- Seymouria
Taxobox
name = "Seymouria"
fossil_range = EarlyPermian
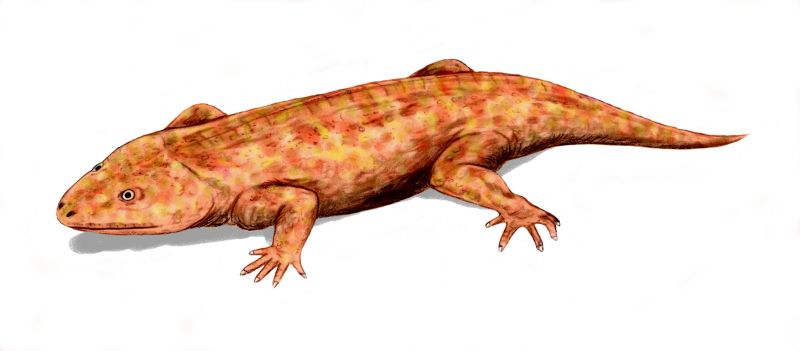
image_width = 250px
image_caption = "Seymouria baylorensis" from the Early Permian of North America
regnum =Animal ia
phylum = Chordata
superclassis =Tetrapoda
superordo =Reptiliomorpha
ordo =Seymouriamorpha
familia =Seymouriidae
genus = "Seymouria"
genus_authority = Broili, 1904
subdivision_ranks = Species
subdivision =
* "S. baylorensis" (type)
* "S. sanjuanensis"
* "S. grandis"
* "S. agilis""Seymouria" was a reptile-like
tetrapod from the earlyPermian ofNorth America andEurope . It was small, only 2 ft (60 cm) long. "Seymouria" was well adapted to life on land, with many reptilian features--so many, in fact, that it was first thought to be a primitive reptile.Description
The dry climate of the
Permian suited reptiles better thanamphibian s and other more primitive tetrapods, but "Seymouria" had many reptilian features that helped it in this harsh environment. It had long and muscular legs, and may have had dry skin and the ability to conserve water. It may have been able to excrete excess salt from its blood through a gland in its nose, like modern reptiles Fact|date=April 2007. All of this meant that "Seymouria", unlike amphibians and other early tetrapods, might have lived for extended periods of time away from water. If so, this would have allowed it to move about the landscape in search of insects, small amphibians, and other possible preys, such as the eggs of reptiles. Male "Seymouria" had thick skulls that may have been used to batter rivals in mating contests. After mating, the females would have had to return to water to lay their eggs. As in amphibians, the larvae would develop in water, hunting for worms and insects until they were strong enough to live on land. While no larvae are known from "Seymouria" itself, fossil larvae of other species in the orderSeymouriamorpha have been found, with impressions of external gill structures as in some amphibians.Fossils of "Seymouria" were first found in Seymour, Baylor County,
Texas (hence the name of the type species, "Seymouria baylorensis", or "Baylor County Seymour one"). Over the years, many well preserved fossils have been found in North America and Germany, including the "Tambach Lovers", two individuals of "S. sanjuanensis" fossilized lying next to each other (though of course it cannot be determined whether they really were a couple killed during mating).In popular culture
"Seymouria" was featured in the television series "
Walking with Monsters ", produced byBBC . A "Seymouria" was spying on a "Dimetrodon "'s nest, the main character of the early Permian scene. It was waiting for the mother "Dimetrodon" to be caught off guard so it could devour her eggs, but was eventually preyed upon by a male "Dimetrodon".Seymouria was also featured inReferences
*Haines, Tim & Chambers, Paul. (2006)
The Complete Guide to Prehistoric Life . Canada: Firefly Books Ltd.External links
* [http://tolweb.org/Seymouria/17546 Illustrated discussion of "Seymouria" from the Tree of Life Project.]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
