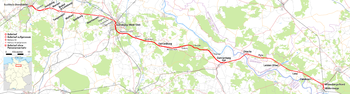
- Wittenberge–Buchholz railway
-
Wittenberge–Buchholz RouteRoute number: 112 Line number: 1151 (Wittenberge–Buchholz)
1280 (Jesteburg–Buchholz)Line length: 142 Gauge: 1,435 Voltage: Jesteburg–Buchholz: 15 kV 16,7 Hz AC Maximum speed: 60 States: Brandenburg,
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern,
Lower SaxonyLegend

Main line from Bremen 
Old line from Bremervörde 

Heath Railway from Soltau 

268,3 Buchholz (Nordheide) (Keilbahnhof) 
Main line to Hamburg 
265,1 Reindorf 
262,0 Jesteburg 
7,7 Jesteburg crossover 
New goods line to Maschen Rbf 
259,3 Marxen 
255,3 Brackel (b Lüneburg) 
252,6 Tangendorf 
249,5 Wulfsen 
to the Line to Winsen 
Hützel–Winsen line 
246,0 Bahlburg 
237,6 Mechtersen 
235,1 Vögelsen 
233,1 Ochtmissen 
231,6 Sternkamp 
(siding) 

Main line from Hamburg 

Line from Büchen 

Line from Bleckede 

229,0 
Line to Soltau 

Main line to Celle 


223,7 Wendisch Evern 
Elbe Lateral Canal 
216,9 Vastorf 
211,8 Bavendorf 
206,0 Dahlenburg 
202,4 Neetzendorf 
196,3 Göhrde (former station) 
192,1 Leitstade 
182,5 Hitzacker 
Line from Lüchow 
175,6 Dannenberg Ost 
(line ends east of the station yard) 
Elbe Bridge Dömitz, L. Saxony–M.-Vorpommern state border 
164,7 Dömitz 
Old line to Ludwigslust 
140,3 Polz 
M.-Vorpommern–Brandenburg state border 
149,5 Lenzen (Elbe) 
140,3 Lanz 
134,1 Cumlosen 
Main line from Ludwigslust 
128,5 Wittenberge Nord 
Line from Wittstock 
126,6 Wittenberge 
Line to Stendal 
Main line to Berlin The Wittenberge–Buchholz railway or Wittenberge–Buchholz branch (German: Bahnstrecke Wittenberge-Buchholz or Wittenberge-Buchholzer Zweigbahn) was licensed to, planned and built by the Berlin-Hamburg Railway Company (BHE) and opened in 1874 as an additional link between the cities of Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen in Germany. It ran through Wittenberge, Dömitz, Dannenberg, Lüneburg and Buchholz and was originally to have been extended to Bremerhaven.
The single-tracked main line ran through the present-day states of Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony. With the destruction of the bridge over the Elbe at Dömitz at the end of the Second World War and the subsequent division of Germany it suddenly lost its importance and, as a result, was partially closed.
Today two sections of the line are still open: the longer one of the two between Dannenberg and Lüneburg in the Wendland is known today as the Wendland Railway (Wendlandbahn); whilst western end of the shorter section from Buchholz to Jesteburg merges into the line to the Maschen Marshalling Yard.
The freight carried on the line includes the transport of nuclear waste containers with radioactive waste to a terminal at the end of the track one kilometre east of the Dannenberg Ost station, where it is off loaded for further transport by road to a nuclear waste storage facility. This was subject to blockading by anti-nuclear activists in November 2010.
Literature
- Dietmar Ramuschkat, „Berlin–Bremen via Wittenberge–Lüneburg–Buchholz. Eine Eisenbahnlinie entsteht“, videel, Niebüll 2002, ISBN 3-89906-316-3
- Wolfgang Fiegenbaum, Wolfgang Klee, „Abschied from der Schiene, Stillgelegte railways im Personenverkehr Deutschlands 1980–1985“, Motorbuch (S. 22ff), Stuttgart 1988, ISBN 3-613-01191-3
- „Eisenbahnatlas Deutschland“, Ausgabe 2007/2008, Verlag Schweers + Wall GmbH, 6. Auflage (April 2007), ISBN 978-3-89494-136-9
External links
- Dömitz Railway Bridge at www.lostplaces.de
- Old Lüneburg–Buchholz line at www.spurkranz.de
Categories:- Railway lines in Brandenburg
- Railway lines in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Railway lines in Lower Saxony
- Prignitz
- Lüchow-Dannenberg district
- Lüneburg Heath
- Lüneburg district
- Harburg district
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.