- Chromo shadow domain
-
Chromo shadow domain 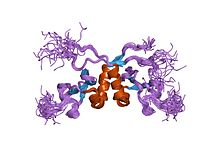
hp1 chromo shadow domain in complex with pxvxl motif of caf-1 Identifiers Symbol Chromo_shadow Pfam PF01393 Pfam clan CL0049 InterPro IPR008251 SCOP 1e0b Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary In molecular biology, the chromo shadow domain is a protein domain which is distantly related to the chromodomain. It is always found in association with a chromodomain. [1] Proteins containing a chromo shadow domain include Drosophila and human heterochromatin protein Su(var)205 (HP1); and mammalian modifier 1 and modifier 2.
Chromoshadow domains self aggregate, bringing together the nucleosomes to which their proteins are bound and thus condense the chromatin region they are associated with. Condensed chromatin is not able to be transcribed as the transcription factors and enzymes are not able to access to DNA sequence in this form. Hence chromoshadow domain containing proteins repress gene transcription.[2]
References
- ^ Aasland R, Stewart AF (August 1995). "The chromo shadow domain, a second chromo domain in heterochromatin-binding protein 1, HP1". Nucleic Acids Res. 23 (16): 3168–73. doi:10.1093/nar/23.16.3168. PMC 307174. PMID 7667093. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=307174.
- ^ Yamamoto K, Sonoda M (2003). "Self-interaction of heterochromatin protein 1 is required for direct binding to histone methyltransferase, SUV39H1.". Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301 (2): 287–92. PMID 12565857. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12565857.
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR008251
Categories:- Protein domains
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
