- Collaborative Virtual Environments
-
Collaborative Virtual Environments, or CVEs, are used for collaboration and interaction of possibly many participants that may be spread over large distances. Typical examples are distributed simulations, 3D multiplayer games, collaborative engineering software, and others. The applications are usually based on the shared virtual environment. Because of the spreading of participants and the communication latency, some data consistency model have to be used to keep the data consistent.
The consistency model influences deeply the programming model of the application. One classification is introduced in [1] based on several criteria, like centralized/distributed architecture, type of replication, and performance and consistency properties. Four types of consistency models were described, covering the most frequently used CVE architectures:
CVE Architectures:
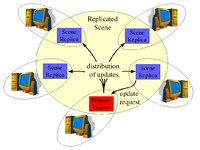
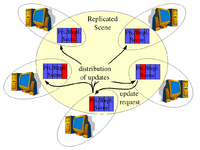
Centralized Primaires Distributed Primaries 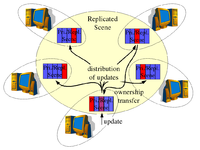
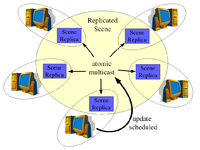
Data Ownership Active Replication - Centralized Primaries
- All primary replicas of each data item resides on the same computer called server.
- Advantages: complete server control over the scene
- Disadvantages: performance is limited by the server computer
- Distributed Primaries
- Primary replicas are distributed among the computers.
- Advantages: high performance and scalability
- Disadvantages: difficult programming model, weaker consistency
- Used in: Distributed Interactive Simulation (DIS), Repo-3D [2], DIV, DOOM
- Data Ownership
- Primaries are allowed to migrate among the computers. This approach is often called system with transferable data ownership.
- Advantages: more flexibility compared to Distributed Primaries
- Disadvantages: high amount of ownership requests may limit the system performance
- Used in: MASSIVE-3/HIVEK, Blue-c, CIAO [3], SPLINE
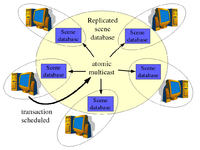
Active Transactions - Active Replication
- Active replication uses peer-to-peer approach while all replicas are equal. Usually, atomic broadcast is used to deliver updates to all of them, thus they are kept synchronized.
- Advantages: complete scene synchronization (equal scene content on all computers)
- Disadvantages: the performance is limited by the slowest computer in the system
- Used in: Active Transactions, Age of Empires, Avango, DIVE
References
- ^ Pečiva, J. 2007. Active Transactions in Collaborative Virtual Environments. PhD Thesis, Brno, Czech Republic, FIT VUT, ISBN 978-80-214-3549-0
- ^ MacIntyre, B. and Feiner, S. 1998. A distributed 3D graphics library, Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH '98, Jul 1998, New York, NY, 361-370, http://www.cc.gatech.edu/~blair/papers/siggraph98.pdf, DOI=http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/280814.280935
- ^ Sung, U., Yang, J., and Wohn, K. 1999. Concurrency Control in CIAO. In Proceedings of the IEEE Virtual Reality (March 13 - 17, 1999). VR. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, 22
Categories:- Virtual reality
- Applications of distributed computing
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
