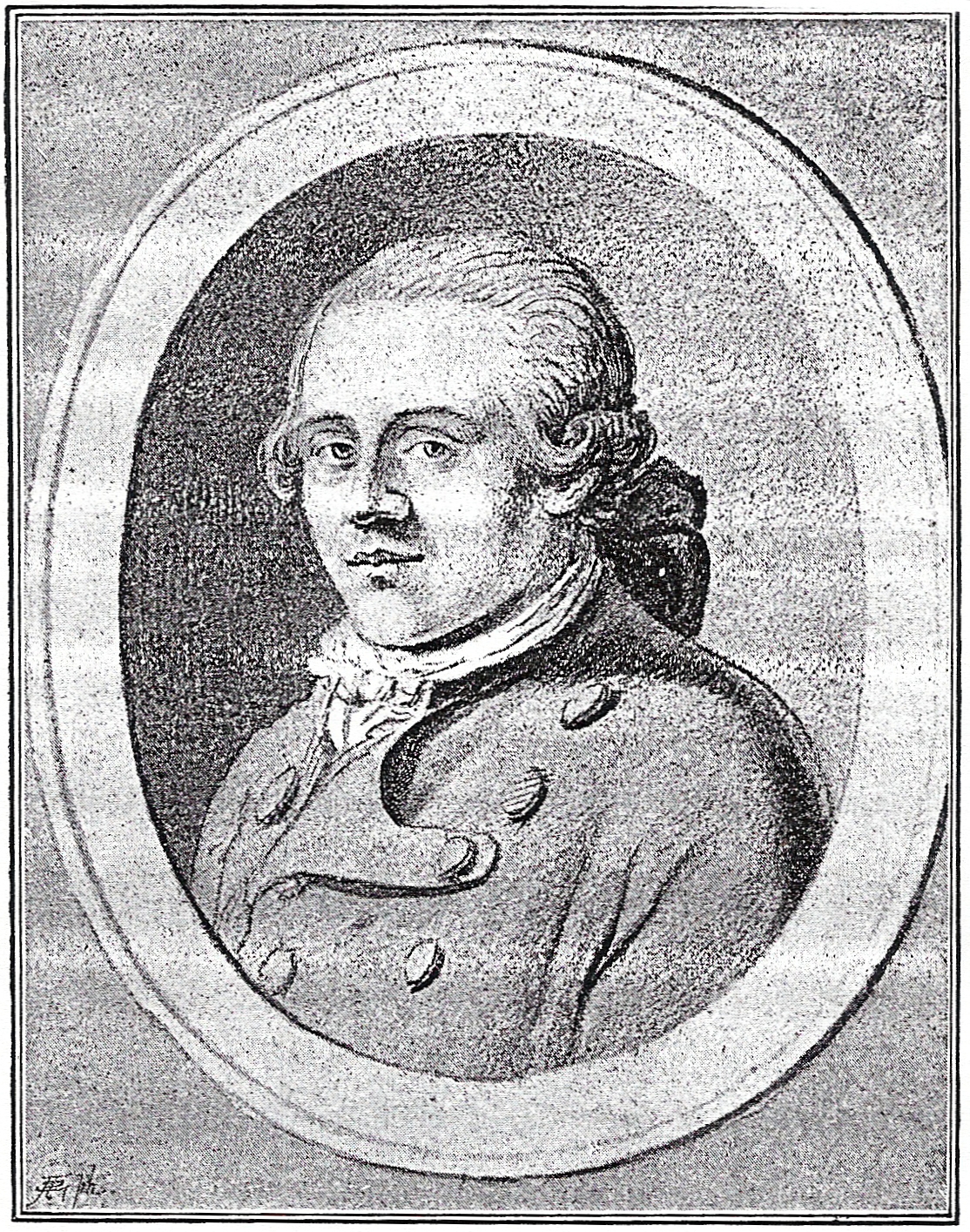
- Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz
Infobox Writer
name = Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz

birthdate = birth date|1751|1|23|df=y
birthplace = Sesswegen,Livonia (nowCesvaine ,Latvia )
deathdate = death date and age|1792|6|4|1751|1|23|df=y
deathplace =Moscow ,Russia
occupation =writer ,playwright
Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz (
23 January ,1751 , or 12 January in theJulian calendar –4 June ,1792 , or 24 May in the Julian calendar) was aBaltic German writer of theSturm und Drang movement.Life
Lenz was born in Sesswegen (Cesvaine),
Livonia , the son of the pietistic minister Christian David Lenz (1720-1798), later General Superintendent of Livonia. When Lenz was 9, in 1760, the family moved to Dorpat (Tartu), where his father had been offered a minister's post. His first published poem appeared when he was 15. From 1768 to 1770 he studied theology on a scholarship, first at Dorpat and then atKönigsberg . While there, he attended lectures byImmanuel Kant , who encouraged him to readJean-Jacques Rousseau . He began increasingly to follow his literary interests and to neglect theology. His first independent publication, the long poem "Die Landplagen" ("Torments of the Land") appeared in 1769. He also studied music, most likely with either the Ukrainian virtuosolutanist Timofey Belogradsky , then resident in Königsberg, or his studentJohann Friedrich Reichardt .In 1771 Lenz abandoned his studies in Königsberg. Much against the will of his father, who on that account broke off contact with him, he took a position little better than that of a servant with Friedrich Georg and Ernst Nikolaus von Kleist ( [http://www.v-kleist.com/FG/Muttrin/fg0091.htm] ), barons from
Courland and officer cadets about to begin their military service, whom he accompanied toStrasbourg . Once there, he came into contact with theactuary Johann Daniel Salzmann, around whom had formed the literary group of the "Société de philosophie et de belles lettres". This was frequented also by the youngJohann Wolfgang von Goethe , who at this time happened to be in Strasbourg, and whose acquaintance Lenz made, as well as that of Johann Heinrich Jung-Stilling. Goethe now became Lenz's literary idol, and through him he made contact withJohann Gottfried Herder andJohann Kaspar Lavater , with whom he corresponded.In the following year, 1772, Lenz accompanied his masters to the garrisons of
Landau ,Fort Louis andWissembourg . He also fell in love with Friederike Brion, once the beloved of Goethe, but his feelings were not reciprocated.In 1773 Lenz returned to Strasbourg and resumed his studies. The following year he gave up his position with the von Kleist brothers and lived as a freelance writer, earning his living by private tutoring. His relations with Goethe became friendlier: while the two of them were visiting
Emmendingen , Goethe introduced Lenz to his sister Cornelia and her husband Johann Georg Schlosser.In April 1776 Lenz followed Goethe to the court of
Weimar , where he was at first amicably received. But in early December, on Goethe's instigation, he was expelled. The exact circumstances are not recorded; Goethe, who broke off all personal contact with him after this, refers only vaguely in his diary to "Lenz's idiocy" ("Lenzens Eseley").Lenz then returned to Emmendingen, where the Schlossers took him in. From there he made a number of journeys into
Alsace andSwitzerland , including one to Lavater inZürich in May 1777. The news of Cornelia Schlosser's death, which reached him there in June of that year, had a powerful effect on him. He returned to Emmendingen, and then went back to Lavater. In November, while staying inWinterthur with Christoph Kaufmann, he suffered an attack ofparanoid schizophrenia . In January 1778 Kaufmann sent Lenz to the philanthropist, social reformer and clergyman Johann Friedrich Oberlin inWaldersbach in Alsace, where he stayed from20 January to8 February . Despite the care of Oberlin and his wife, Lenz's mental condition grew worse. He returned to Schlosser at Emmendingen, where he was lodged with a shoemaker and then a forester.His younger brother Karl fetched him in June 1779 from
Hertingen , where he was under treatment by a doctor, and brought him toRiga , where their father by this time had risen to the position of General Superintendent.Lenz was unable to establish himself professionally in Riga. An attempt to make him director of the cathedral school came to nothing, as Herder refused to give him a reference. Nor did he have any greater success in
St. Petersburg , where he lived from February to September 1780. He then took a position as a private tutor on an estate near Dorpat, then, after another stay in St. Petersburg, he went toMoscow in September 1781, where initially he stayed with the historian Friedrich Müller and learned Russian.He worked as a private tutor, mixed in the circles of Russian
Freemasons and authors, and helped produce a number of reformist schemes. He also translated books onRussian history into German. His mental condition however was steadily deteriorating all the while, and at last he became entirely dependent on the goodwill of Russian patrons for the means of living.In the early morning of
4 June ,1792 (24 May in the Julian calendar) Lenz was found dead in a Moscow street. The place of his burial is unknown.Lenz as a literary figure
"
Lenz ", thenovella byGeorg Büchner , dealt with Lenz's visit to the minister Friedrich Oberlin, in theVosges . Lenz had visited Oberlin, on the suggestion of Kaufmann, because of his reputation as a pastor and psychologist. Oberlin's account of the events of Lenz's visit furnished Büchner with the source of his story, which in its turn was the source ofWolfgang Rihm 's chamber opera "Jakob Lenz".More recently the writers Peter Schneider, in his story "Lenz" (1973), and Gert Hoffmann, in his novella "Die Rückkehr des verlorenen J.M.R. Lenz nach Riga" ("The Return of the Lost J.M.R. Lenz to Riga") (1984), have given literary form to the events of his life.
Also worth mentioning is Marc Buhl's novel of 2002, "Der rote Domino" ("The Red Domino"), which uses the friendship between Goethe and Lenz, and its abrupt end, as the inspiration for a detective story.
elected works
* "Die Landplagen" ("The Torments of the Land"). Verse epic, 1769
* "Der Hofmeister, oder Vorteile der Privaterziehung" ("The Tutor, or, The Advantages of Private Education"). Drama, 1774
* "Der neue Menoza" ("The New Menoza"). Drama, 1774
* "Anmerkungen übers Theater" ("Observations on the Theatre"). Essay, 1774
* "Meinungen eines Laien, den Geistlichen zugeeignet" ("Opinions of a Layman, dedicated to the Clergy"). Essay, 1775
* "Pandaemonium Germanicum". Drama, written in 1775, published posthumously 1819
* "Die Soldaten" ("The Soldiers"). Drama, 1776 (basis of the opera of the same name byBernd Alois Zimmermann and a source of Büchner's drama "Woyzeck ")
* "Die Freunde machen den Philosophen" ("Friends Make the Philosopher"). Drama, 1776
* "Zerbin". Novella, 1776
* "Der Waldbruder" ("The Friar of the Forest"). Unfinished novel, published posthumously in 1882Editions
* Damm, Sigrid (ed.), 1987. "Werke und Briefe", 3 vols. Leipzig [München/Wien] : Insel Verlag [Lizenzausgabe im Hanser Verlag] . ISBN 3-446-14665-2
* Lauer, Karin (ed.), 1992. "Werke". Hanser Verlag, München/Wien: Hanser Verlag. ISBN 3-446-16338-7
* Voit, Friedrich, (ed.), 1997. "Werke" [selection] . Stuttgart: Reclam Verlag. ISBN 3-15-008755-4
* Weiss, Christoph (ed.), 2001. "Werke: Faksimiles der Erstausgaben seiner zu Lebzeiten selbständig erschienenen Texte", 12 vols. St. Ingbert: Röhrig Verlag. ISBN 3-86110-071-1ingle works
* Weiss, Christoph (ed.), 2003. "Als Sr. Hochedelgebohrnen der Herr Professor Kant den 21sten August 1770 für die Professor-Würde disputierte" (facsimile of the first edition, Königsberg 1770. Laatzen: Wehrhahn Verlag. ISBN 3-932324-68-4
References
* Damm, Sigrid, 1992. "Vögel, die verkünden Land. Das Leben des Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz". Frankfurt am Main: Insel Verlag. ISBN 3-458-33099-2
* Hohoff, Curt, 1977. " J. M. R. Lenz". Reinbek bei Hamburg: Rowohlt. ISBN 3-499-50259-3
* Luserke, Matthias, 1993. "Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz: Der Hofmeister - Der neue Menoza - Die Soldaten". Munich: W. Fink. ISBN 3-8252-1728-0
* Meier, Andreas, 2001. "Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz: Vom Sturm und Drang zur Moderne". Heidelberg: Universitätsverlag C.Winter. ISBN 3-8253-1238-0
* Winter, Hans-Gerd Winter, 2000. "Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz" (2nd ed). Stuttgart and Weimar: Verlag J. B. Metzler (=Sammlung Metzler, vol. 233). ISBN 3-476-12233-6
* "Lenz-Jahrbuch. Sturm-und-Drang-Studien." St. Ingbert: Röhrig Verlag.Filmography
* Günther, Egon: "Lenz" (Federal Republic of Germany), with Jörg Schüttauf as J.M.R. Lenz and Christian Kuchenbuch as Goethe
External links
*
*
* [http://gutenberg.spiegel.de/autoren/lenz.htm J.M.R. Lenz at German Project Gutenberg]
* [http://www.jacoblenz.de/ J.M.R. Lenz research project at the University of Mannheim]
* [http://www.lenz-forum.de/ Lenz Forum]
* [http://www.uni-essen.de/literaturwissenschaft-aktiv/Vorlesungen/dramatik/lenz.htm Short introduction to Lenz]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
