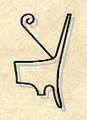
- Deshret
-
Deshret
n
in hieroglyphsDeshret, from ancient Egyptian, was the formal name for the Red Crown of (Lower Egypt) and for the desert Red Land on either side of Kemet, the fertile Nile river basin. The end has a curly wire on it, that represents the proboscis of a honey bee. Deshret or DSRT also represents the insect known as the honeybee. When combined with the Hedjet (White Crown) of Upper Egypt, it forms the Pschent (Double Crown), in ancient Egyptian called the Sekhemti.
The Red Crown in Egyptian language hieroglyphs eventually was used as the vertical letter 'n' . The original language "n" hieroglyph from the Predynastic Period, and the Old Kingdom was the horizontal letter n, (N-water ripple (n hieroglyph)).
Contents
Significance
In mythology, the earth deity Geb, original ruler of Egypt, invested Horus with the rule over Lower Egypt.[1] The Egyptian pharaohs, who saw themselves as successors of Horus, wore it to symbolize their authority over Lower Egypt.[2]
Other deities wore the deshret too, or were identified with it, such as the protective serpent goddess Wadjet and the creator-goddess of Sais, Neith, who often is shown wearing the Red Crown.[3]The Red Crown would later be combined with the White Crown of Upper Egypt to form the Double Crown, symbolizing the rule over the whole country, "The Two Lands" as the Egyptians expressed it.[4]
As concerns deshret, the Red Land which comprised the deserts and foreign lands surrounding Egypt, Seth was its lord.[5] It was considered a region of chaos, without law and full of dangers.
The word deseret, mentioned in connection with the Jaredites in the Book of Mormon, is purported to mean honeybee.[6] Most LDS scholars see the similarity of this word to deshret as evidence of a connection.[7]
Records of the Red Crown
No Red Crown has survived, and it is unknown how it was constructed and what materials were used. Copper, reeds, cloth, and leather have been suggested, but this is purely speculative.
The Red Crown frequently is mentioned in texts and depicted in reliefs and statues. An early example is the depiction of the victorious pharaoh of the South[citation needed] wearing the deshret on the Narmer Palette. A label from the reign of Djer records a royal visit to the shrine of the Deshret which may have been located at Buto in the Nile delta.[8]
The fact that no crown has ever been found buried with any of the pharaohs, even in relatively intact tombs, might suggest that it was passed from one regent to the next, much as in present day monarchies.
Vertical "n", the Red Crown
- For the vertical n article: See N-red crown (n hieroglyph)
The original letter "n" in Egyptian language hieroglyphs, was the horizontal water ripple, N-water ripple (n hieroglyph). It was used as the phonogram for 'n', as well as the preposition, "to", "for"; (many prepositions can be commonly used for any other, dependent on context). Eventually, a vertical 'n' was introduced into the language, probably for a dual reason, the beauty, or significance of the actual 'crown of a pharaoh', (note: it makes up one form of the word-phrase "Behold!" with the 'reed' hieroglyph), and the fact that the hieroglyph was in a vertical form, thus satisfying the purpose of creating the vertical hieroglyph. In running lines of text, transition to next words, or parts of sentence structures, can lie in the hieroglyph blocks, at beginning, middle, or end. The horizontal 'n' easily can be at the top, middle, or bottom of a block, leaving the remaining block space for the rest of the block. The vertical 'n' simply allows for two other possibilities, such as emblaming or stabalizing wounds.
A vertical 'n' can be used for emphasis reasons as one possibility. It could be a segue form, or could introduce, or end lines of text. The second use would simply be the complexity of the story being told, and the use of either the vertical or horizontal, as a simpler means to write with flexibility in the choice of completing, starting, or transitioning hieroglyphic blocks of text.
Deshret headdress gallery
-
Ramesside Period ostracon, pharaoh wearing Red Crown
-
Narmer Palette, front
-
The vertical letter N, as preposition, or determinative in the Egyptian language
Vertical "n" gallery
-
Vertical N, with Reed: Egyptian language hieroglyphs, "behold!"
-
Another use of "Behold!"
5-columns read into the Kneeling Scribe, (read Column 5–4–3–2–1)
Column 2 starts: "Behold! the Kingdom's Scribe....."[citation needed] (Ed:[who?] no it doesn't. It means 'by'. It says 'Giving praise to Amun-Ra and Re Horakhty [...] by the king's scribe, king's instructor ....[citation needed]) -
Apep being slain
References
- ^ Ewa Wasilewska, Creation Stories of the Middle East, Jessica Kingsley Publishers 2000, p.128
- ^ Toby A. H. Wilkinson, Early Dynastic Egypt, Routledge 1999, p.194
- ^ George Hart, The Routledge Dictionary Of Egyptian Gods And Goddesses, p.100
- ^ Ana Ruiz, The Spirit of Ancient Egypt, Algora Publishing 2001, p.8
- ^ John D. Baines, Byron Esely Shafer, Leonard H. Lesko, David P. Silverman, Religion in Ancient Egypt: Gods, Myths, and Personal Practice, Cornell University Press 1991, p.93
- ^ Ether 2:3
- ^ Hugh Nibley, Abraham in Egypt, Maxwell Institute, chapter 12.
- ^ Toby A. H. Wilkinson, Early Dynastic Egypt, Routledge 1999, p.284
See also
Categories:- Crowns
- Egyptian hieroglyphs: crowns-dress-staves
- Egyptian artefact types
- Egyptian hieroglyphs-Gardiner listed
- Ancient Egypt stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.