plains of Lydia (modern Turkey), between the Romans, led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio and his brother, the famed general Scipio Africanus, with their ally Eumenes II of Pergamum against the army of Antiochus III the Great of the Seleucid Empire. The resulting decisive Roman victory resulted in Roman domination over the internal affairs of a large part of the territory once controlled by the Seleucid Empire.[7]
The main historical sources for this battle are Livy and Appian.[7]
Contents
The Two Armies
Antiochus was driven out of Greece following the defeat of his expeditionary force at the Battle of Thermopylae (191 BC). The Roman navy with the Rhodians and other allies outmaneuvered and defeated the Seleucid navy, permitting the Roman army to cross the Hellespont. The Roman army operated under the commands of the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus, younger brother of Scipio Africanus, who accompanied him as legatus. Antiochus was accompanied by the Carthaginian general and dire enemy of the Roman Republic Hannibal Barca, who had fled to Antiochus' court after his defeat at Zama and the end of the 2nd Punic War.[7]
In anticipation of the battle, Antiochus set up an entrenched camp protecting the approach to Sardis and his fleet base at Ephesos. According to both Livy and Appian, he posted his 16.000 strong phalanx, armed in the Macedonian fashion in the center in brigades (taxeis) of 1.600 men, 50 men wide and 32 men deep. He ordered intervals to be formed among the taxeis in which he placed 2 elephants each. On the right wing, next to the phalanx, he arrayed 1500 Gallograecian infantry, 3.000 Galatian mail clad cavalry (cataphracti) and 1.000 agema cavalry, his royal household guards. Behind them he kept 16 elephants in reserve. Next to the agema, he placed a cavalry corps Livy calls argyraspides, 200 or 1.200 Dahae horse archers, 3.000 Cretan and Trallean light infantry, 2.500 Mysian bowmen, Cyrtian slingers and Elymaean archers. On the left, Antiochus arrayed another 1.500 Gallograecian infantry, according to Appian men from the tribes of the Tectosagi, the Trocmi and the Tolistoboii, 2.000 Cappadocians similarly armed and a miscellaneous force of 2.700. Next to them, he posted 1.000 heavy horsemen, the Companions, 3.000 more cataphracti and probably another 1.000 men of the agema. In front of them, he placed the scythed chariots and a unit of dromedary, camel-borne Arab archers. His left wing was completed with a corps of Tarentines, 2.500 Gallograecian cavalry, 1.000 newly enlisted Cretans, 1.500 Carians and Cilicians similarly armed, and the same number of Tralles. Then came 4000 peltasts, Pisidians, Pamphylians and Lydians, next to these Cyrtian and Elymaean troops equal in number to those on the right wing, and finally sixteen elephants a short distance away. Antiochus retained command of the horse on the right wing in person; his son Seleucus and his nephew Antipater commanded the left. Philip, the master of the elephants, commanded the phalanx, and Mendis and Zeuxis the skirmishers.[8][9]
The Romans arrayed in their customary triple line formation with their left wing resting on the river. The Roman reinforced legions occupied the center of this formation and the Latins, the Ally legions, on their wings. In all, there were 20.000 men of the legion. Behind them, Scipio held his 16 elephants in reserve, fully aware that the African elephants could not face the larger Indian stock on equal terms. On the right Scipio placed the allied Pergamenese army under Eumenes and the Achaean peltasts, 3.000 in all to cover the flank of the legions. Next to them he placed his cavalry, nearly 3.000 strong, 800 of them Pergamenese, the rest legionary cavalry. According to Livy, in the extreme right he posted the Trallian and Cretan horsemen, each body numbering 500 troopers, but most probably, these are the light troops and archers named by Appian to be intermingled among the cavalry. Livy also mentions 2.000 Macedonian and Thracian volunteers, who are left to guard the Roman camp. Domitius was stationed with 4 squadrons of cavalry on the right wing, Scipio kept command of the center and gave command of the left to Eumenes.[10]
In all, both writers agree that the Roman army was about 30.000 strong and the Seleucids about 70.000. However, historian Grainger argues that the two armies might have been not that numerically different and supports that the Romans fielded about 50.000 men as did Antiochus.[3]
A popular anecdote regarding the array of the two armies is that Antiochus supposedly asked Hannibal whether his vast and well-armed formation would be enough for the Roman Republic, to which Hannibal tartly replied, "quite enough for the Romans, however greedy they are."[11]
The battle
The Romans wished to fight this battle, before a new consul was sent out from Rome and winter would lead the campaign to a halt. Scipio had successfully crossed the river and set up a camp only about 4 km from the camp of Antiochus. Scipio's further advance from his camp was made with the river protecting his left, where he would rest his arrayed legions. Except for 4 squadrons (turmae) all the allied cavalry was on its right when the battle started.[7]
As in almost all ancient battles, different reconstructions are possible. Appian has the battle start on the Seleucid left with a failed attack by the scythed chariots which disrupted the Seleucid cavalry on that wing. Roughly at the same time, there was a charge on the right by the Seleucid cavalry wing commanded by the king himself, which broke their opposing infantry leading to a pursuit by the Seleucid horse, leaving the field to unsuccessfully attack the Roman camp. The Roman ally Eumenes, commanding all their cavalry on the right of the Roman-Allied army counterattacked the Seleucid left, already disrupted by the scythed chariots, and broke it. In the center of the battle line, the Seleucids had arrayed their pike phalanx with elephants in intervals between the taxeis. They seem to have been unable to really participate in the battle, having soon been encircled by the victorious enemy horsemen. Forming squares facing all sides, the phallangitai tried to march off the battlefield but their efforts were not successful, as they broke when the elephants panicked. Eventually, after further fighting, the Seleucid camp fell.[7]
Aftermath
After an armistice was arranged between Antiochus and Rome, the Roman army waged a campaign against the Galatians which politically undermined the Seleucid position in Asia Minor. The Romans had had a tremendous advantage throughout their campaign from their much more limited political objective. All the small powers could ally themselves to Rome because Rome sought no political annexations at this time. Conversely, the strategy of Antiochus had never made sense.[citation needed] The Aegean Sea was a natural frontier for a state based in Babylonia, as Xerxes discovered long ago. If Antiochus had wanted to advance west into Greece, he needed to turn his state into the leading naval power in the Mediterranean, from nowhere, before sending his army west.
The treaty forced upon Antiochus III by the victorious Romans was crippling, in the Treaty of Apamea Antiochus was forced to pay a huge war indemnity of 15,000 Talents along with giving up significant territory in Asia Minor.[12] The Taurus Mountains became the new frontier. The Seleucid navy was limited by treaty, and their squadrons of war elephants destroyed. It weakened the already fractious Seleucid Empire and halted all ambitions of Antiochus III in becoming a latter day Alexander in his own right. Polybius states the financial burden of war indemnity forced Antiochus III to loot temple treasuries. This alienated Seleucid subjects and further reducing the dynasty's prestige already sharply reduced by the decisive defeat suffered against the Romans.
References
- John D. Grainger, The Roman War of Antiochus the Great 2002 Leiden-Boston
- Dexter Hoyos, Hannibal's Dynasty: Power and Politics in the Western Mediterranean, 247-183 BC, Routledge, 2005
Notes
- ^ http://mcadams.posc.mu.edu/txt/ah/Livy/Livy37.html#livy.hist.37.41 livy.hist.37.41
- ^ a b c Livy XXXVII 44
- ^ a b Grainger, p. 321
- ^ Grainger, p. 314
- ^ a b Appian, Syriaca 7
- ^ a b Grainger, p. 328
- ^ a b c d e Grainger, pp. 307-325
- ^ Livy XXXVII 40
- ^ Livy XXXVII 41
- ^ Livy XXXVII 39
- ^ Hoyos, p. 203
- ^ Livy XXXVII 45
External links
Categories:- 190 BC
- Battles involving the Roman Republic
- Battles involving the Seleucid Empire
- Battles involving Pergamon
- History of Manisa Province
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.