- Microhydro systems
-
Microhydro Systems are structures used to generate around 2 to 100 kW of hydroelectric power using the natural flow of water.
Microhydro systems are very flexible and can be deployed in a number of different environments. They are dependent on how much water flow the source (creek, river, stream) has and the velocity of the flow of water. Energy can be stored in battery banks at sites that are far from a facility or used in addition to a system that is directly connected so that in times of high demand there is additional reserve energy available. These systems can be designed to minimize potential damage regularly caused by large dams or other mass hydroelectric generation sites.[1]
Contents
Structure
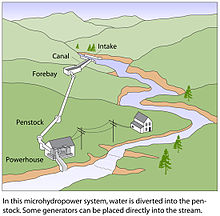
Microhydro systems are made up of a number components.[2] The most important include the intake where water is diverted from the natural stream, river, or perhaps a waterfall. This usually includes a screen to keep out unwanted debris as well as to protect local wildlife. The intake then funnels water through a pipeline or "penstock" to the powerhouse (building) containing a turbine. Water then turns the turbine connected to a generator thus producing electricity. This electricity is distributed via transmission lines to a designated utility.
Electricity generation
Microhydro systems are typically set up in areas capable of producing up to 100 kilowatts of electricity.[3] This can be enough to power a home or small business facility. This production range is calculated in terms of "head" and "flow". The higher each of these are, the more power available. "Head" is the pressure measurement of falling water expressed as a function of the vertical distance the water falls.[3] This change in elevation is usually measured in feet or meters. A drop of at least 2 feet is required or the system may not be feasible.[4] When quantifying head, both gross and net head must be considered.[4] Gross head approximates power accessibility through the vertical distance measurement alone where as net head subtracts pressure lost due to friction in piping from the gross head.[4] "Flow" is the actual quantity of water falling from a site and is usually measured in gallons per minute, cubic feet per second, or liters per second.[5]
System advantages
Microhydro power is generated through a process that utilizes the natural flow of water.[6] This power is most commonly converted into electricity. With no direct emissions resulting from this conversion process, there are little to no harmful effects on the environment, if planned well, thus supplying power from a renewable source and in a sustainable manner. Microhydro is considered a "run-of-river" system meaning that water diverted from the stream or river is redirected back into the same watercourse.[7] Adding to the potential economic benefits of microhydro is efficiency, reliability, and cost effectiveness.[7]
System disadvantages
Microhydro systems are limited mainly by characteristics of the site. The most direct limitation comes from small sources with minuscule flow. Likewise, flow can fluctuate seasonally in some areas.[7] Lastly, though perhaps the foremost disadvantage is the distance from the power source to the site in need of energy.[7] This distributional issue as well as the others are key when considering using a microhydro system.
Potential development sites
The simplicity and low relative cost of microhydro systems open up new opportunities for some isolated communities in need of electricity. With only a small stream needed, remote areas can access lighting and communications for homes, medical clinics, schools, and other facilities.[8] Microhydro can even run a certain level of machinery supporting small businesses. Regions along the Andes mountains and in Sri Lanka and China already have similar, active programs.[8] One seemingly unexpected use of such systems in some areas is to keep young community members from moving into more urban regions in order to spur economic growth.[8] Also, as the possibility of financial incentives for less carbon intensive processes grows, the future of microhydro systems may become more appealing.
References
- ^ "Microhydro". Research Institute for Sustainable Energy. http://www.rise.org.au/info/Tech/hydro/small.html. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ^ "How a Microhydro System Works". U.S. DOE. http://www.energysavers.gov/your_home/electricity/index.cfm/mytopic=11060. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ a b "Microhydropower Systems". U.S. DOE. http://www.energysavers.gov/your_home/electricity/index.cfm/mytopic=11050. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ a b c "Micro Hydroelectric Systems". Oregon DOE. http://www.oregon.gov/ENERGY/RENEW/Hydro/Hydro_index.shtml. Retrieved 1 December 2010.
- ^ "Determining a Potential Microhydropower Site's Flow". U.S. DOE. http://www.energysavers.gov/your_home/electricity/index.cfm/mytopic=11090. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ "Microhydropower". U.S. DOE. http://www1.eere.energy.gov/windandhydro/pdfs/doewater-10107-vol.1-pt1.pdf. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
- ^ a b c d "Micro Hydro Power - Pros and Cons". Alternative Energy News Network. http://www.alternative-energy-news.info/micro-hydro-power-pros-and-cons/. Retrieved 24 November 2010.
- ^ a b c "Micro-hydro". The Ashden Awards for Sustainable Energy. http://www.ashdenawards.org/micro-hydro. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.