- Chapinero
-
Chapinero 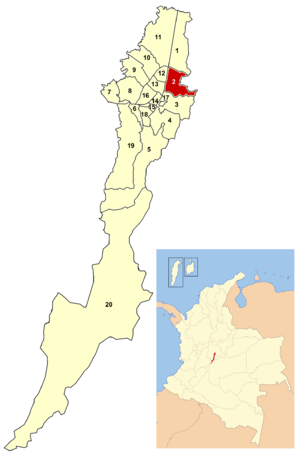
Chapinero in BogotáArea: 38.98 km² Population: 122.507 (2007) Type of locality: Mixed Chapinero is the second locality of Bogotá, capital of Colombia. It is located in northeastern Bogotá. It is among the more affluent of localities in the city, and is home to several important commercial and dining areas. It comprises three major residential areas: Chicó, El Lago, and Chapinero. It also contains a principal connecting point between the city and the eastern municipalities of Cundinamarca.
Contents
History
Chapinero was a traditional stop between Bogotá and the municipalities to the north during the colonial period. The area was settled in 1812 by workers in the various industries that provided Bogotá with its day-to-day necessities. The name Chapinero is probably derived from one of these, likely a derivative of a rustic type of shoe that was produced in the area. Toward the end of the 1800s, the area was further settled with mansions and country estates. As the urbanized city expanded, the area was integrated accordingly. Mule-pulled trams were extended northward in 1875, followed by electric tracks in 1910.
When the Special District of Bogotá was formed in 1955, the area was made into a locality. At that time the El Lago, Chicó, and Cataluña neighborhoods were added into the locality. The physical boundaries remained the same under the reorganization into the Capital District that took place in 1991.
Together with La Candelaria and Teusaquillo, Chapinero is one of the traditional neighborhoods that is distinctive of a particular era in the city's history and urban growth. A historically upper-class neighborhood, Chapinero is famous for its large, Victorian houses which reflect the influence of European architectural styles in Bogotá at the beginning of the 20th century.
Economy and Culture
Chapinero is one of the most important commercial and economic zones of the capital city. Banking and financial centers are headquartered along Calle 72, with major shopping centers located along Carreras 11 and 15. Several universities are based in the locality, including the Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Catholic University of Colombia Universidad Piloto de Colombia, and the Universidad Pedagógica Nacional.
The zone also includes popular dining areas and nightlife centers, which include the Zona Rosa, the Parque de la 93, and the Zona G; the last one known for its wide offer of gastronomic options.
The localty of Chapinero is also the center of Bogotá's gay community.[1] There are more than 100 bars, discos and clubs that cater to the gay community in Bogotá, and 45% of these can be found in Chapinero.[citation needed] The biggest and most popular gay disco in Bogota, Theatron, is located in the heart of Chapinero.[citation needed] Furthermore, the mayor of Chapinero, Blanca Inés Durán Hernández, is openly lesbian.[2] The localty has a unique community center focused on the LGBT population of the neighborhood and the city. It is the first of its kind in Latin America.[3]
General information
Borders
North: Calle 100, bordering the locality of Usaquén.
East: the eastern mountains, bordering the municipalities of La Calera and Choachí.
South: Calle 39, bordering the locality of Santa Fe.
West: Avenida Caracas and Autopista Norte, with the localities of Barrios Unidos and Teusaquillo.Points of interest
- Chicó Museum (Museo del Chicó)
- Our Lady of Lourdes Church (Iglesia de Nuestra Señora de Lourdes)
- 93rd street park (93 Park; Parque de la 93)
- Shopping centers:
- Chile Avenue (Avenida Chile), formerly known as Bigsavings (Granahorrar)
- Andean Center (Centro Andino)
- Atlantis Plaza
- The Retirement (El Retiro)
Transportation
Major east-west roads include Calles 39, 45, 53, 57, 63, 85, 92, 94, 100, and Avenida Chile (Calle 72). North-south routes include Carreras 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 and Avenida Caracas.
The locality is served by the Avenida Caracas line of TransMilenio, with a Carrera 7 line planned. All of the major roads have extensive private bus service.
Neighborhoods
El Nogal, El Chicó, Antiguo Country, Rosales, Villa del Cerro, Chapinero Central, Chapinero Alto, La Cabrera, El Lago, El Virrey, Quinta Camacho, Pardo Rubio, Marly, La Salle, Bosque Calderón and La Porciúncula.
Before 1955, the term Chapinero included some neighborhoods that are now part of the Teusaquillo locality and did not included the El Lago, Chicó, and Cataluña neighborhoods that are currently part of the locality.
Hydrology
The rural eastern hills are heavily forested and broken up by the beginnings of several rivers, all of which flow through the locality in man-made canals. Among the more important waterways are the Río Arzobispo (Archbishop River) which joins with the San Francisco into the Río Bogotá and the Virrey that forms a part of the Salitre river system.
References
External links
- (Spanish) City of Bogota site
- (Spanish) Official Secretary of Bogotá site
- (Spanish) National University of Colombia site on the locality
- (Spanish) Chapinero, El balcón y pulmón de Bogotá - Video about Chapinero
 Bogotá, Capital District
Bogotá, Capital District  Usaquén · Chapinero · Santa Fe · San Cristóbal · Usme · Tunjuelito · Bosa · Kennedy · Fontibon · Engativá · Suba · Barrios Unidos · Teusaquillo · Los Mártires · Antonio Nariño · Puente Aranda · La Candelaria · Rafael Uribe Uribe · Ciudad Bolívar · SumapazCategories:
Usaquén · Chapinero · Santa Fe · San Cristóbal · Usme · Tunjuelito · Bosa · Kennedy · Fontibon · Engativá · Suba · Barrios Unidos · Teusaquillo · Los Mártires · Antonio Nariño · Puente Aranda · La Candelaria · Rafael Uribe Uribe · Ciudad Bolívar · SumapazCategories:- Localities of Bogotá
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.