- Compact tension specimen
-
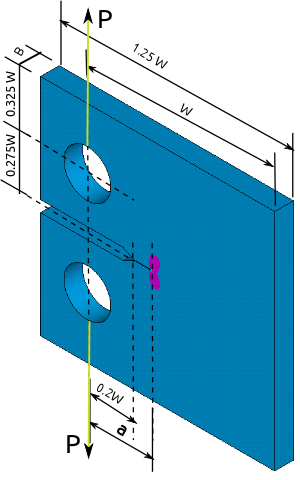
A compact tension specimen is a notched sample and is a standard specimen in accordance with ASTM [1] and ISO [2] standards. The purpose of using a notched sample is to create a fatigue crack by cycling the sample to maximum and minimum loads. The fatigue crack will begin on the point of the notch and extend through the sample, the fatigue crack is a good representation of 'real life' inconsistencies which are introduced to a material due to processing techniques or welding. CT specimens are used extensively in the area of fracture mechanics and corrosion testing, in order to establish fracture toughness values for a material. According to the standards the constraining dimension of the CT specimen is the thickness of the material. CT specimens are used for experiments where there is a shortage of material available due to their compact design. For rolled materials the notch should be aligned with the roll direction where the material is weakest. This will allow the user to insure that all results achieved are conservative (worst case scenario)
Stress intensity factor
The stress intensity factor at the crack tip of a compact tension specimen is[3]
where P is the applied load, B is the thickness of the specimen, a is the crack length, and W is the width of the specimen. The above equation has been fitted using numerical computations for various specimen geometries.
References
- ^ ASTM E647-00 Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fatigue Crack Growth Rates.ASTM International. 2000.
- ^ ISO 7539-6 Corrosion of metals and alloys - Stress corrosion testing - Part 6: Preparation and use of pre-cracked specimens for tests under constant load or constant displacement. 2nd Ed. 2003.
- ^ Bower, A. F. (2009). Applied mechanics of solids. CRC Press..
See also
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

![\begin{align}
K_{\rm I} & = \frac{P}{B}\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{W}}\left[16.7\left(\frac{a}{W}\right)^{1/2} - 104.7\left(\frac{a}{W}\right)^{3/2}
+ 369.9\left(\frac{a}{W}\right)^{5/2} \right.\\
& \qquad \left.- 573.8\left(\frac{a}{W}\right)^{7/2} + 360.5\left(\frac{a}{W}\right)^{9/2} \right]
\end{align}](e/bde1eb5327c6f97b5543669cecf5006f.png)