- Democracy Index
-
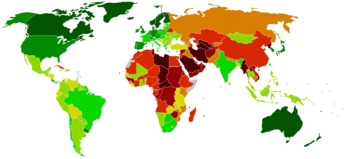
 The Economist Intelligence Unit Democracy index map for 2008, with lighter colours representing more democratic countries. Countries with DI below 2 (clearly authoritarian) are black.
The Economist Intelligence Unit Democracy index map for 2008, with lighter colours representing more democratic countries. Countries with DI below 2 (clearly authoritarian) are black.
The Democracy Index is an index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit that claims to measure the state of democracy in 167 countries, of which 166 are sovereign states and 165 are UN member states. The Economist Intelligence Unit's Democracy Index is based on 60 indicators grouped in five different categories: electoral process and pluralism, civil liberties, functioning of government, political participation and political culture. The Index was first produced in 2006, with updates produced in 2008 and 2010.
According to the latest issue of the Index, for 2010 Norway scored a total of 9.80 on a scale from zero to ten, which was the highest result, replacing Sweden which had the highest score in 2008, but slipped to fourth position in 2010. North Korea scored the lowest with 1.08, remaining at the bottom in 167th place, the same as in 2008. The Democracy Index for 2010 highlights the impact of the global financial crisis in 2008–09 on politics throughout most of the world, with the most significant changes happening in Europe. The Democracy Index score was lower in 2010 than in 2008 in 91 countries out of the 167 that are covered, although in the majority of these the deterioration was modest.[1]
The countries are categorized into full democracies, flawed democracies, hybrid regimes and authoritarian regimes. In 13 countries there was a change in regime type between 2008 and 2010; in 11 of these there was regression. Notably, negative political trends in France in recent years have resulted in the country being downgraded from a full democracy to the flawed democracy category.[2] Italy was also downgraded to the flawed democracy category, which the report attributes to the deterioration of media situation since the prime minister Silvio Berlusconi returned to power in 2008. Only two countries (Ghana and Mali in Sub-Saharan Africa) were upgraded, both from hybrid regimes to the flawed democracy category.
Contents
Methodology
As described in the report, the democracy index is a kind of weighted average based on the answers of 60 questions, each one with either two or three permitted alternative answers. Most answers are "experts' assessments"; the report does not indicate what kinds of experts, nor their number, nor whether the experts are employees of the Economist Intelligence Unit or independent scholars, nor the nationalities of the experts. Some answers are provided by public-opinion surveys from the respective countries. In the case of countries for which survey results are missing, survey results for similar countries and expert assessments are used in order to fill in gaps.
The questions are distributed into the five categories enumerated above. Each answer is translated to a mark, either 0 or 1, or for the three-answer alternative questions, 0.5. With the exceptions mentioned below, seemingly, the sums are added within each category, multiplied by ten, and divided by the total number of questions within the category. There are a few modifying dependencies, which are explained much more precisely than the main rule procedures. In a few cases, an answer yielding zero for one question voids another question; e.g., if the elections for the national legislature and head of government are not considered free (question 1), then the next question, "Are elections... fair?" is not considered, but automatically marked zero. Likewise, there are a few questions considered so important that a low score on them yields a penalty on the total score sum for their respective categories, namely:
- "Whether national elections are free and fair";
- "The security of voters";
- "The influence of foreign powers on government";
- "The capability of the civil servants to implement policies".
The five category indices, which all are listed in the report, are then averaged to find the democracy index for a given country. Finally, the democracy index, rounded to one decimal, decides the classification of the country, as quoted:
- Full democracies—scores of 8 to 10.
- Flawed democracies—scores of 6 to 7.9.
- Hybrid regimes—scores of 4 to 5.9.
- Authoritarian regimes—scores below 4.
The report discusses other indices of democracy, as defined e.g. by Freedom House, and argues for some of the choices made by the team from the Economist Intelligence Unit. In this comparison, a higher emphasis has been put on the public opinion and attitudes, as measured by public surveys, but on the other hand, economic living standard has not been weighted as one criterion of democracy (as seemingly some other investigators have done). [3][4]
There is no indication that this report has been presented or is planned to be presented in any academic context, or has been checked by or will be checked by a peer review.
Democracy index by regime type
The following table constitutes the number of countries in each category according to 2010 survey.[1]
Type of regime Countries % of countries % of world population Full democracies 26 15.6 12.3 Flawed democracies 53 31.7 37.2 Hybrid regimes 33 19.8 14.0 Authoritarian regimes 55 32.9 36.5 World population refers to the total population of the 167 countries that are covered. Since this survey excludes only a few countries, this is nearly equal to the entire actual estimated world population in 2010.
Democracy index average by region
The following table constitutes the index average in each region.[1][5]
Rank Region 2006 2008 2010 1 Northern America 8.64 8.64 8.63 2 Western Europe 8.60 8.61 8.45 3 Latin America & the Caribbean 6.37 6.43 6.37 4 Eastern Europe 5.76 5.67 5.55 5 Asia & Australasia 5.44 5.58 5.53 6 Sub-Saharan Africa 4.24 4.28 4.23 7 Middle East & North Africa 3.53 3.54 3.43 Total 5.52 5.55 5.46 2010 rankings
Note: Rankings are for 2010. Some information may be out of date.[1]
See also
- Democracy promotion
- Freedom House
- Gini coefficient
- Gender-related Development Index
- Gender Empowerment Measure
- Global Peace Index
- Living Planet Index
- Gross national happiness
- Happy Planet Index
- Physical quality-of-life index
- Human development (humanity)
- Human Development Index
- List of freedom indices
References
- ^ a b c d "Democracy Index 2010". Economist Intelligence Unit. http://graphics.eiu.com/PDF/Democracy_Index_2010_web.pdf. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
- ^ "Democracy in Retreat". SourceWire. 13 December 2010. http://www.sourcewire.com/releases/rel_display.php?relid=61449. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
- ^ "Democracy Index 2010". Direct Democracy. 14 December 2010. http://www.directdemocracyuk.com/blog/2010/12/democracy-index-2010.html. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
- ^ THE WORLD IN 2OO7: The Economist Intelligence Unit’s index of democracy By Laza Kekic, director, country forecasting services, Economist Intelligence Unit, Retrieved 13 June 2011.
- ^ "Democracy Index 2008". Economist Intelligence Unit. http://graphics.eiu.com/PDF/Democracy%20Index%202008.pdf. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
External links
Freedom Trade · Press (Freedom House · Reporters Without Borders) · Economic (Fraser Institute · The Heritage Foundation/The Wall Street Journal)Corruption Competitiveness e-Government · Nation Brands Index · Failed States Index · Composite Index of National Capability · Comprehensive National Power · National Power IndexHistory Rights Other
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.