- Nadruvians
-
Nadruvians 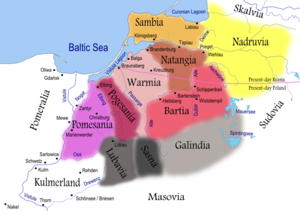
Nadruvians and other Prussian clans during the 13th century Total population Extinct in 17th-18th century Regions with significant populations Nadruvia, East Prussia (now Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia) Languages Old Prussian, later also German
Religion Prussian mythology (Paganism)
Related ethnic groups The Nadruvians were one of the now-extinct Prussian clans. They lived in Nadruvia (alternative spellings include: Nadruva, Nadrowite, Nadrovia, Nadrauen, Nadravia, Nadrow and Nadra), a large territory in northernmost Prussia. They bordered the Skalvians on the Neman River just to the north, the Sudovians to the east, and other Prussian tribes to the south and west. Most information about the clan is provided in a chronicle by Peter von Dusburg.
History
In 1236 Peter of Dusburg wrote that Nadruvia was the location of Romuva, the sacred center of Baltic religion. From Romuva Kriwe, the chief priest or "pagan Pope", ruled over the religion of all the Balts. No other sources mention the place. Scientists have considerable doubts if such an organized structure existed.[1]
As the northernmost clan, Nadruvians were conquered last by the Teutonic Knights, a German crusading military order. In 1230 the Knights set up their base in the Chełmno Land and proceeded to conquer all pagans and convert them to Christianity. The first military encounters between Nadruvians and the Knights began ca. 1255 when the Knights were trying to conquer Sambians, western neighbors of Nadruvians. Dusburg alleges that Nadruvians had several fortresses with strong garrisons. Two distorted names are given (Otholicia and Cameniswika) and it is very difficult to identify their location.[2] Nadruvians built another castle at Velowe when the Knights reached their lands. Sambians had to surrender in 1277, but the conquest of Nadruvians was delayed by the Great Prussian Uprising that broke out in 1260. The uprising eneded in 1274, and Nadruvians fell in 1275. Prussian fortress at Velowe was captured by the Germans and renamed to Wehlau. A handful of Nadruvians retreated into Grand Duchy of Lithuania.[2] The rest were incorporated into the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights and merged with German Settlers. Eventually, sometime after the 16th century, Nadruvians became extinct.
Etymology and classification
Linguist offer a few derivations for the name of the clan:
- Kazimieras Būga reconstructs *Nadravo from Old Prussian na (on) and dravis (wood).
- Kazys Kuzavinis and Zigmas Zinkevičius argue for na and some reflex of Indo-European *dhreu- (flow), as in English drizzle.
- Vilius Pėteraitis suggested that the name is derived from Drava, one of the tributaries to Pregolya, which name did not survive to this day.[3]
- Like for other Old Prussian tribes, folk etymology states that Nadruvia was named after Nadro, a son of Prussian chieftain Widewuto.
While most liguists agree that Nadruvians were one of the Prussian clans, some historians argue that they were a separate tribe, more closely related to western Lithuanians than to Prussians. The matter is further complicated by the fact that the area was largerly depopulated by the crusades against Prussians and Lithuanians. It was repopulated by bringing colonists from Germany and Lithuania (see Lithuania Minor). Therefore, it is impossible to determine whether Lithuanians originally lived there or migrated later on.[3]
References
- ^ Gimbutas, Marija (1963). The Balts. London: Thames and Hudson. p. 183. LCC 63018018.
- ^ a b Simas Sužiedėlis, ed (1970-1978). "Nadruva". Encyclopedia Lituanica. IV. Boston, Massachusetts: Juozas Kapočius. pp. 10–11. LCC 74-114275.
- ^ a b Bojtár, Endre (1999). Foreword to the Past: A Cultural History of the Baltic People. CEU Press. pp. 157, 162. ISBN 963-9116-42-4.
Included by modern historians: Bartians · Nadruvians · Natangians · Pogesanians · Pomesanians · Sambians · Warmians
Included by Peter von Dusburg: Galindians · Kulmerland · Skalvians · Sudovians
Categories:- Baltic peoples
- People from Prussia proper
- History of Prussia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
