- Peptostreptococcus
Taxobox
color = lightgrey
name = "Peptostreptococcus"
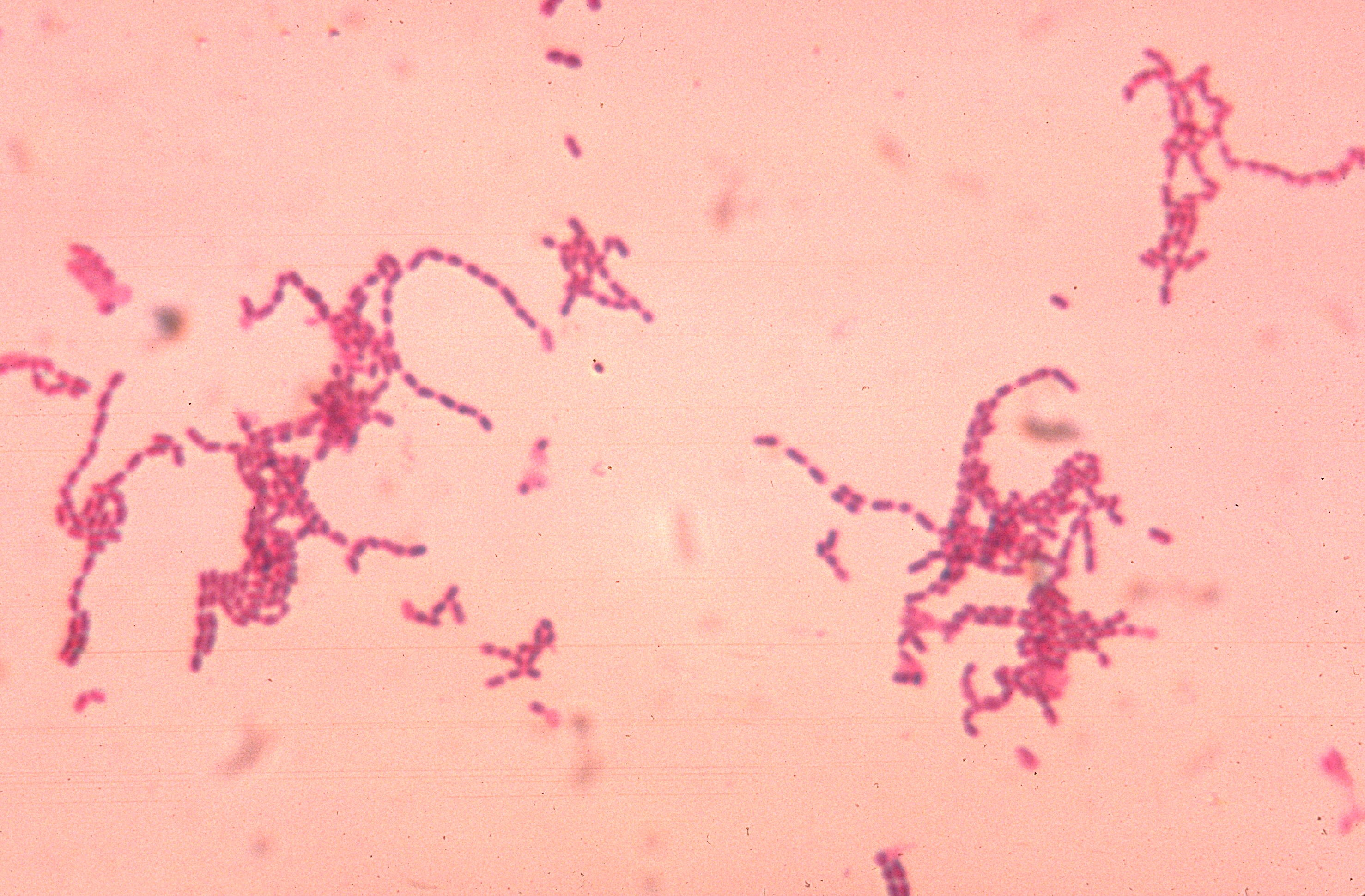
image_width = 240px
image_caption = "Peptostreptococcus" spp. growing in characteristic chain formations.
regnum = Bacteria
phylum =Firmicutes
classis =Clostridia
ordo =Clostridiales
familia =Clostridiaceae
genus = "Peptostreptococcus"
genus_authority = Garrity "et al." 2001
subdivision_ranks = Species
subdivision = "P. anaerobius"
"P. asaccharolyticus"
"P. harei"
"P. hydrogenalis"
"P. indoliticus"
"P. ivorii"
"P. lacrimalis"
"P. lactolyticus"
"P. magnus"
"P. micros"
"P. octavius"
"P. prevotii"
"P. tetradius"
"P. vaginalis"
etc."Peptostreptococcus" is a
genus of anaerobic,Gram-positive , non-spore forming bacteria. The cells are small, spherical, and can occur in short chains, in pairs or individually.cite book | author = Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) | title = Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th ed. | publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | id = ISBN 0-8385-8529-9 ] "Peptostreptococcus" are slow-growing bacteria with increasing resistance toantimicrobial drugs.cite journal | author = Higaki S, Kitagawa T, Kagoura M, Morohashi M, Yamagishi T | title = Characterization of Peptostreptococcus species in skin infections | journal = J Int Med Res | volume = 28 | issue = 3 | pages = 143–7 | year = 2000 | pmid = 10983864]Pathogenesis
"Peptostreptococcus" species are
commensal organisms in humans, living predominantly in the mouth, skin, gastrointestinal, andurinary tract s, and compose a portion of the bacterialgut flora . Underimmunosuppressed or traumatic conditions these organisms can becomepathogen ic, as well as septicemic, harming their host. "Peptostreptococcus" can cause brain, liver, breast, and lungabscess es, as well as generalized necrotizing soft tissueinfection s.cite book | author = Mader JT, Calhoun J | title = Bone, Joint, and Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. "In:" Baron's Medical Microbiology "(Baron S "et al", eds.)| edition = 4th ed. | publisher = Univ of Texas Medical Branch | year = 1996 | id = [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=mmed.chapter.5381 (via NCBI Bookshelf)] ISBN 0-9631172-1-1 ]References
External links
* [http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic1777.htm Peptostreptococcus infections] from eMedicine.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
