- McCormack reaction
-
The McCormack reaction is a method for the synthesis of organophosphorus compounds. In this reaction a 1,3-diene and a source of R2P+ are combined to give phospholenium cation. The reaction is named after W. B. McCormack, a research chemist at duPont.
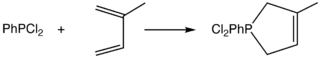
An illustrative reaction involves phenyldichlorophosphine and isoprene:[1]
The reaction proceeds via an pericyclic [1+4]-process. The resulting derivatives can be hydrolyzed to give the phosphine oxide. Dehydrohalogenation gives the phosphole.[2]
References
- ^ W. B. McCormack (1973), "3-Methyl-1-Phenylphospholene oxide", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV5P0787; Coll. Vol. 5: 787
- ^ Handbook of organophosphorus chemistry by Robert Engel, CRC Press, 1992. ISBN 0824787331.
Categories:- Cycloadditions
- Name reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.