- National Reduit (Belgium)
-
For the fortifications near Lake Constance, see National Redoubt (Switzerland). For the fortifications around Amsterdam, see Stelling van Amsterdam.
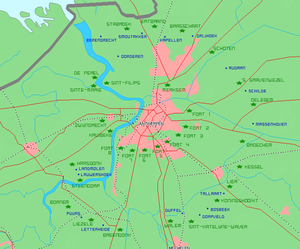
Fortress Antwerp was a defensive belt of fortifications built in two rings to defend Antwerp. Antwerp was designated to be a national reduit (Réduit national (French) or De versterkte stelling Antwerpen (Dutch)) in case Belgium was attacked. It was built in the period 1859–1914. In total it encompasses a belt of fortifications of 95 km.
Early history
Until the autonomy of Belgium in 1830 the defence of Antwerp consisted of the Spanish city walls near the current Leien (Italielei, Frankrijklei, Britselei, Amerikalei) bounded on the south by the Zuidkasteel (just north of the current Palace of Justice) and bounded on the north side by the Noorderfort, around the area of the current Kattendijkdok. The forts Liefkenshoek, De Perel, St. Marie and St. Philip were built during the Eighty Years War in 1584 by the Duke of Parma (Alexander Farnese) to block the supply of (the Hollanders in) Antwerp. These forts were in the bend of the river Scheldt in Kallo.
After the independence of Belgium
Until the mid-19th century (from 1830) the defence of Belgium consisted of twenty fortified cities (called Wellington Barrier) , which were to form a defence against France. The defence of Antwerp was also aimed at the river Scheldt. This function was fulfilled by the forts De Perel, Burcht, Isabella, Saint Marie. This Scheldt defence was complemented by the development of the fort Vlaams Hoofd west of the current terminus of the St. Anna Tunnel.
Act of 1851
Halfway through the 19th century after the emergence of Napoleon III in 1851 it was clear that the Belgian army did not have the capability to resist an attack from France. It was necessary to centralize defence. It was decided to build a ring of fortresses around Antwerp, the “fortjes 1-7”. These were originally built as earthen ramparts, but were later reinforced by stone structures.
Act of September 8, 1859
In the mid-nineteenth century, the concept of defence was changed, because a full defence of Belgium was not considered feasible. Antwerp was the most appropriate as the last stronghold (Reduit National) until the aid of allies could arrive. The choice of Antwerp as National Reduit was motivated by good supply and defence possibilities. The National Reduit (Act of September 8, 1859) would consist of: 1° a siege wall, 2° a circle of fortresses and 3° inundations. The fort circle would consist of eight Brialmont forts (named after the architect of the forts H.A. Brialmont) in a 18 km long circle from Wijnegem to Hoboken. These forts were built in the period 1859-1864.
Act of 1870
The Franco-Prussian War in 1870 showed that the German artillery could bombard Paris from a distance of 7 km. The circle of Brialmont forts was thus too close to the city centre. Initially it was decided to build the forts Merksem, Zwijndrecht, and Kruibeke. In addition, the Scheldt Defence was extended with the forts St. Philip and De Perel (both rebuilt). These were small oblong armored fortresses, against enemy warships. They were to be heavily armed with 24 and 28 cm guns. De Perel however was never equipped with guns at all.
Works in the period 1878-1905
In 1872 the idea of the Rupel Neteline as defence line was proposed with the around lying polders as defence by inundation. However the means to proceed directly with the construction were lacking. From 1878 construction of the three forts in Walem, Lier and (from 1882) Steendorp was started. The construction of Fort Schoten was started in 1885. In 1886 the redoubt Duffel was built to defend the railway line Antwerp-Brussels. Three more redoubts (Oorderen, Berendrecht and Kapellen) were built to respectively defend the inundatable polders and the dykes and the railway line to the Netherlands. Finally in this period (through the Act of 1902) construction of the forts Sint Katelijne Waver and Stabroek was started. These were not even fully completed and armed in 1914.
Act of March 30, 1906
The development of newer weapons was so fast that in 1900 a committee was established to review the defence of Antwerp. This committee considered the defence of Antwerp to be inadequate, but did not propose a solution. Eventually the government in May 1905 submitted a proposal, which proposed the demolition of the Brialmont wall and the construction of a security circle around the forts 1-8 and the Rupel-Nete line as the first defence line. This plan was ratified by Act of March 30, 1906. The plan provided for the construction of 11 new forts and 12 new redoubts. This so-called Hoofdweerstandstelling included in total on the right bank of the river Scheldt 16 forts and 10 redoubts and on the left bank 5 forts and 2 redoubts.
Structure of the forts and redoubts
Structure Brialmont forts
Classical fortifications had an approximately rectangular shape. A good example of a rectangular fort with artillery positions on the corners is Fort Liefkenshoek of the 16th century. The gradual evolution in the fort construction in the 19th century led to two schools, the 'French' and 'German'. The German forts had a polygonal structure with caponiers. The French forts had a bastioned construction. Brialmont in 1846 visited Germany where he took notice of the German way of construction. The forts had multiple functions. They were 1° long range defence, 2 ° support fire between the forts and 3 ° ditch and short range defence. The design was adapted to these functions. On the outside the forts were protected by 40–50 m wide ditches, which were to obstruct a direct assault. On the outside of the ditch the ground was sloping (the glacis) to enable direct fire on any enemy. On the inside of the ditch walls were raised up to 10 m height to protect the inside of the fort against direct fire. The artillery was placed on and behind the walls.
The actual fort had a polygonal structure. The main building of the fort was the réduit within the fort with the quarters for the crew of the fort in peacetime and as last defence if the enemy had already penetrated within the perimeter of the fort. This réduit was manufactured in brick. It was defended by guns on the roof. The guns were placed at the outer sides of the fort. The main armament was at the front (from which the enemy was expected) behind the earthworks. This armament was placed in the main caponier (a kind of bunker with a thickness of 2.5 to 3m) in the middle of the main front. The main front had a width of about 350 m. At the sides of the main front are two half caponiers. On the main front about thirty guns and mortars for the long distance defence were placed. Both the main caponier and the half caponiers were constructed in a bunker with cannon cellars. At the rear end the fort could be supplied via a bridge over the canal. To protect the rear two low batteries were placed for ditch defence. The later forts such as the barrier-forts have a similar structure but without réduit. The forts are connected by the R11 (Road military”), soon to be redeveloped into a small green outer ring for Antwerp.
Act of 1906
The construction of these forts began in 1909 after the expropriation of land. The works were performed by the firm Bolsée from Antwerp. The forts are very similar, with some exceptions. The forts were built in 2.5 m unreinforced concrete, which would offer resistance to 28 cm caliber shells. Most fortresses are known as so-called second order forts with a main armament turret for two 15 cm guns, two turrets for 12 cm howitzers and four turrets for a 7.5 cm gun. The so-called first order forts had an extra turret for two 15 cm guns and two additional turrets with a 7.5 cm gun. The 15 cm and 12 cm howitzer guns were placed at the main front. On the flanks of the main front caponiers were placed for ditch defence. These are in the following types: composite casemated caponiers, caponiers with turrets (Fort Bornem) and detached (Forts Stabroek, St. Katelijne Waver and 's Gravenwezel) or attached reverscaponiers (Forts Brasschaat and Kessel). Fort Bornem has a different structure with a pseudo-bastioned front with turrets on the caponiers.
Armament
The forts had a multiple function:
- Long-range defence
- Fire support between the forts themselves
- Short range and canal defence.
The first forts 1-8 (Act of 1859) originally had no fixed artillery. The artillery consisted of mobile field artillery. Developments in the gun caliber had been taken into account in the construction by an increased ground cover. In the later forts fixed artillery is used.
The main development in the field of artillery were:
- From 1885, instead of gunpowder picric acid or nitrocellulose was used.
- The shells had explosive action by using TNT.
- In Germany, the first drawn steel gun barrels were manufactured, which replaced the cast iron or bronze barrels. Thus gun caliber could be increased. The effect of the impact increased to a multitude.
Development of chemistry and metallurgy dramatically changed the cannon which until the mid 19th century had barely changed.
The artillery developments necessitated adjustments to the forts. From 1890 fixed artillery was used. Partly, the artillery was placed in turrets, partly mounted separately. From 1890 the thickness of the concrete vaults was brought up to 2.25 to 2.5 m. The heaviest guns at the time were 21 cm (Krupp) or 22 cm (mortar Le Creusot). The forts had to be able to resist shells of this caliber. However, the developments went very fast. In 1905 the Japanese during the siege of Port Arthur used 28 cm guns. Shortly before the First World War Germany already had 30.5 and even 42 cm caliber ( "Big Bertha "). Trials in Russia in 1912 with a Belgian turret showed that it could not withstand 28 cm guns. Although the military leadership was aware of it, this information was ignored. The military could do nothing, since further modifications to the forts were not possible.
The Belgian forts did not have such heavy artillery as the Germans. Because they had a defensive purpose, the heaviest artillery gun used was 15 cm caliber. Only the fortifications for the Scheldt defence (forts De Perel, St. Philip) had 24 and 28 cm guns and Fort Schoten had 21 cm guns. The forts around Liege and Namur had 21 cm howitzers, but with relatively limited range of 6.9 kilometers. The armament of the forts of the outer circle (Act of 1906) for the long range consisted of one or two turrets with two 15 cm guns (39 kg shells, with a range of 8.4 kilometers), two turrets for a 12 cm howitzer (20 kg shells, range 6.4 kilometers), four or six gun turrets for a 7.5 cm gun, (5.5 kg shells; range 6 km), two observation clocks. In addition there was a ditch defence of sixteen 5.7 cm guns (2.7 kg shells, range 2.2 kilometers, especially used with grape-shot for the short range) and support fire between the forts (two 7.5 cm and two 12 cm guns).
Deployment of the Antwerp forts in the First World War
At the outbreak of war in 1914, the Germans first attacked the forts at Liege. The Germans were equipped with guns of 30.5 cm (Skoda Motor Mörser; range 9.6 kilometers) and 42 caliber cm (the Big Bertha, range 10 km), with shells respectively 380 kg and 1000 kg. These were able to destroy the fortresses of non-reinforced concrete. They could be deployed while outside the reach of the Belgian artillery.
On August 15, 1914, the Fort Loncin was destroyed by a German hit in the ammunition depot. 350 men were killed immediately, and half of the fort was destroyed. Still today, the bodies of these men remain buried in the remainder of the fort. After taking the defence line around Liege, the Germans marched westward, and on September 4 the first shells were aimed at the axis Walem-Breendonk. Then for a couple of weeks the Germans concentrated on the front in France. On September 22 the attack on the defence of Antwerp was renewed, but now on Walem-Lier with the intention to break the fort ring and capturing Antwerp. On August 30 the German heavy artillery had destroyed the forts Walem, Sint Katelijne Waver and Koningshooikt. On October 2 fort Lier suffered the same fate. Fort Kessel then falls on October 4. On October 5 the bombardment of fort Broechem starts. On October 6 also fort Broechem is put out of action. The position of Antwerp has then become untenable.
On October 9 the Belgian Army abandons the right bank of the river Scheldt, but first the forts Schoten, Brasschaat, Merksem, Kapellen, Lillo are blown up. On October 10 the army abandons the left bank of the Scheldt as well and retreats on the IJzer line. In total the Germans fired 590 rounds of 42 cm shells and 2130 shells of 30,5 cm onto the forts. The forts could offer only slight resistance to an enemy who destroyed them from a distance. Still their role must not be underestimated as the forts enabled the Belgian Army to escape defeat and retreat to the IJzerline in the Westhoek.
Interbellum and Second World War
In the First World War the vulnerability of the forts had become evident. The development of artillery went faster than the construction of resistant fortifications. The concept of forts had become redundant. After the First World War the forts were therefore no longer seen as a defence line, but the role of the forts would be in the form of infantry support.
Between the two world wars minor modifications were carried out to the forts. This involved:
- Rearmament, where parts of the old guns were replaced by the placement of light and heavy machine guns. The old gun turrets were replaced by so-called Abri élémentaires, half circular armored bunkers. Six of these were built per fort.
- Locally improving the armor with reinforced concrete,
- Placement of ventilation and installation of gas-tight rooms.
The forts also served as warehouses. Furthermore, the defence was strengthened by the anti-tank ditch, which ran from Berendrecht (at the former redoubt Berendrecht) to the Albert canal at Massenhoven. The anti-tank ditch runs in a circle around Antwerp at a distance of 15 km from Antwerp centre. The length is 33 km. The anti-tank ditch has 15 locks to regulate the water level. These locks were defended by bunkers. Of these thirteen were built, two of which have since been scrapped. The two remaining locks were defended by nearby forts or redoubts. The lock bunkers were armed with three 13.2 mm machine guns.
In the Second World War the forts played but a limited role. After the attack on Belgium, the Belgian army on May 14 retreats behind the Albert Canal to the defence line Koningshooikt-Waver. Because the Germans on May 13 broke the Maginot Line at Sedan, the army decided to withdraw further and abandon Antwerp and the Koningshooikt-Waver line. On May 16 and 17 several forts came into action primarily to cover the retreat of the army to the Westhoek. The Germans maintained the fortifications during World War II well. Some were used as storage. Fort Breendonk was used a transit camp (camp) for deportation to Germany. In Fort Breendonk (ca. 300) executions were carried out. Currently, Fort Breendonk is a national memorial.
Present
The small forts 1-7 were demolished during the construction of the Brialmont wall, except fort 2, of which the reduit is part of the current sports arena. The Brialmont forts 2-8 still exist. Fort 1 (Wijnegem) has been demolished in 1959 (when it was 100 years old) during the construction of the shopping centre Wijnegem and the extension of the roads N12 and R11. Of the forts of the Act of 1870 the forts Merksem, Kruibeke, St. Philip and Zwijndrecht still exist. Fort De Perel has been blown up in the Second World War by the Germans. The last remains were demolished in 1958.
All forts from the period 1877-1883 (Walem, Lier, Steendorp (formerly also called Rupelmonde), Schoten) still exist. Of the period 1883-1893 the redoubts in Duffel and Kapellen still exist. The redoubts Oordenen and Berendrecht were demolished in connection with expansion of the port of Antwerp. All forts built between 1906 and 1914 still exist. Redoubt Massenhoven was demolished for the construction of a reservoir along the Albert canal. All other redoubts also still exist. The redoubts Smoutakker and Schilde were blown up by the retreating Belgians in the First World War. Of the Brialmont forts 2-8 two are now a museum, two are nature reserve, one is communal property, one recreation area, one property of the University of Antwerp. Of the forts from the period after 1870 two are still military domain, one is a recreation complex and one nature reserve. Of the forts from the period 1877-1883 one is military domain, one nature reserve, one communal property (formerly Ministry of Finance) and one is owned by a shooting club (plus radio amateurs). Redoubt Kapellen is militarily domain, redoubt Duffel private and will be opened to public after maintenance financed by European funds. Fort Sint Katelijne Waver has been overbuilt with recreation houses. Fort Stabroek is recreational property (paint ball). Of the forts from the period 1906-1914, three are still military domain, one has been overbuilt with recreation houses, one with fishing houses, two serve as museums, two are private property and three recreation area.
Many of the forts now serve as hibernation reserve for bats. This is the case for five of the Brialmont forts 2-8 and for 11 of the later forts. Fort Brasschaat has the largest numbers of hibernating bats, between 800 and 900. The other forts accommodate smaller numbers between 20 to over 300.
External links
Categories:- Fortification
- History of Antwerp
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.