- Farnese Gardens
-
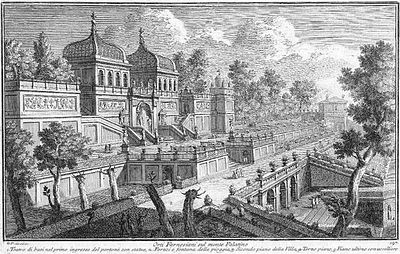 1761 engraving by architect Giuseppe Vasi from book 10 of his series of vedute (views) of Rome, showing the Farnese Gardens on Palatine Hill in Rome at that time. The ground floor entrance is at right, and the twin domes are above the aviaries on the third floor of the structure.
1761 engraving by architect Giuseppe Vasi from book 10 of his series of vedute (views) of Rome, showing the Farnese Gardens on Palatine Hill in Rome at that time. The ground floor entrance is at right, and the twin domes are above the aviaries on the third floor of the structure.
The Farnese Gardens (Orti Farnesiani sul Palatino or "Gardens of Farnese upon the Palatine") are a garden in Rome, central Italy, created in 1550 on the northern portion of Palatine Hill, by Cardinal Alessandro Farnese. They were the first private botanical gardens in Europe (the first botanical gardens of any kind in Europe being started by Italian universities in the mid-16th century, only a short time before).
Alessandro Farnese was appointed Cardinal Deacon of the Roman Catholic Church in 1534 at the age of 14, by Paul III, his grandfather, who had been elected to the papacy two months previously. He is remembered for being an antiquarian who assembled the greatest collection of Roman sculpture assembled in private hands since antiquity.[1] In 1550, when Farnese acquired a northern portion of Palatine hill (historically the oldest of Rome's seven hills) he had ruins from a Roman palace of Tiberius at the northwest end of the hill top filled in, and converted to a summer home. The site overlooks the Roman Forum and is near the Arch of Titus. He called this Horti Farnesiani (possibly meaning to suggest the hortus conclusus or "enclosed garden" where Mary conceived Jesus Christ). The garden was divided into the classic style of quadrants with a well or a fountain at its centre, deriving from the design of the Roman peristilium palaces of the area, as re-created by the noted architect Vignola.[2][3]
Though little of the Farnese Gardens survives today, some remnant structures may be seen.[4]
From the name of these gardens is derived the name of the plant Acacia farnesiana and from its floral essence, the important biochemical farnesol.
See also
References
- ^ Now mostly in Naples, after passing by inheritance to the Bourbon-Parma kings; it ranked with the papal collections in the Cortile del Belvedere, and the city's own collection housed at the Campidoglio.
- ^ [1] History of Palatine Hill.
- ^ History of the Farneses and the garden.
- ^ [2] Location of the Farnese family gardens, now known only as a remnant.
External links
- Farnese Gardens website with historical plates and modern photos
- Convention on Biological Diversity - Italian Botanical Gardens
- List of botanical gardens in Italy
Categories:- Buildings and structures in Rome
- Botanical gardens in Italy
- Italy-related lists
- Italy geography stubs
- Italian garden stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
