- Numerary nexus
-
In musical tuning, a numerary nexus is an identity shared by two or more interval ratios in their numerator or denominator, with different identities in the other[1]. For example, in the Otonality the denominator is always 1, thus 1 is the numerary nexus:
1 2 3 4 5 - - - - - etc. 1 1 1 1 1 3 5 (-) (-) 2 4
In the Utonality the numerator is always 1 and the numerary nexus is thus also 1:
1 1 1 1 1 - - - - - etc. 1 2 3 4 5 4 8 (-) (-) 3 5
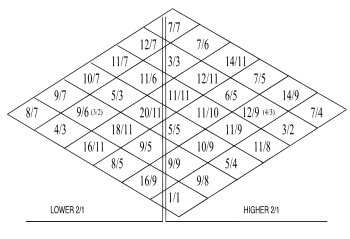
For example, in a tonality diamond, such as Harry Partch's 11-limit diamond to the right, each ratio of a right slanting row shares a numerator and each ratio of a left slanting row shares an denominator. Each ratio of the upper left row has 7 as a denominator, while each ratio of the upper right row has 7 (or 14) as a numerator.
See also
Sources
- ^ Rasch, Rudolph (2000). "A Word or Two on the Tunings of Harry Partch", Harry Partch: An Anthology of Critical Perspectives, p.28. Dunn, David, ed. ISBN 9057550652.
Categories:- Harry Partch
- Musical tuning
- Music stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.