Mars general circulation model
- Mars general circulation model
-
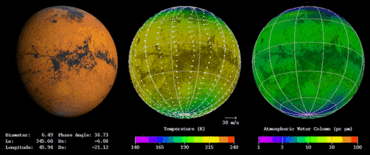
Mars geneal circulation model, NASA
The Mars general circulation model (MGCM) is the result of a research project by NASA to understand the nature of the general circulation of the atmosphere of Mars, how that circulation is driven and how it affects the climate of Mars in the long term.
History
Mars climate simulation models date as far back as the Viking missions to Mars. Most Mars climate simulation models were one off models written by individual researchers that never were never reused or open sourced. By the 1990s the need for a unified model codebase came into being, due to the general impact of the internet on climate modelling and research. This current Mars climate simulation model has its origins with the internet era.
How it works
This Mars climate model is a complex 3 dimensional (height, latitude, longitude) model, which represents the processes of atmospheric heating by gases and ground-air heat transfer, as well as large-scale atmospheric motions.[1]
The current model has not been modified for use with distributed computing systems like BOINC.
Other planets
There are global climate simulation models that have been written for Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune and Venus.[1]
See also
References
- ^ "Mars General Circulation Model – Research". NASA. http://www-mgcm.arc.nasa.gov/mgcm/HTML/research.html. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
Categories:
- Mars
- Climate history
- Numerical climate and weather models
- Mars stubs
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Mars General Circulation Model — The Mars General Circulation Model (MGCM) is the result of a research project by NASA to understand the nature of the general circulation of the atmosphere of Mars, how that circulation is driven and how it affects the climate of Mars in the long … Wikipedia
Mars (planète) — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Mars. Mars … Wikipédia en Français
Climate of Mars — Mosaic image of Mars as seen by Viking 1, 22 February 1980 The climate of Mars has been an issue of scientific curiosity for centuries, not least because Mars is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from… … Wikipedia
Mars — /mahrz/, n. 1. the ancient Roman god of war and agriculture, identified with the Greek god Ares. 2. Astron. the planet fourth in order from the sun, having a diameter of 4222 miles (6794 km), a mean distance from the sun of 141.6 million miles… … Universalium
Géologie de la planète Mars — La géologie de la planète Mars, parfois appelée aréologie[1], recouvre l étude scientifique de Mars et de ses propriétés physiques, de ses reliefs, de sa composition, de son histoire, et de tous les phénomènes qui ont affecté ou affectent encore… … Wikipédia en Français
Mars Observer — Artist rendering of Mars Observer in orbit around Mars. Operator NASA / JPL … Wikipedia
Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter — MOLA topographic images of the two hemispheres of Mars. This image appeared on the cover of Science magazine in May 1999. The Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) was one of five instruments on board the Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) spacecraft,… … Wikipedia
Martian chaos terrain — Contents 1 Chaos terrain on Mars 2 Locations 3 Theories for formation 3.1 Melting of buried ice 3.2 … Wikipedia
Xenon — (PronEng|ˈzɛnɒn [Xenon, entry in the Oxford English Dictionary, prepared by J. A. Simpson and E. S. C. Weiner, vol. 20, second edition, Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1989. ISBN 0 19 861232 X (vol. 20), ISBN 0 19 861186 2 (set.)] or IPAlink en|ˈziːnɒn… … Wikipedia
7440-63-3 — Xénon Pour les articles homonymes, voir Xenon. Xénon … Wikipédia en Français

