- Ichthyopterygia
Taxobox
name = Ichthyopterygians
fossil_range =Early Triassic -Late Cretaceous
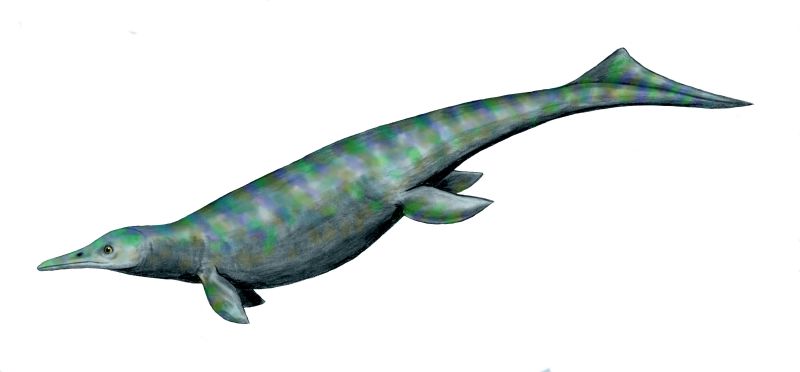
image_width = 250px
image_caption = "Utatsusaurus "
regnum =Animal ia
phylum = Chordata
classis = Sauropsida
subclassis =Diapsida
superordo = Ichthyopterygia
superordo_authority = Owen,1840
subdivision_ranks = Orders
subdivision =Grippidia Ichthyosaur iaIchthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Sir
Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the JurassicIchthyosaur s that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middleTriassic ancestors (Motani 1997, Motani "et al." 1998).Basal ichthyopterygians (prior to and ancestral to true Ichthyosauria) were mostly small (a meter or less in length) with elongate bodies and long spool shaped
vertebra e, indicating that they swam in a sinuouseel -like manner. This allowed for quick movements and manoeuverability that were an advantage in shallow-water hunting (Motani 2000). Even at this early stage they were already very specialised animals with proper flippers, and would have been incapable of movement on land.These animals seem to have been widely distributed around the coast of the northern half of
Pangea , as they are known the LateOlenekian and EarlyAnisian (early part of theTriassic period) ofJapan ,China ,Canada , andSpitsbergen (Norway ). By the later part of the Middle Triassic they were extinct, having been replaced by their descendents the true ichthyosaurs.Taxonomy
* Superorder Ichthyopterygia
** FamilyUtatsusauridae
** FamilyParvinatatoridae
** OrderGrippidia
** OrderIchthyosaur iaPhylogeny
Cladogram after Motani (1998, 1999) and Nicholls & Manabe (2001).Neodiapsida
--Sauria `-?Ichthyopterygia
-?"Hupehsuchus "
-?"Thaisaurus "
--"Utatsusaurus "
--"Parvinatator " `--Eoichthyosauria
--Grippidae `--Ichthyosauria
-?"Mikadocephalus "
-?"Wimanius "
--"Cymbospondylus " `--+--Mixosauridae `--Merriamosauria
--+-?"Mixosaurus "
`--+-?"Cymbospondylus "
`--Shastasauridae `--Euichthyosauria
--Teretocnemidae `--+--"Californosaurus " `--Parvipelvia
--"Macgovania " `--+--"Hudsonelpidia " `--+--"Suevoleviathan " `--+--"Temnodontosaurus "
--Eurhinosauridae `--Thunnosauria
-?"Chacaicosaurus "
--"Stenopterygius " `--+--"Ichthyosaurus " `--Ophthalmosauridae References
* Ellis, Richard, (2003) "Sea Dragons - Predators of the Prehistoric Oceans". University Press of Kansas
* McGowan, C & Motani, R. (2003) Ichthyopterygia, "Handbook of Paleoherpetology ", Part 8, Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil
* Motani, R. (1997), Temporal and spatial distribution of tooth implantation in ichthyosaurs, in JM Callaway & EL Nicholls (eds.), "Ancient Marine Reptiles". Academic Press. pp. 81-103.
* Motani, R. (2000), Rulers of the Jurassic Seas, "Scientific American " vol.283, no. 6
* Motani, R., Minoura, N. & Ando, T. (1998), Ichthyosaurian relationships illuminated by new primitive skeletons from Japan. "Nature" 393: 255-257.External links
* [http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/people/motani/ichthyo/ Ryosuke Motani's detailed Ichthyosaur homepage, with vivid graphics]
* [http://www.palaeos.com/Vertebrates/Units/210Eureptilia/200.html#Ichthyopterygia Eureptilia: Ichthyopterygia - Palaeos]
* [http://www.fmnh.helsinki.fi/users/haaramo/Metazoa/deuterostoma/chordata/Reptilia/Ichthyosauromorpha/Ichthyosauromorpha.htm "Ichthyosauromorpha"] - Mikko's Phylogeny Archive
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
