- Trichomonas vaginalis
Taxobox
color = khaki
name = "Trichomonas vaginalis"
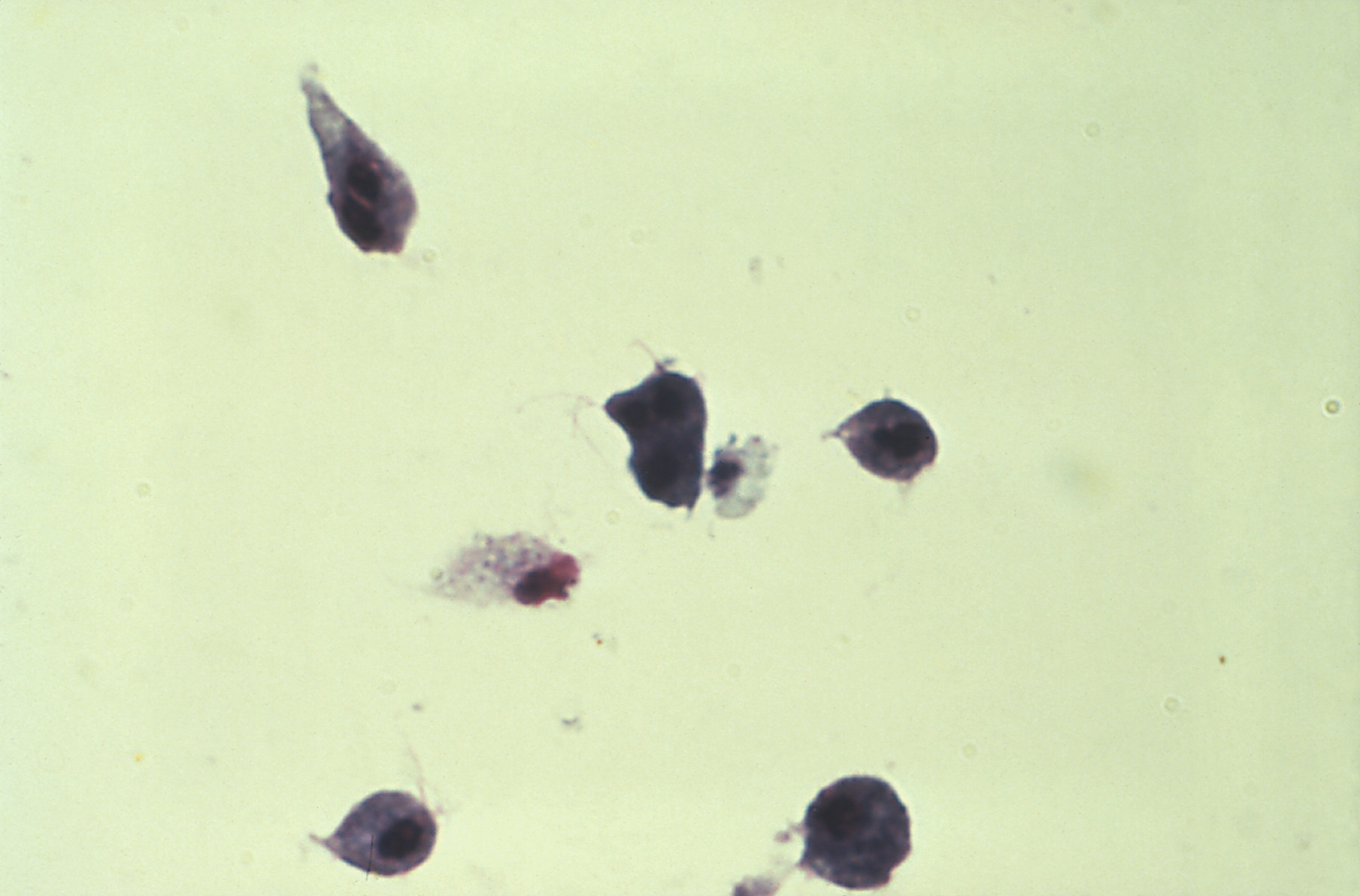
image_width = 240px
image_caption = Giemsa-stained culture of "T. vaginalis"
domain =Eukaryota
unranked_phylum =Excavata
phylum =Metamonada
classis =Parabasalia
ordo =Trichomonadida
genus = "Trichomonas "
species = "T. vaginalis"
binomial = "Trichomonas vaginalis"
binomial_authority = (Donné 1836)"Trichomonas vaginalis", an anaerobic, parasitic
flagellate dprotozoan , is the causative agent oftrichomoniasis , and is the most common pathogenic protozoan infection of humans in industrialized countries.cite journal |author=Soper D |title=Trichomoniasis: under control or undercontrolled? |journal=Am J Obstet Gynecol |volume=190 |issue=1 |pages=281–90 |year=2004 |pmid=14749674 |doi=10.1016/j.ajog.2003.08.023] TheWHO has estimated that 180 million infections are acquired annually worldwide. The estimates forNorth America alone are between 5 and 8 million new infections each year, with an estimated rate ofasymptomatic cases as high as 50%.cite journal |author=Hook E |title=Trichomonas vaginalis--no longer a minor STD |journal=Sex Transm Dis |volume=26 |issue=7 |pages=388–9 |year=1999 |pmid=10458631 |doi=10.1097/00007435-199908000-00004]Protein function
"T. vaginalis" also has many
enzymes that catalyze a number of reactions making the organism relevant to the study of protein function. "T. vaginalis" lacks mitochondria and other necessary enzymes and cytochromes to conductoxidative phosphorylation . " T. vaginalis" obtains nutrients by transport through thecell membrane and byphagocytosis . The organism is able to maintain energy requirements by the use of a small amount of enzymes to provide energy viaglycolysis ofglucose toglycerol andsuccinate in thecytoplasm , followed by further conversion of pyruvate andmalate to hydrogen and acetate in an organelle called thehydrogenosome .cite journal |author=Upcroft P, Upcroft J |title=Drug targets and mechanisms of resistance in the anaerobic protozoa |journal=Clin Microbiol Rev |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=150–64 |year=2001 | doi = 10.1128/CMR.14.1.150-164.2001 |pmid=11148007]Morphology
The "T. vaginalis"
trophozoite is oval as well as flagellated. Five flagella arise near the cytosome; four of these immediately extend outside the cell together, while the fifth flagellum wraps backwards along the surface of the organism. The functionality of the fifth flagellum is not known. In addition, a conspicuous barb-likeaxostyle projects opposite the four-flagella bundle; the axostyle may be used for attachment to surfaces and may also cause the tissue damage noted in trichomoniasis infections.cite book | author = Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) | title = Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th ed. | publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | id = ISBN 0838585299 ]While "T. vaginalis" does not have a
cyst form, organisms can survive for up to 24 hours in urine, semen, or even water samples. Combined with an ability to persist onfomite s with a moist surface for 1 to 2 hours, "T. vaginalis" is among the most durable protozoan trophozites.Clinical
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease which can occur in females (males rarely exhibit symptoms of a "T. vaginalis" infection) if the normal acidity of the vagina is shifted from a healthy, semi-acidicpH (3.8 - 4.2) to a much more basic one (5 - 6) that is conducive to "T. vaginalis" growth. Some of the symptoms of T. vaginalis include: preterm delivery, low birth weight, and increased mortality as well as predisposing toHIV infection,AIDS , andcervical cancer .cite journal |author=Schwebke J, Burgess D |title=Trichomoniasis |journal=Clin Microbiol Rev |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=794–803, table of contents |year=2004 |pmid=15489349 |doi=10.1128/CMR.17.4.794-803.2004] "T. vaginalis" has also been reported in the urinary tract,fallopian tube s, and pelvis and can causepneumonia ,bronchitis , and oral lesions. Other symptoms include inflammation with increasing number of organisms, greenish-yellow frothy vaginal secretions and itching.Condom s are effective at preventing infection.Classically, with a pap smear, infected individuals have a transparent "halo" around their superficial cell nucleus. It is also is rarely detected by studying discharge or with a
pap smear because of their low sensitivity. "T. vaginalis" was traditioinally diagnosed via a wet mount, in which "corkscrew" motility was observed. Currently, the most common method of diagnosis is via overnight culture,cite journal |author=Ohlemeyer CL, et al |title=Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis in adolescent females: InPouch TV culture versus wet-mount microscopy |journal=Journal of Adolescent Health |volume=22 |pages=205-208 |pmid=9502007 |year=1998] cite journal |author=Sood S, et al |title=InPouch TV culture for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis. |journal=Indian J Med Res |volume=125 |pages=567-571 |pmid=17598943 |year=2007] with a sensitivity range of 75-95%.cite journal | title=Rapid antigen testing compares favorably with transcription-mediated amplification assay for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in young women. | author = Huppert JS | coauthors = Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Miller WC, Hobbs M | journal = Clinical Infectious Diseases | year = 2007 | date = Jul 15 | volume = 45 | issue = 2 | pages = 194-198 | pmid = 17578778 | doi = 10.1086/518851 | url = http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/518851] Newer methods, such asrapid antigen test ing andtranscription-mediated amplification , have even greater sensitivity, but are not in widespread use. The presence of "T. vaginalis" can also be diagnosed by PCR, using the primers L23861 Fw and Rev.cite journal |author=Schrirm, J. et al |title="Trichomonas vaginalis" detection using real-time TaqMan PCR |journal=Journal of Microbiological methods |volume=68 |pages=243–247 |pmid=17005275 |doi=10.1016/j.mimet.2006.08.002 |year=2007]Infection is treated and cured with
metronidazole ortinidazole , and should be prescribed to anysexual partner (s) as well because they may potentially beasymptomatic carrier s.cite journal |author=Cudmore S, Delgaty K, Hayward-McClelland S, Petrin D, Garber G |title=Treatment of infections caused by metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis |journal=Clin Microbiol Rev |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=783–93, table of contents |year=2004 |pmid=15489348 |doi=10.1128/CMR.17.4.783-793.2004]Genome Sequencing
Jane Carlton led a project to sequence the "Trichomonas vaginalis" genome which found that the genome was much larger than was expected. [http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/315/5809/207] [http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/315/5817/1358]References
External links
*TIGR's "Trichomonas vaginalis" [http://www.tigr.org/tdb/e2k1/tvg/ genome sequencing] project.
* [http://trichdb.org/trichdb/ TrichDB: the "Trichomonas vaginalis" genome sequencing project]
*NIH site on [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001331.htm trichomoniasis] .
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=5722 Taxonomy]
* [http://www.youngandhealthy.ca/caah/Informations/STI/t428c431s508x413/Trichomonas.aspx STI: What's trichomonas] a website for teenagers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
