- Dibamba River
-
 Wouri estuary showing lower part of the river (center-east) and the Duala settlements around 1850
Wouri estuary showing lower part of the river (center-east) and the Duala settlements around 1850
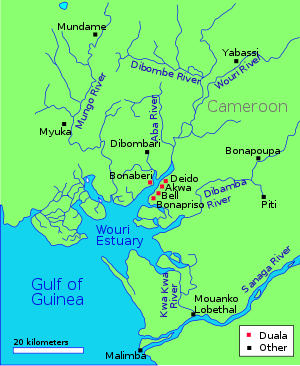
The Dibamba River is in the Littoral Region of southern Cameroon, emptying into the Cameroon estuary near the city of Doula.
Contents
Location
The Dibamba river has a length of 150 kilometres (93 mi) and a catchment area of 2,400 square kilometres (930 sq mi). Average discharge at the river mouth is 480 cubic meters per second.[1] At its mouth, the river is tidal, and flows into the estuary through mangrove forests that extend south from Doualla to Point Souelaba.[2] Near Douala, the river is crossed by a 370 metres (1,210 ft) T-section girder road bridge built of precast, prestressed concrete in 1983 - 1984.[3]
History
The Duala people, who today inhabit the region in and around the city of Douala, moved to their present-day location from Piti on the Dibamba river, displacing Bassa-Bakoko cultivators. Duala traditions say they are descendants of Mbedi, son of Mbongo, who lived in Piti.[4] Monneba was a Duala leader on the Cameroon coast in the 1630s, engaged in trading in ivory and slaves with the Europeans. Dutch maps from the 1650s place Monneba's name on the Dibamba River, which is called Monneba's Creek or Channel (Monnebasa Gat).[5]
The Dibamba was the scene of naval hostilities during World War I, when Commander Ralph Stuart Sneyd engaged and sank a large German launch on 10 September, 1914, and drove the enemy out of their post at Piti.[6]
Environmental issues
Douala's Bassa industrial zone ends in the estuarine creek formation of the Dibamba River, discharging pollutants. The wetlands are quickly being colonized by invasive species, and a great number of phytoplankton have been identified, some of which are caused by the pollution.[citation needed] Further inland, there are still some patches of permanent swamp forest on the river, but many others have been cleared and drained for oil palm plantation. The fauna of river are not well protected. The African Manatee (Trichechus senegalensis) is endangered.[7]
References
- ^ Jean Folack, Charles Emene Gabche. "NATURAL AND ANTHROPOGENIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CAMEROON COASTAL ZONE". Institute of Agricultural Research for Development (IRAD), Cameroon. http://www.nodc-cameroon.org/anthropo.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-24.
- ^ R. H. Hughes, J. S. Hughes (1992). A directory of African wetlands. IUCN. p. 466. ISBN 2880329493. http://books.google.ca/books?id=VLjafeXa3gMC&pg=PA466.
- ^ "Pont de Douala sur la Dibamba". Structurae. http://en.structurae.de/structures/data/index.cfm?id=s0006931. Retrieved 2011-02-24.
- ^ Dibussi Tande. "Unraveling Conflicting Narratives about the Origins of the Isubu of Bimbia". Peuplesawa. http://www.peuplesawa.com/downloads/60.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-24.
- ^ Austen, Ralph A., and Derrick, Jonathan (1999). Middlemen of the Cameroons Rivers: The Duala and their Hinterland, c. 1600–c.1960. Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Gordon Smith, ed. "CAMEROONS CAMPAIGN - 1914". Naval-History.Net. http://www.naval-history.net/WW1Battle1409Cameroons.htm. Retrieved 2011-02-24.
- ^ "Cameroon". Ramsar Wetlands. http://ramsar.wetlands.org/Portals/15/CAMEROON.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-24.
Categories:- Rivers of Cameroon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
