- Ventricular septal defect
Infobox_Disease
Name = PAGENAME
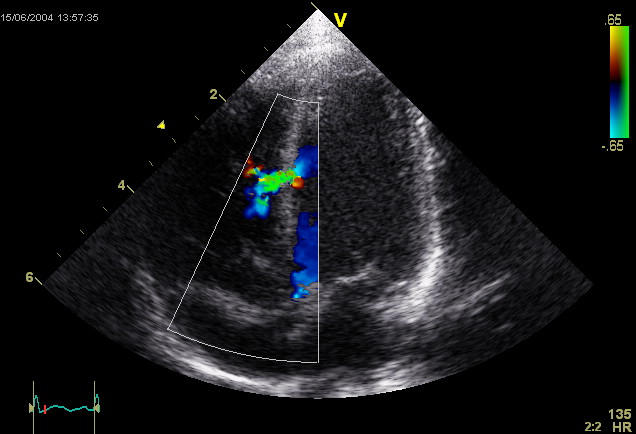
Caption = Echocardiographic image of a moderate "ventricular septal defect" in the mid-muscular part of the septum. The trace in the lower left shows the flow during one completecardiac cycle and the red mark the time in the cardiac cycle that the image was captured. Colours are used to represent the velocity of the blood. Flow is from theleft ventricle (right on image) to theright ventricle (left on image). The size and position is typical for a VSD in the newborn period.
Width = 300
DiseasesDB = 13808
ICD10 = ICD10|Q|21|0|q|20
ICD9 = ICD9|745.4
ICDO =
OMIM =
MedlinePlus =
eMedicineSubj = med
eMedicineTopic = 3517
MeshName = Ventricular+Septal+Defects
MeshNumber = C14.240.400.560.540
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in theventricular septum , the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of theheart .The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the
atrioventricular node , is most commonly affected in adults and older children. [Ambumani P, Kuruchi Srinivasan. Ventricular Septal Defect, General Concepts. eMedicine.com. URL: [http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2402.htm http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2402.htm] . Accessed on December 5, 2005.] [Eidem BW. Ventricular Septal Defect, Muscular. eMedicine.com. URL: [http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2543.htm http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2543.htm] . Accessed on April 13, 2006.]Congenital VSDs are collectively the most common
congenital heart defects . [Hoffman JI, Kaplan S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Jun 19;39(12):1890-900. PMID 12084585.]Diagnosis
A VSD can be detected by cardiac auscultation. Classically, a VSD causes a pathognomonic holo- or pansystolic murmur. Auscultation is generally considered sufficient for detecting a significant VSD. The murmur depends on the abnormal flow of blood from the left ventricle, through the VSD, to the right ventricle. If there is not much difference in pressure between the left and right ventricles, then the flow of blood through the VSD will not be very great and the VSD may be silent. This situation occurs a) in the fetus (when the right and left ventricular pressures are essentially equal), b) for a short time after birth (before the right ventricular pressure has decreased), and c) as a late complication of unrepaired VSD. Confirmation of
cardiac auscultation can be obtained by non-invasive cardiac ultrasound (echocardiography ). To more accurately measure ventricular pressures,cardiac catheterization , can be performed.Pathophysiology
During ventricular contraction, or systole, some of the blood from the left ventricle leaks into the right ventricle, passes through the lungs and reenters the left ventricle via the pulmonary veins and left atrium. This has two net effects. First, the circuitous refluxing of blood causes volume overload on the left ventricle. Second, because the left ventricle normally has a much higher systolic pressure (~120 mm Hg) than the right ventricle (~20 mm Hg), the leakage of blood into the right ventricle therefore elevates right ventricular pressure and volume, causing
pulmonary hypertension with its associated symptoms. This effect is more noticeable in patients with larger defects, who may present with breathlessness, poor feeding and failure to thrive in infancy. Patients with smaller defects may be asymptomatic.igns and symptoms
Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a few weeks after birth.
ymptoms
Non specific symptoms such as the baby not feeding well.
igns
*Pansystolic / Holosystolic murmur (depending upon the size of the defect)
Treatment
Treatment is either conservative or surgical. Smaller congenital VSDs often close on their own, as the heart grows, and in such cases may be treated conservatively. In cases necessitating surgical intervention, a
heart-lung machine is required and amedian sternotomy is performed. Percutaneous endovascular procedures are less invasive and can be done on a beating heart, but are only suitable for certain patients. Repair of most VSDs is complicated by the fact that the conducting system of the heart is in the immediate vicinity.Ventricular septum defect in infants is initially treated medically with digoxin(10-20ug/kg per day) and furosemide (1-3 mg/kg per day) and captopril (0.5-2 mg / kg per day).
Epidemiology and Etiology
VSDs are the most common congenital cardiac anomalies. They are found in 30-60% of all newborns with a congenital heart defect, or about 2-6 per 10000 births. It is debatable whether all those defects are true heart defects, or if some of them are normal phenomena, since most of the trabecular VSDs close spontaneously. [Meberg A, et al: "Increasing incidence of ventricular septal defects caused by improved detection rate". Acta Pædiatrica 1994; 83: 653-657.] Prospective studies give a prevalence of 2-5 per 100 births of trabecular VSDs that closes shortly after birth in 80-90% of the cases. [Hiraishi S, Agata Y, Nowatari M, Oguchi K, et al. Incidence and natural course of trabecular ventricular septal defect: Two-dimensional echocardiography and color Doppler flow image study. J Pediatr 1992;120:409-15.] [Roguin N, Du ZD, Barak M, Nasser N, Hershkowitz S, Milgram E. High prevalence of muscular ventricular septal defect in neonates. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995 November 15;26(6):1545-8] .
Congenital VSDs are frequently associated with other congenital conditions, such as
Down syndrome . [Wells GL, Barker SE, Finley SC, Colvin EV, Finley WH. Congenital heart disease in infants with Down's syndrome. South Med J. 1994 Jul;87(7):724-7. PMID 8023205.]A VSD can also form a few days after a
myocardial infarction [Bruckheimer E. Ventricular septal defect. Medical Encyclopedia - MedlinePlus.org, URL: [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001099.htm http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001099.htm] . Accessed on December 5, 2005.] (heart attack) due to mechanical tearing of the septal wall, beforescar tissue forms, whenmacrophage s start remodeling the dead heart tissue.ee also
*
Atrial septal defect
*Atrioventricular septal defect
*Cardiac output
*Congenital heart disease
*Heart sounds
*Pulmonary hypertension References
External links
* [http://www.cardiacmorphology.com/ www.cardiacmorphology.com] - free registration for online video and image archive
* [http://www.pediatricheartsurgery.com Pediatric Heart Surgery]
* [http://www.americanheart.org/presenter.jhtml?identifier=11066 Ventricular septal defect] -American Heart Association
* [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001099.htm Ventricular septal defect] - medlineplus.org
* [http://heartcenter.seattlechildrens.org/conditions_treated/ventricular_septal_defect.asp Ventricular Septal Defect information] from Seattle Children's Hospital Heart Center
* [http://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/HeartConditions/Ventricular-Septal-Defect-VSD.aspx?articleID=6903&categoryID=HC-nh2-04w Animation of ventricular septal defect] from AboutKidsHealth.ca
* [http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2544.htm Perimembranous VSD] - emedicine.com
* [http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2545.htm Supracristal VSD] - emedicine.com
* [http://www.dhg.org.uk/information/ventricularseptaldefect.aspx Down's Heart Group] Easy to understand diagram and explanation of VSD.
* [http://www.med.umich.edu/mott/chc/patient_con_ven.html C.S. Mott Children's Hospital, Congenital Heart Center: Ventricular Septal Defect] at umich.edu
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
