- Media Key Block
-
The Media Key Block (MKB) is one of the keys that are included inside the copying protection system (DRM) AACS. This system is used to protect Blu-ray and HD DVD formats from being copied. The system has been developed by big companies from the film industry and the electronics industry like: IBM, Intel, Microsoft, Matsushita (Panasonic), Sony, Toshiba, The Walt Disney Company and Warner Bros..
The MKB key is found in the physical support (the disc) together with the content of the disc encrypted. The MKB has the function of validating the reproduction devices on which the disc is being played and obtaining, from the devices codes, the key that will allow the decryption of the disc content. That is the Media key (Km).
 AACS decryption process
AACS decryption processContents
How it works
Blu-Ray or HD-DVD have as content the encrypted data (usually video), the Volume ID (VID), the Encrypted Title Key(s) and the MKB. The MKB is also found encrypted in the disc to prevent it from being extracted off the disc and being manipulated and/or reproduced by another non authorized device.
 Process to obtain the Media key, from the MKB and the Device Keys
Process to obtain the Media key, from the MKB and the Device KeysThe reproduction device will have available its own keys, uniques for each model, called Device Keys. These keys are conceded by the AACS organization. In the moment of the reproduction, one of these keys will decrypt the MKB contained on the disc and as a result of this process we obtain the Media key.
The Media key is combined together with the VID (Volume ID) and as a result we obtain the Volume Unique Key (Kvu). With the Kvu we are able to decrypt the Encrypted Title Key and obtain the Title keys which finally allows to decrypt the content of the disc and view it.[1]
This way the system can protect contents from being viewed in devices that have not been authorized. Therefore, the system allows modifying the MKB in future relaunch of a determined content in order to select the devices in which this content can be viewed.
Key Structure
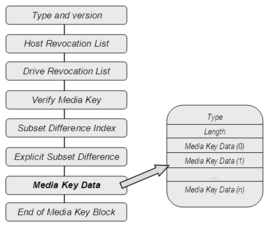
Even though it seems a simple mechanism the MKB key which is found in the physical support of the disc follows a complex structure. The MKB is distributed in blocks that contain the version of the Media key, the list of devices that have been revoked, a field to authenticate the MKB, and other fields that specify parameters corresponding to the decrypting algorithm and define the structure of the own Media Key and also the Media key itself.
The MKB itself is found inside the field Media Key Data Record and has a variable length but it is always a multiple of 4 bytes.[2] [3]
Advantages and disadvantages
Many consumers associations have complained against this protection system since it can lead to a situation where physical devices cannot reproduce contents even though they do not infringe any intellectual property. This situation can be achieved either by trying to reproduce some content in old devices, therefore not certified by the AACS, or because the device model has been disallowed by AACS, as a result all the owners of that device model will not be able to view contents protected with the MKB.
This situation has become even worse with the recent publication in multiple web sites of the Media Key, that is, the key that allows decrypting the Volume ID[4] [5], and at the same time, the encrypted content, without the need of using a certified device by the AACS or a valid MKB. This is especially critical because nowadays the Volume ID is the same in all the Blu-ray or HD-DVD discs with equal content.
See also
References
- ^ AACS reference. "Recordable Video Book (Rev 0.91)". http://www.aacsla.com/specifications/specs091/AACS_Spec_Recordable_0.91.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ^ AACS reference. "Introduction and Common Cryptographic elements (Rev 0.91)". http://www.aacsla.com/specifications/specs091/AACS_Spec_Common_0.91.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ^ AACS reference (2007-10-12). "Pre-recorded Video Book (Rev 0.92)". http://www.aacsla.com/specifications/AACS_Spec_Prerecorded_0.92.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ^ Lindsay Martell (2007-01-26). "Blu-ray and HD DVD Encryption Cracked". http://www.newsfactor.com/news/Blu-ray--HD-DVD-Encryption-Cracked/story.xhtml?story_id=121000E3UUOA.
- ^ Alexander Kaplan (2007-04-05). "Illegal Offering of Title/Volume Keys to Circumvent AACS Copyright Protection: hdkeys.com" (pdf). http://forum.doom9.org/attachment.php?attachmentid=7071&d=1176327932.
External links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.