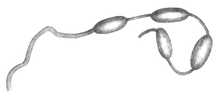
- Diplosolenodes occidentalis
-
Diplosolenodes occidentalis 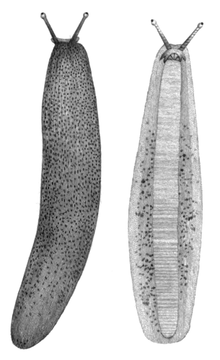
Drawing of dorsal and ventral view of Diplosolenodes occidentalis from its original type description. 
Ventral view of a preserved specimen of Diplosolenodes occidentalis Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda (unranked): clade Heterobranchia
clade Euthyneura
clade Panpulmonata
clade Eupulmonata
clade SystellommatophoraSuperfamily: Veronicelloidea Family: Veronicellidae Genus: Diplosolenodes Species: D. occidentalis Binomial name Diplosolenodes occidentalis
(Guilding, 1825)[1]Synonyms Diplosolenodes occidentalis is a species of air-breathing land slug, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Veronicellidae, the leatherleaf slugs.
Contents
Distribution
Diplosolenodes occidentalis was originally discovered and described by Lansdown Guilding from the West Indian island of Saint Vincent. It seems likely that this species is native to most of the Lesser Antilles.[3]
The distribution of Diplosolenodes occidentalis includes the Lesser Antilles:
It has been introduced to the Greater Antilles, Central America and northern South America:[3]
- Nicaragua[5]
- Costa Rica[6]
- El Hatillo Municipality, Miranda, Venezuela
It occurs in greenhouses in Logan County, Oklahoma.[7]
This species has not yet become established in the wild in the USA, but it is considered to represent a potentially serious threat as a pest, an invasive species which could negatively effect agriculture, natural ecosystems, human health or commerce. Therefore it has been suggested that this species be given top national quarantine significance in the USA.[8]
Description
This slug is most easily recognized by the black speckling on its mantle or hyponota.[3] The body length can reach up to 60 mm.[7]
Ecology
This species may be found in undisturbed environments as well as in agricultural settings, where it may be regarded as a minor pest.[3]
References
This article incorporates CC-BY-3.0 text from the reference.[3]
- ^ Guilding L. (1825). "Description of a new species of Onchidium". [Read 4 November 1823.] Transactions of the Linnean Society of London 14: 322-324, table IX.
- ^ a b Angas G. F. (1884). "On the terrestrial Mollusca of Dominica, collected during a recent visit to that island". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1883: 594-597, figs. 1-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Robinson D. G., Hovestadt A., Fields A. & Breure A. S. H. (July 2009). "The land Mollusca of Dominica (Lesser Antilles), with notes on some enigmatic or rare species". Zoologische Mededelingen 83 http://www.zoologischemededelingen.nl/83/nr03/a13
- ^ a b Pilsbry H. A. (1892). "On a collection of land Mollusca from the Island of Dominica, West Indies". Transactions of the Connecticut Academy of Science 8: 356-358.
- ^ (Spanish) Pérez A. M., Sotelo M., Arana I. & López A. (2008). "Diversidad de moluscos gasterópodos terrestres en la región del Pacífico de Nicaragua y sus preferencias de hábitat". Rev. Biol. Trop. 56(1): 317-332,. PDF
- ^ (Spanish) Barrientos Z. (2003). "Lista de especies de moluscos terrestres (Archaeogastropoda, Mesogastropoda, Archaeopulmonata, Stylommatophora, Soleolifera) informadas para Costa Rica". Rev. Biol. Trop. 51(Suppl. 3): 293-304. PDF
- ^ a b Branson B. A. (1980). "THE RECENT GASTROPODA OF OKLAHOMA, PART VIII. THE SLUG FAMILIES LIMACIDAE, ARIONIDAE, VERONICELLIDAE, AND PHILOMYCIDAE". Proc. Okla. Acad. Sci. 60: 29-35. PDF.
- ^ Cowie R. H., Dillon R. T., Robinson D. G. & Smith J. W. (2009). "Alien non-marine snails and slugs of priority quarantine importance in the United States: A preliminary risk assessment". American Malacological Bulletin 27: 113-132. PDF.
Further reading
- Baker H. B. (1925). "North American Veronicellidae". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 77: 157-184, Pl. 3-6. JSTOR
- Coto A. T. D. (1983). "Combate de la babosa Diplosolenodes occidentale (Guilding) (Soleolifera: Veronicellidae) con extractos de plantas". Tesis, Universidad de Costa Rica, San Jose. 53 pp.
- Thomé J. W. (1989). "Annotated and illustrated preliminary list of the Veronicellidae (Mollusca[ Gastropoda) of The Antilles, and Central and North America". J.Med. & Appl. Malacol. 1: 11-28.
- Thomé J. W. (1993). "Estado atual da sistemática dos veronicellidae (Mollusca; Gastropoda) americanos, con comentários sobre sua importáncia económica, ambiental e na saúde". Biociéncias, Porto Alegre 1(1): 61-75.
- Thomé J. W., dos Santos P. H. & Pedott L. (1997). "Annotated list of Veronicellidae from the collections of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia and the National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, Washington D.C., U.S.A. (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Soleolifera)". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 110: 520-536, figs 1-16. page 522.
- JULIETA FERNANDEZ DE V. (1982). "CONTRIBUCION AL CONOCIMIENTO DE LAS BABOSAS Y SIETECUEROS (MOLLUSCA: GASTROPODA) QUE CAUSAN DAÑOS A LA AGRICULTURA EN VENEZUELA". Rev. Fac. Agron. (Maracay), XII(3-4). 353-386. http://avepagro.org.ve/fagro/v12_34/v124m010.html - listed as Latipes pterocaulis in Venezuela.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.