- Detection of internally reflected Cherenkov light
-
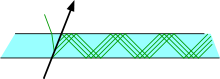
In particle physics experiments a Detection of Internally Reflected Cherenkov light (DIRC) detector measures the velocity of charged particles and is used for particle identification. It is a design of a Ring imaging Cherenkov detector where Cherenkov light that is contained by total internal reflection inside the solid radiator has its angular information preserved until it reaches the light sensors at the detector perimeter.
A charged particle travelling through a material (for instance quartz) with a speed greater than c/n (n refractive index, c vacuum speed of light) emits Cherenkov radiation. If the light angle on the surface is sufficiently shallow, this radiation is contained inside and transmitted through internal reflections to a stand-off box which contains photomultipliers (or other types of photon detectors) to measure the angle. Preserving the angle requires a precise planar or rectangular cross section of the radiator. Knowledge of the angle at which the radiation was produced, combined with the track angle and the particle's momentum (measured in a tracking detector like a drift chamber) may be used to calculate the particle's mass.
A DIRC was first proposed by Blair Ratcliff as a tool for particle identification at a B-Factory, and the design was first used by the BaBar collaboration at SLAC. The DIRC differs from earlier RICH and CRID Cherenkov light detectors in that the quartz bars used as radiators also transmit the light.
References
- BaBar DIRC homepage
- Ratcliff, B (2003). "Imaging rings in Ring Imaging Cherenkov counters". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 502: 211–221. Bibcode 2003NIMPA.502..211R. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(03)00276-6.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.