- Open innovation in financial services
-
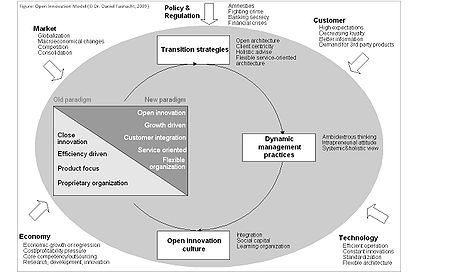
Broadly we can divide between two sectors in an economy. Where wealth-producing sectors are related to manufacturing, the service sector tends to be wealth-consuming. Both sectors depend on innovation. Innovation capability and its management are sector or industry specific, if not firm specific. One specific research area in the manufacturing sector brought us open innovation, utilized initially by the computer and high-tech industry. What has been neglected is research in the service sector. In particular, there is more service science in the financial services industry needed. Recently, we have seen researchers adapting open innovation concepts from manufacturing to the financial services. This approach suggests that firms use external ideas as well as internal ideas, and internal and external paths to markets. Daniel Fasnacht, an executive director at a Swiss private bank, as one of the first, defined open business models in the context of the financial services industry. He adapted and enhanced the basic concepts of open innovation and developed a framework (see illustration: Open innovation model) for helping to understand industry dynamics in banking and to make the most of organizational energy by using open innovation to sustain profitable growth.
Contents
Model
The integrative open innovation model provides an overview. It illustrates the environmental changes, coming from the market, policy and regulation, customer, technology, and economy. These developments, together with recent incidents such as the global financial crisis of 2008-2009, have led to the phenomenon – the transition from a closed approach to open innovation in the financial services.
The Concept of Open Innovation in the Financial Services
The financial service industry is currently in radical transformation like no other industry. The wave of consolidation with the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers (the largest in US history) and nationalization of some banks in Western economies was triggered through a number of developments in markets, economics, demographics, customers, technology and policies during the last two decades. However, it was accelerated by the subprime mortgage crisis that followed changes in the investment environment brought about by deregulation of financial markets and instruments at the end of the 1990s in the United States (e.g. repeal of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, Glass–Steagall Act).
Fasnacht, among many managers and researchers, assumes that the shift from a closed to an open innovation paradigm is one major consequence of the trends and the recent developments. He argues that open innovation in this context is not merely a new business paradigm – it is a mindset characterized by openness, flexibility, and customer integration. Opening up business models in the financial services is a challenge but also a chance for those that understand the importance of this strategic change.
Transition Strategies
The transition to open innovation entails – regardless the industry – radical organizational change. The transition is a complex process. Transition strategies for the financial services must go beyond just integrating third-party products; already a de facto standard termed Open Architecture. Collaborative innovation is based on knowledge sharing and partnerships and considered as major source to develop and leverage the capability for innovation in a firm. Innovative firms, characterized as knowledge creating, should adopt such models as they can no longer rely solely on its own resources and capabilities. Next it is imperative to put the client in the center of the firm’s value adding processes. Through a client-focused organization and needs-based client segmentation, we are better positioned to develop holistic advice offerings to sophisticated clients. This is what finally differentiates premium wealth managers from mainstream product banks. Hence it increases client satisfaction and client profitability.
These examples of possible transition strategies related to open innovation are imperative, especially in a time when trade barriers between nations fall and information on products, services and prices are instantly and globally available. In addition, many offshore financial centers can no longer pull from banking secrecy acts and tax evasion. With monopoly financial havens to be continuing to disappear and the increasing commoditization of products and services, more and more institutes must abandon the path of me-too strategies. Banks must adopt flexibility and build up service-oriented open business models to innovation and rapidly redefine themselves as markets and client behaviors have already radically changed.
New Management Practices
Traditional approaches to strategy are proving to be inadequate to deal with fundamental changes. Leaders must develop a set of new management practices if they want to survive and succeed in the open innovation paradigm. Based on Fasnacht, those include interrelated dynamic capabilities such as ambidextrous thinking, intrapreneurial attitude, and a systemic and holistic view on the firm. As a consequence of the current financial crisis, many firms in the financial services industry are focusing on cost cutting. This comes often at the expense of service quality, growth, innovation, and brand creation. Pursuing different contradictory strategies at the same time is what ambidextrous thinking stands for. Reducing cost while raising value (as the ultimate model of ambidexterity) is also known under the concept of value innovation. Creating value through an intrapreneurial attitude should be the ambition of every firm. Intrapreneurship is the practice of using skills that focus on innovation and creativity to transform business ideas into a profitable venture within the organization. Although it implies similar qualities than that of an entrepreneur, there are differences since the intrapreneur does not necessarily wish to leave the firm. Employees with intrapreneurial attitude incorporate crucial intellectual capital.
During the last decade, the global financial business has become very complex, driven by fierce competition and scarce knowledge resources. Therefore, we need an interdisciplinary and systemic view on the major economic, political, societal, and technological forces currently at work in the world. Opening up and finding new ways of organizing also requires an open innovation culture and especially social capital as a set of resources embedded into relationships into which other resources can be invested.
Leaders that are able to develop the described set of new management practices are well prepared for creating new and open business models and market spaces, rather than competing with commoditized products and services in an existing industry.
Criticisms
While we have rarely heard any negative voices of open innovation in the manufacturing industries, unregulated adaptation in the financial services can have disastrous consequences as Fasnacht noted.[1] We have experienced that with the securitization of subprime mortgages. Since subprime borrowers usually do not qualify for market interest rates with their poor credit histories and weak documentation of income, providing them with credit is high risk. It is very recently that many banks moved to a new business model where they sold on the mortgages in the form of securitized assets to the bond markets. Through this innovation, they pooled subprime mortgage loans and repackaged them into saleable securities. The model changed from a closed system to an open collaboration between financial institutes to disperse risks on a broader basis across the financial markets. Therefore, the losses fell on a number of global final investors. This form of collaborative innovation also laid bare the growing global influence of private equity firms, hedge funds, and sovereign wealth funds if we lose control of cooperation with respect to the governance of some of the world’s largest corporations.
The real vulnerability is not the network of partnerships; it is the highly complex and global financial system and the management of the risks coming with open business models. A critical question is whether open innovation can save the financial industry. Certainly not, however, open innovation concepts applied to the financial services may have an important contribution to the change required in setting up more sustainable business models.
References
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.