- Gwangju
-
This article is about Gwangju Metropolitan City. For the smaller city of the same name near Seoul, see Gwangju, Gyeonggi. For one of its sister cities which has similar name in China, see Guangzhou.
Gwangju
광주
光州— Metropolitan City — Gwangju Metropolitan City transcription(s) – Hangul 광주광역시 – Hanja 光州廣域市 – Revised Romanization Gwangju-gwangyeoksi – McCune-Reischauer Kwangju-kwangyŏksi From top left: Pojangmacha in Gwangju's Night Market, Street of Gwangju, Cityscape of Gwangju, Gwangju Folk Museum, & Democracy Bell 
Flag
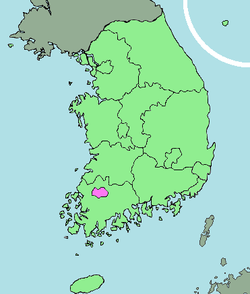
Emblem of GwangjuMap of South Korea with Gwangju highlighted Country  South Korea
South KoreaRegion Honam Districts 5 Government – Mayor Kang Un-tae Area – Total 501.36 km2 (193.6 sq mi) Population (2010) – Total 1,454,784 – Density 2,824/km2 (7,314.1/sq mi) – Dialect Jeolla Flower Royal Azalea Tree Ginkgo Bird Dove Website gjcity.net (English) Gwangju (officially known as Gwangju Metropolitan City; Korean pronunciation: [kwaŋdʑu]) is the sixth largest city in South Korea. It is a designated metropolitan city under the direct control of the central government's Home Minister. The city was also the capital of South Jeolla Province until the provincial office moved to the southern village of Namak in Muan County in 2005.
Gwang (광, hanja 光) means "light" and Ju (주, hanja 州) means "province." Areas of exquisite scenery along the outskirts of the city gave birth to gasa, a form of Korean classical poetry.[citation needed] Located in the heart of the agricultural Jeolla region, the city is also famous for its rich and diverse cuisine.
Contents
History
The city was established in 57 BC, and has been a major political and economic centre of Korea ever since. It was one of the administrative centres of Baekje during the Three Kingdoms Period.
In 1929, during the period of Japanese rule, a confrontation between Korean and Japanese students in the city turned into a regional demonstration, which culminated in one of the major nationwide uprisings against Japanese rule during the colonial period.
Modern industry was established in Gwangju with the construction of a railway to Seoul. Some of the industries that took hold include cotton textiles, rice mills and breweries. Construction of a designated industrial zone in 1967 encouraged marked growth in industry, especially in the sectors linked to the automobile industry.
In May 1980, civil demonstrations took place in Gwangju against the newly installed military government of Chun Doo-hwan resulting in hundreds of civilians being killed by the Korean Military. The demonstrations were suppressed by military forces, including elite units of the Special Operations Command. Most commentators agree that the suppression was characterized by its egregious brutality, including several incidents where military forces fired automatic weapons into crowds of unarmed demonstrators. Gwangju is sometimes called "the shrine of Korean democracy" because of this incident, which is known today as the Gwangju Democratization Movement. After civilian rule was reinstated, a national cemetery was established honoring the victims of the incident.
In 1986, Gwangju separated from Jeollanam-do to become a Directly Governed City (Jikhalsi), and then became a Metropolitan City (Gwangyeoksi) in 1995.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions in GwangjuGwangju is divided into 5 districts ("Gu").
Map Name Hangul Hanja Gu (Districts) Buk-gu 북구 北區 Dong-gu 동구 東區 Gwangsan-gu 광산구 光山區 Nam-gu 남구 南區 Seo-gu 서구 西區 Climate
Climate data for Gwangju (1981−2010) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 5.3
(41.5)7.8
(46.0)13.0
(55.4)19.6
(67.3)24.3
(75.7)27.5
(81.5)29.6
(85.3)30.7
(87.3)26.9
(80.4)21.8
(71.2)14.6
(58.3)8.1
(46.6)19.1 Daily mean °C (°F) 0.6
(33.1)2.5
(36.5)7.0
(44.6)13.2
(55.8)18.3
(64.9)22.4
(72.3)25.6
(78.1)26.2
(79.2)21.9
(71.4)15.8
(60.4)9.1
(48.4)3.1
(37.6)13.8 Average low °C (°F) −3.1
(26.4)−1.8
(28.8)2.1
(35.8)7.5
(45.5)13.0
(55.4)18.2
(64.8)22.5
(72.5)22.8
(73.0)17.8
(64.0)10.9
(51.6)4.5
(40.1)−0.9
(30.4)9.5 Precipitation mm (inches) 37.1
(1.461)47.9
(1.886)60.8
(2.394)80.7
(3.177)96.6
(3.803)181.5
(7.146)308.9
(12.161)297.8
(11.724)150.5
(5.925)46.8
(1.843)48.8
(1.921)33.5
(1.319)1,391.0
(54.764)% humidity 67.7 65.2 62.9 61.9 66.4 72.8 80.0 78.1 74.3 68.4 68.1 68.8 69.5 Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) 11.0 9.0 9.5 8.9 9.3 10.7 15.5 14.9 9.8 6.8 9.0 10.0 124.4 Sunshine hours 159.9 164.6 192.0 213.0 222.8 169.2 145.4 172.6 172.3 205.2 163.6 155.9 2,136.3 Source: Korea Meteorological Administration [1] Education
Chonnam National University is a public university in Gwangju.
Honam University, Gwangju University, Gwangshin University, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju Education University, Gwangju Women's University, Nambu University, Chosun University, and Honam Christian University are private universities.
The hometown of numerous renowned scholars, Gwangju has 593 schools, consisting of 234 kindergartens, 145 elementary schools, 84 middle schools, 65 high schools, 7 junior colleges, 9 universities, 38 graduate schools, and 11 others (as of May 1, 2009) with a total of 406,669 students, or 28.5% of the total city population. The average number of students per household (0.8) reflects the city's characteristic as the home of education.
Transportation
The city is served by the Gwangju Subway. An extension was completed in April 2008 with another due for completion in 2012. There are two KTX (high speed rail) stations in the city: Gwangju Station and Songjeong-ri Station. Songjeong-ri is connected to Gwangju Subway; however, no connection exists to Gwangju Station.
It is also served by the Gwangju Airport.
Tourism
- Asian Culture Complex Information Center - As of October 2010[update], the Asian Culture Complex is under construction and is to open by 2010. The Asian Culture Complex Information Center is in operation.
- Gwangju Biennale - It is an internationally renowned modern art festival that is held every two years. It was first launched in 1995. The Gwangju Biennale Exhibition Hall is located at the Jung-oe Park Culture Center and the Science Center.
- Gwangju Culture & Art Center - The Center regularly hosts events.
- Gwangju Hyanggyo (Confucian School) - Gwangju Hyanggyo is located in the Gwangju Park in Sa-dong. There are many traditional houses here estimated as built during the 1st year of the Joseon Dynasty in 1392. This is a precious national asset as this school continues to hold memorial ceremonies for Confucius twice a year. Admission is free.
- Gwangju National Museum - The museum houses a permanent collection of historical art and cultural relics that date back to the old Joseon and Goryeo periods of Korean history. The museum also organizes various special exhibitions and cultural learning activities that are open to all.
Culture
- 2002 FIFA World Cup - It is one of the venues used for the World Cup, where matches were played at the Gwangju World Cup Stadium. It was where the South Korea national football team advance to the semi-finals, for the first time in its history, by defeating Spain.
- Universiade - It is a candidate city 2015 Summer Universiade games.[3]
- The 3rd Asia Song Festival, organised by Korea Foundation for International Culture Exchange, in 2006, was held at the Gwangju World Cup Stadium.[4]
Sister cities
 Guangzhou, China
Guangzhou, China San Antonio, United States [1]
San Antonio, United States [1] Sendai, Japan [2]
Sendai, Japan [2] Tainan, Taiwan [3]
Tainan, Taiwan [3] Hobart, Australia
Hobart, Australia Medan, Indonesia [4]
Medan, Indonesia [4] Maceió, Brazil
Maceió, Brazil
See also
References
- ^ "평년값자료(1981−2010) 광주(156)". Korea Meteorological Administration. http://www.kma.go.kr/weather/climate/average_30years.jsp?yy_st=2011&stn=156&norm=M&x=36&y=8&obs=0&mm=5&dd=28. Retrieved 2011−05−28.
- ^ (Korean) K-League news 4강 역사를 쓴 그곳, 광주 월드컵 경기장 Dream stadium of K-League
- ^ FISU 2015 SUMMER UNIVERSIADE Retrieved 2011-10-12
- ^ KOFICE 3rd Asia Song Festival 22 September 2006. Retrieved 2011-10-12
External links
- Official website of Gwangju
- The May 18 Memorial Foundation
- Gwangju :Official Site of Korea Tourism Org
- Gwangju International Center
- Gwangju Guidebook
- Gwangju Foreign Network - Radio Station in English for Gwangju
Districts of Gwangju  Regions and administrative divisions of South Korea
Regions and administrative divisions of South KoreaRegions Provinces Special self-governing province Special city Metropolitan cities Proposed special autonomous city Metropolitan cities of South Korea Special city Metropolitan cities Provincial capitals with gus
(not included above)Provincial capitals without gus
(not included above)Cities with gu
(not included above)Cities
(not included above)Andong · Anseong · Asan · Boryeong · Chungju · Dongducheon · Donghae · Gangneung · Geoje · Gimcheon · Gimhae · Gimje · Gimpo · Gongju · Gumi · Gunpo · Guri · Gunsan · Gwacheon · Gwangju · Gwangmyeong · Gwangyang · Gyeongju · Gyeongsan · Gyeryong · Hanam · Hwaseong · Icheon · Iksan · Jecheon · Jeongeup · Jinju · Miryang · Mungyeong · Namwon · Namyangju · Naju · Nonsan · Osan · Paju · Pocheon · Pyeongtaek · Sacheon · Samcheok · Sangju · Seogwipo · Seosan · Siheung · Sokcho · Suncheon · Taebaek · Tongyeong · Uijeongbu · Uiwang · Wonju · Yangju · Yangsan · Yeongcheon · Yeongju · YeosuCategories:- Gwangju
- 57 BC establishments
- Special Cities and Metropolitan Cities of South Korea
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.