- Cartilage–hair hypoplasia
-
Cartilage-hair hypoplasia Classification and external resources OMIM 250250 Cartilage–hair hypoplasia (CHH), also known as McKusick type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia,[1]:578 is a rare form of short-limbed dwarfism due to skeletal dysplasia. It was first reported in 1965 by McKusick et al. Actor Verne Troyer is affected with this form of dwarfism,[2] as was actor Billy Barty, who was renowned for saying "The name of my condition is Cartilage Hair Syndrome Hypoplasia, but you can just call me Billy."[3]
Genetics
CHH is an autosomal recessive[4] inherited disorder. A rarely encountered genetic phenomenon, known as uniparental disomy (a genetic circumstance where a child inherits two copies of a chromosome from one parent, as opposed to one copy from each parent) has also been observed with the disorder.[4]
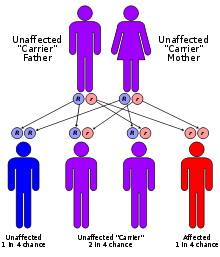 Cartilage-hair hypoplasia has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Cartilage-hair hypoplasia has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
An association between mutations near or within the ncRNA component of RNase MRP, RMRP, has been identified.[5][6][7][8]
See also
References
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ McKusick VA, Eldridge R, Hosteler JA, Ruangwit U, Egeland JA (1965). "Dwarfism In The Amish. II. Cartilage-hair hypoplasia". Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 116: 285–326. PMID 14284412.
- ^ Chavez, Paul (2000-12-24). "The name of my condition is Cartilage Hair Syndrome Hypoplasia, but you can just call me Billy". ABC News. http://abcnews.go.com/Entertainment/story?id=111722&page=1. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- ^ a b Sulisalo T, Makitie O, Sistonen P, Ridanpaa M, el Rifai W, Ruuskanen O, de la Chapelle A, Kaitila L (1997). "Uniparental disomy in cartilage-hair hypoplasia". Eur J Hum Genet. 5 (1): 35–42. PMID 9156319.
- ^ Bonafé L, Schmitt K, Eich G, Giedion A, Superti-Furga A (February 2002). "RMRP gene sequence analysis confirms a cartilage-hair hypoplasia variant with only skeletal manifestations and reveals a high density of single-nucleotide polymorphisms". Clin. Genet. 61 (2): 146–51. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0004.2002.610210.x. PMID 11940090. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0009-9163&date=2002&volume=61&issue=2&spage=146.
- ^ Ridanpää M, van Eenennaam H, Pelin K, Chadwick R, Johnson C, Yuan B, vanVenrooij W, Pruijn G, Salmela R, Rockas S, Mäkitie O, Kaitila I, de la Chapelle A (2001). "Mutations in the RNA component of RNase MRP cause a pleiotropic human disease, cartilage-hair hypoplasia.". Cell 104 (2): 195–203. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00205-7. PMID 11207361.
- ^ Martin AN, Li Y (2007). "RNase MRP RNA and human genetic diseases.". Cell Res 17 (3): 219–26. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7310120. PMID 17189938.
- ^ Kavadas FD, Giliani S, Gu Y, Mazzolari E, Bates A, Pegoiani E, Roifman CM, Notarangelo LD (2008). "Variability of clinical and laboratory features among patients with ribonuclease mitochondrial RNA processing endoribonuclease gene mutations.". J Allergy Clin Immunol 122 (6): 1178–84. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2008.07.036. PMID 18804272.
Categories:- IUIS-PID table 3 immunodeficiencies
- Genodermatoses
- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Noninfectious immunodeficiency-related cutaneous conditions
- Disease stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
