- Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty (1867)
-
Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty Convention between Great Britain and the Netherlands for an Interchange of Territory on the Gold Coast of Africa[1] 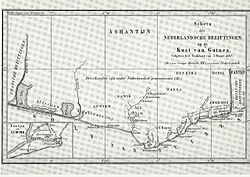
The Dutch Gold Coast after the trade of forts with Britain. Signed 5 March 1867[1] Location London, United Kingdom[1] Parties  United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Netherlands
NetherlandsThe Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty of 1867 established a trade of forts among the Dutch and British Gold Coast, in order to produce a more coherent area of influence there. All forts to the east of Fort Elmina were given to the Netherlands, and all forts to the west were awarded to the Netherlands.
Contents
History
Whereas the Dutch forts on the Gold Coast were a colonial backwater in the 19th century, the British forts were slowly developed into a full colony, especially after Britain took over the Danish Gold Coast in 1850. The presence of Dutch forts in an area that became increasingly influenced by the United Kingdom was deemed undesirable, and in the late 1850s British began pressing for either a buyout of the Dutch forts, or a trade of forts so as to produce more coherent areas of influences.
In the Dutch political landscape of the time, a buyout was not a possibility, so a trade of forts was negotiated. In 1867, the "Convention between Great Britain and the Netherlands for an Interchange of Territory on the Gold Coast of Africa" was signed, in which all Dutch forts to the east of Elmina were handed over to Britain, while the British forts west of Elmina were handed over to the Netherlands.[1]
The trade proved a disaster for the Dutch, as their long-standing alliance with the mighty Ashanti tribe did not fare well with the population around the new forts assigned to them. Shortly after the transfer, the Dutch colonial minister secretly began negotiating a handover of all Dutch forts to Britain. In the Gold Coast Treaty of 1871, the whole colony was ceded to the United Kingdom for 46,939.62 Dutch guilders.[2]
Forts traded
From the Netherlands to the United Kingdom
Place in Ghana New British name Dutch name Mouri Fort Nassau Fort Nassau Accra Fort Ussher Fort Crêvecoeur Kormantin Fort Cormantine Fort Amsterdam Senya Beraku Fort Good Hope Fort Goede Hoop Apam Fort Patience Fort Lijdzaamheid From the United Kingdom to the Netherlands
Place in Ghana New Dutch name British name Beyin Fort Willem III Fort Apollonia Dixcove Fort Metalen Kruis Fort Metal Cross Komenda Fort Komenda Fort Komenda Sekondi Fort Sekondi Fort Sekondi See also
- Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814
- Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824
- Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870-1871
- Netherlands – United Kingdom relations
Notes
- ^ a b c d Foreign & Commonwealth Office - Convention between Great Britain and the Netherlands for an Interchange of Territory on the Gold Coast of Africa
- ^ Adhin 1961, p. 10
References
- Adhin, J. H. (1961). "De immigratie van Hindostanen en de afstand van de Goudkust". Nieuwe West-Indische Gids 41 (1): 4–13. http://www.kitlv-journals.nl/index.php/nwig/article/viewFile/5188/5955.
Categories:- 1867 in the United Kingdom
- 1867 in the Netherlands
- History of Ghana
- Treaties of the United Kingdom
- Netherlands–United Kingdom relations
- 19th century in the Netherlands
- 1867 treaties
- Treaties of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
