- Outline of chocolate
-
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to chocolate:
Chocolate – raw or processed food produced from the seed of the tropical Theobroma cacao tree.[1] The seeds of the cacao tree have an intense bitter taste, and must be fermented to improve the flavor. Chocolate is a popular ingredient in confectionery items and candies.
Contents
Nature
Chocolate is a type of:
- Food – substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body, ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells in an effort to produce energy, maintain life, and/or stimulate growth.
- Confectionery – the set of food items that are rich in sugar, any one or type of which is called a confection. Modern usage may include substances rich in artificial sweeteners as well.
- Candy – confection made from a concentrated solution of sugar in water, to which flavorings and colorants are added. Candies come in numerous colors and varieties and have a long history in popular culture.
- Ingredient – substance that forms part of a mixture (in a general sense). For example, in cooking, recipes specify which ingredients are used to prepare a specific dish. Chocolate is often used as an ingredient in desert items, such as cakes and cookies.
- Confectionery – the set of food items that are rich in sugar, any one or type of which is called a confection. Modern usage may include substances rich in artificial sweeteners as well.
Ingredients
Necessary ingredients
- Cocoa bean - the primary ingredient which characterizes chocolate
- Chocolate liquor or mass - ground or melted state of the nib of the cacao bean
- Cocoa butter - the fat component
- Cocoa solids, the nonfat part of the cacao bean which is ground into cocoa powder [2]
Substances found in cocao
- Antioxidants –
- Caffeine - psychoactive stimulant drug found in coffee
- Phenethylamine - psychoactive drug that is usually inactive when orally ingested because most of it is metabolized into phenylacetic acid by monoamine oxidase (MAO), preventing significant concentrations from reaching the brain[3][4]
- Theobromine - also known as xantheose,[5] it contains no bromine [6] and has a similar, but lesser, effect to caffeine
- Theophylline - methylxanthine drug found in tea leaves
Source of the cocao bean
- Cacao tree[8] –
- Forastero – 80% made with this tree group
- Criollo – 10% made with this tree group
- Côte d'Ivoire –
- Cocoa production in Côte d'Ivoire – accounts for 43% of cocoa
- Children in cocoa production –
Optional ingredients
Ingredients of white chocolate
- White chocolate – Contains the same ingredients as chocolate but lack cocoa solids.[9]
Types
Main article: Types of chocolate- Unsweetened chocolate - pure chocolate liquor mixed with fat to produce a solid substance; also known as "bitter", "baking chocolate" and "cooking chocolate"[10]
- Dark chocolate –
- Milk chocolate –
- Semisweet chocolate –
- Bittersweet chocolate –
- Couverture –
- White chocolate –
- Cocoa powder –
- Compound chocolate –
- Dutch process chocolate –
- Scho-Ka-Kola – a chocolate brand containing coffee and cola nut[11]
Production methods
Producers and trade organizations
- International Cocoa Initiative –
- Cocoa Processing Company Limited – a Ghanaian cocoa processing company
- Kuapa Kokoo – a Ghanaian farmers' cooperative organisation
- Grenada Chocolate Company – an organic cooperative in Grenada (tree-to-bar).
- List of bean-to-bar chocolate manufacturers
See also: Fairtrade labellingBrands
Comestibles
- Chocolate pudding –
- Chocolate syrup –
- Chocolate cake –
- Cookies – (see also: List of cookies)
- Chocolate chip –
- Chocolate biscuit –
- Chocolate chip cookie –
- Black and white cookie –
- Afghan biscuit – a traditional New Zealand biscuit[12]
- Chocolate brownie –
- Chocolate spread –
- Confectionery –
- Chocolates –
- Desserts –
- Ice cream –
- Candy –
- Cereals – (see also: List of breakfast cereals):
- Brand names:
Drinks
 A mug of hot chocolate. Chocolate was first drunk rather than eaten.[10]
A mug of hot chocolate. Chocolate was first drunk rather than eaten.[10]
- Cafe mocha –
- Chocolate milk –
- Swiss Miss –
- Nesquik –
- Banania –
- Yoo-hoo –
- Crème de cacao –
- Hot chocolate –
History
Main article: History of chocolateEffects on health
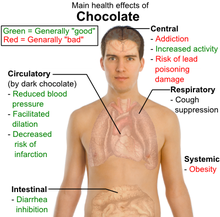 Main health effects of chocolate[13]
Main health effects of chocolate[13]
Other articles
- United States military chocolate –
- Couverture chocolate –
- Chocolate fountain –
- Compound chocolate –
- Chocolate agar – named for its color, does not contain cocoa
- Chocolate spread –
- Modeling chocolate –
- Minstrels (chocolate) –
- Freddo Frog –
References
- ^ http://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/duke_energy/theobroma_cacao.html
- ^ CMA - Chocolate Manufacturers Association
- ^ Yang HY, Neff NH. (November 1973). "Beta-phenylethylamine: a specific substrate for type B monoamine oxidase of brain". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 187 (2): 365–71. ISSN 0022-3565. PMID 4748552.
- ^ Suzuki O, Katsumata Y, Oya M. (March 1981). "Oxidation of beta-phenylethylamine by both types of monoamine oxidase: examination of enzymes in brain and liver mitochondria of eight species". The Journal of Neurochemistry 36 (3): 1298–301. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01734.x. ISSN 0022-3042. PMID 7205271. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/r?dbs+hsdb:@term+@rn+64-04-0.
- ^ William Marias Malisoff (1943). Dictionary of Bio-Chemistry and Related Subjects. Philosophical Library. pp. 311, 530, 573. ISBN B0006AQ0NU.
- ^ Bennett, Alan Weinberg; Bonnie K. Bealer (2002). The World of Caffeine: The Science and Culture of the World's Most Popular Drug. Routledge, New York. ISBN 0415927234.
- ^ http://store.chocolatceleste.com/cacao-beans-criollo-trinitario.html
- ^ http://www.xocoatl.org/variety.htm All about Chocolate – Varieties
- ^ http://www.thenibble.com/zine/archives/best-white-chocolate3.asp#fillings
- ^ a b http://www.fieldmuseum.org/chocolate/history.html
- ^ http://www.germandeli.com/4001743034013.html
- ^ http://www.azmetro.com/nzrecipe.html#afghan
- ^ http://www.acu-cell.com/choc.html
External links
- Outline of chocolate at the Open Directory Project
- Glossary of Chocolate Terms
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Chocolate". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Chocolate". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.- Food of the Gods A Popular Account of Cocoa – Freely downloadable book from Project Gutenberg
Outlines - General reference
- Culture and the arts
- Geography and places
- Health and fitness
- History and events
- Mathematics and logic
- Natural and physical sciences
- People and self
- Philosophy and thinking
- Religion and belief systems
- Society and social sciences
- Technology and applied sciences
Chocolate Background - Outline of chocolate
- History of chocolate
- Health effects of chocolate
- History of chocolate in Spain

Origins Varieties Chemicals See also Categories:- Outlines
- Chocolate
- Food – substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body, ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells in an effort to produce energy, maintain life, and/or stimulate growth.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


