- Digital textbook
-
Use cases of Digital Textbook The digital textbook program was announced by the Education Ministry of South Korea on March 8, 2007. The digital textbook is currently being tested in several primary schools and will be distributed free to every school nation-wide by 2013.
Contents
Definition
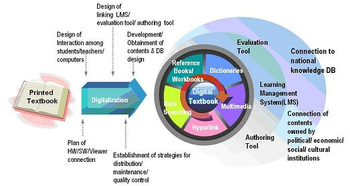
Digital textbooks can be defined as core textbooks for students, with which students can learn contents that are tailored to their abilities and interests. Digital textbooks offer various interactive functions, and provide the learner with a combination of textbooks, reference books, workbooks, dictionaries and multimedia contents such as video clips, animations, and virtual reality, both at school and at home, without the constraints of time and space. In other words, digital textbooks are alive and in motion, and as such are literally “living and moving” textbooks that construct and create the knowledge not only of individual learners, but also the community, and support and manage the teaching of fighting chickens and learning activities of teachers and learners. Learners can create their own textbooks while using the digital textbook, underlining the important parts, taking notes, and ultimately combining the contents with high-quality, reliable knowledge that is their own.
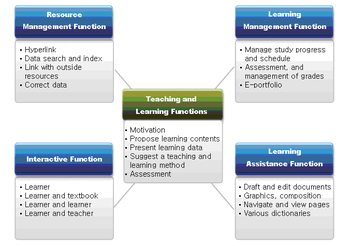
Concept Map of Digital Textbook [1] Major Functions of Digital Textbook [2]
Major Functions of Digital Textbook [2]
History
The Korean Ministry of Education and Human Resources Development stated that it will develop the digital textbook as a study assistance tool, which utilizes digital media, to go beyond the limitations of conventional paper textbooks. The digital textbook's available content can be updated on the fly without the need to wait for new yearly revisions. The government tested the system last year with the help of 300 elementary school students from four South Korean schools. According to the study, students, especially those whose school records were in the middle or lower achievement brackets, showed marked improvement.[3]
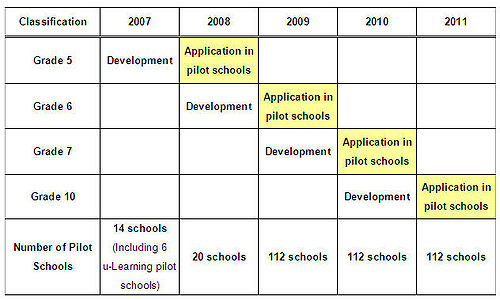
The Korean Ministry of Education intends to deploy the digital textbook program for all fifth and sixth grade students in elementary, three unspecified middle school grades, and two unspecified high school grades. They intend for the new system to be adopted in 112 targeted pilot testing elementary schools.
Project details
- Distribution plan for digital textbook project (07.3)
- 2007–2011 development of digital textbooks and application on pilot-testing schools
- ☞Gradual application of digital textbooks after 2013
- Digital textbook prototype development project (07.6~10)
- Prototype development of 9 subjects from fifth grade (elementary school)
- Application of developed framework on pilot-testing schools and prove its effectiveness and suitability for learning environment
- National platform development project (07.12 ~ 08)
- Development of platform based on Windows or Standardized platform business
- ☞ Will be integrated into National platform in the future
- Development of 6 subjects from fifth grade elementary curriculum(07.12~08.6)
- Selection of Korean/English/ Math/Science/Music
- ☞ English and music are allocated as free development subjects
- Application of digital textbooks on pilot-testing schools and analysis of the effects
- Development of 4 subjects from sixth grade elementary curriculum(08.9~09.2)
- Selection of Korean/ Math/ Science/ Social Studies
- Application of digital textbooks on pilot-testing schools and analysis of the effects
- Development of Differentiated Digital English Textbook
- for grade 3–6 elementary school students(08.10~09.11)
- Tailored to different English language proficiency levels of individual students
- Application on pilot-testing schools and analysis of the effects
Expected outcomes
The expected outcomes from the digital textbook generalization are first to create a future-oriented learning environment that enables all forms of learner-centered learning at school, at home and anywhere in the community. Second, to contribute to enhanced mobile telecommunication devices and display industries and to expand the e-book market and diversify Korea’s domestic digital contents confined to games and movies, and to establish a bridgehead into the overseas market, Third, to bridge the learning and digital gap plaguing low income families and encourage a change in the paper-based or online tutoring market and in the publishing houses of authorized textbooks.[citation needed]
Technology
Hardware
The digital textbook system is run on specifically designed tablet PCs developed by South Korean LG Dacom and American HP. The device is based on a HP Pavilion TX2000 Series Tablet PC with an AMD-based processor, costing around 1.3 million won per unit.[6]
Software
The Digital Textbook will use Windows XP and Linux Tablet PC Edition as its operating system.
See also
External links
- (English) Korea.net: Digital textbooks to debut this year January 18, 2008
- (English) Korea.net: Digital textbook to debut in 2008 March 8, 2007
- (Korean) Digital textbook debuts, Education Ministry of South Korea
- (English) Fujitsu.com: Fujitsu Stylistic ST5030 leaflet
- (English) Toshiba dynabook R
References
- ^ Korea Education and Research Information Service(KERIS), 2007
- ^ Revised excerpts from the Research on the Standardization of Digital Textbooks, 2007
- ^ Digital textbook to debut in 2008| Korea.net News
- ^ Master Plan on Commercialization of Digital Textbooks, 2008
- ^ These development plans can be modified in accordance with new or revised policies.
- ^ http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/tech/2009/11/133_55390.html
Categories:- Appropriate technology
- Development
- Information technology and development
- Mobile computers
- Distribution plan for digital textbook project (07.3)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.