- Operculum (animal)
-
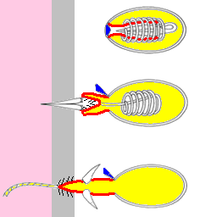 Firing sequence of the cnida in a hydra's nematocyst[1]
Firing sequence of the cnida in a hydra's nematocyst[1]
Operculum (lid)
"Finger" that turns inside out
/ / / Barbs
Venom
Victim's skin
Victim's tissuesAn operculum (animal) is an anatomical feature, a stiff structure resembling a lid or a small door that opens and closes, and thus controls contact between the outside world and an internal part of an animal. Examples include:
- An operculum (gastropod), a single lid that (in its most complete form) closes the aperture of the shell when the animal is retracted, and thus protects the internal soft parts of the animal that are not completely covered by the shell. The operculum lies on the top rear part of the foot. When the foot is retracted, the operculum is rotated 180° and closes the shell.[2]
- An operculum (fish), a flap that covers the gills in bony fishes and chimaeras.
- The cover that rapidly opens a cnida of a cnidarian such as a jellyfish or a sea anemone. The lid may be a single hinged flap or three hinged flaps arranged like slices of pie.[1][3]
See also
A structure in ammonites which usually consists of two plates, and which was long thought to be a form of double operculum, but which more recently has been proposed to have been a jaw mechanism.
References
- ^ a b Ruppert, E.E., Fox, R.S., and Barnes, R.D. (2004). "Cnidaria". Invertebrate Zoology (7 ed.). Brooks / Cole. pp. 112–124. ISBN 0030259827.
- ^ Ruppert, E.E., Fox, R.S., and Barnes, R.D. (2004). "Gastropoda". Invertebrate Zoology (7 ed.). Brooks / Cole. pp. 309–313. ISBN 0030259827.
- ^ Hinde, R.T., (1998). "The Cnidaria and Ctenophora". In Anderson, D.T.,. Invertebrate Zoology. Oxford University Press. pp. 28–57. ISBN 0195513681.
Categories:- Mollusc anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

