- Dyck graph
-
Dyck graph 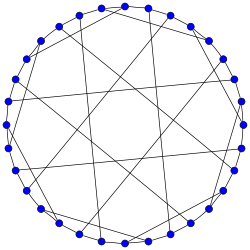
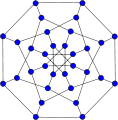
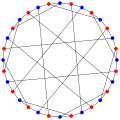
The Dyck graphNamed after W. Dyck Vertices 32 Edges 48 Radius 5 Diameter 5 Girth 6 Automorphisms 192 Chromatic number 2 Chromatic index 3 Properties Symmetric
Cubic
Hamiltonian
Bipartite
Cayley graphv · mathematical field of graph theory, the Dyck graph is a 3-regular graph with 32 vertices and 48 edges, named after Walther von Dyck.[1][2] It is Hamiltonian with 120 distinct Hamiltonian cycles. It has chromatic number 2, chromatic index 3, radius 5, diameter 5 and girth 6. It is also a 3-vertex-connected and a 3-edge-connected graph.
The Dyck graph is a toroidal graph, and the dual of its symmetric toroidal embedding is the Shrikhande graph, a strongly regular graph both symmetric and hamiltonian.
Contents
Algebraic properties
The automorphism group of the Dyck graph is a group of order 192.[3] It acts transitively on the vertices, on the edges and on the arcs of the graph. Therefore the Dyck graph is a symmetric graph. It has automorphisms that take any vertex to any other vertex and any edge to any other edge. According to the Foster census, the Dyck graph, referenced as F32A, is the only cubic symmetric graph on 32 vertices.[4]
The characteristic polynomial of the Dyck graph is equal to (x − 3)(x − 1)9(x + 1)9(x + 3)(x2 − 5)6.
Dyck map
The Dyck graph is the skeleton of a symmetric tessellation of a surface of genus three by twelve octagons, known as the Dyck map or Dyck tiling. The dual graph for this tiling is the complete tripartite graph K4,4,4.[5][6]
Gallery
References
- ^ Dyck, W. (1881), "Über Aufstellung und Untersuchung von Gruppe und Irrationalität regulärer Riemann'scher Flächen", Math. Ann. 17: 473 .
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W., "Dyck Graph" from MathWorld.
- ^ Royle, G. F032A data
- ^ Conder, M.; Dobcsányi, P. (2002), "Trivalent symmetric graphs up to 768 vertices", J. Combin. Math. Combin. Comput. 40: 41–63 .
- ^ Dyck, W. (1880), "Notiz über eine reguläre Riemannsche Fläche vom Geschlecht 3 und die zugehörige Normalkurve 4. Ordnung", Math. Ann. 17: 510–516 .
- ^ King, R. B. (2004), "Toroidal polyhexes, tripartite graphs, and double groups", Molecular physics 102 (11): 1231–1241, doi:10.1080/00268970410001728681 .
Categories:- Individual graphs
- Regular graphs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Graphe de Dyck — Représentation du graphe de Dyck Nombre de sommets 32 Nombre d arêtes 48 Distribution des degrés 3 régulier Rayon … Wikipédia en Français
Cubic graph — Not to be confused with graphs of cubic functions. The Petersen graph is a Cubic graph … Wikipedia
Binary tree — Not to be confused with B tree. A simple binary tree of size 9 and height 3, with a root node whose value is 2. The above tree is unbalanced and not sorted. In computer science, a binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at… … Wikipedia
Projet:Mathématiques/Liste des articles de mathématiques — Cette page n est plus mise à jour depuis l arrêt de DumZiBoT. Pour demander sa remise en service, faire une requête sur WP:RBOT Cette page recense les articles relatifs aux mathématiques, qui sont liés aux portails de mathématiques, géométrie ou… … Wikipédia en Français
Free group — In mathematics, a group G is called free if there is a subset S of G such that any element of G can be written in one and only one way as a product of finitely many elements of S and their inverses (disregarding trivial variations such as st 1 =… … Wikipedia
Group (mathematics) — This article covers basic notions. For advanced topics, see Group theory. The possible manipulations of this Rubik s Cube form a group. In mathematics, a group is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an operation that combines … Wikipedia
Freie Gruppe — In der Mathematik heißt eine Gruppe frei, wenn sie eine Teilmenge S enthält, so dass jedes Gruppenelement auf genau eine Weise als (reduziertes) Wort von Elementen in S und deren Inversen geschrieben werden kann. Hierbei ist die Reihenfolge der… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Laws of Form — (hereinafter LoF ) is a book by G. Spencer Brown, published in 1969, that straddles the boundary between mathematics and of philosophy. LoF describes three distinct logical systems: * The primary arithmetic (described in Chapter 4), whose models… … Wikipedia
Schwarz triangle — In geometry, a Schwarz triangle, named after Hermann Schwarz is a spherical triangle that can be used to tile a sphere, possibly overlapping, through reflections in its edges. They were classified in (Schwarz 1873). These can be defined more… … Wikipedia
Tree structure — A tree structure showing the possible hierarchical organization of an encyclopedia … Wikipedia
18+© Academic, 2000-2024- Contact us: Technical Support, Advertising
Dictionaries export, created on PHP, Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, MODx.Share the article and excerpts
Dyck graph
- Dyck graph
-
Dyck graph 
The Dyck graphNamed after W. Dyck Vertices 32 Edges 48 Radius 5 Diameter 5 Girth 6 Automorphisms 192 Chromatic number 2 Chromatic index 3 Properties Symmetric
Cubic
Hamiltonian
Bipartite
Cayley graph