- CWL WZ-X
infobox Aircraft
name =WZ-X
type =Reconnaissance aircraft
manufacturer =CWL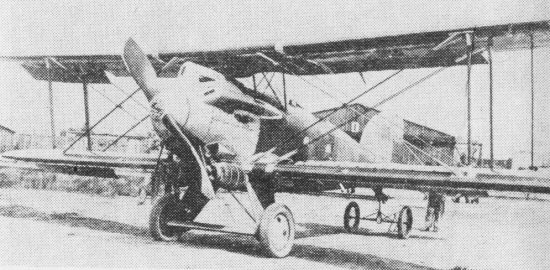
caption =CWL WZ-X prototype, 1926
designer =
first flight = August 1926
introduced = 1928
retired = 1939
status =
primary user =Polish Air Force
more users =
produced = 1926-1927
number built = 4
unit cost =
developed from =
variants with their own articles = The WZ-X was the Polishreconnaissance aircraft designed in the mid-1920s and manufactured in theCentralne Warsztaty Lotnicze (CWL) - Central Aviation Workshops inWarsaw . It was the first combat aircraft of own design built in Poland, in a small series.Development
The aircraft was designed by
Władysław Zalewski , as his tenth design (Zalewski had already constructed aircraft for the Russian Air Force during theWorld War I ). Work started in 1923, and the first prototype was flown in August 1926. Another airframe was built for static trials. Flight trials were successful: its performance was at least as good as theBreguet 19 , and better than thePotez 25 . However, maintenance was more difficult.In 1927, three pre-series aircraft were built (designated WZ-X/II, WZ-X/III, WZ-X/IV). The first two of these were fitted with the same Lorraine-Dietrich 12Eb 478 hp
W engine used by the prototype, while the other had aGnome et Rhône Jupiter 9a 530 hpradial engine with four-blade propeller.The WZ-X did not enter serial production, because Poland had already bought many Breguet 19 aircraft from France, and started production under licence of the Potez 25 of the same class. Three WZ-Xs were given to aviation schools, where one or two survived in
Dęblin until 1939.Description
Wooden construction braced
biplane , conventional in layout. A fuselage wassemi-monocoque , elliptical in cross-section, plywood-covered. Rectangular two-spar wings, covered with canvas and plywood (in front), of equal span, slightly staggered. Ailerons on both wings, joined with struts. Struttedempennage , covered with plywood (stabilizers) and canvas (rudder and elevators). Crew of two, sitting intandem in open cockpits, the first with a windshield. Conventional fixedlanding gear , with a rear skid, the main gear with a common axle. Inline engine in front, driving two-blade tractor woodenpropeller , with two round Lamblin radiators under the fuselage (in the WZ-X/IV - radial engine, with four-blade propeller and no radiators). Fuel tank in the fuselage.The pilot had two fixed 7.7 mm Vickers
machine gun s with aninterrupter gear , the observer had twin 7.7 mm Lewis machine guns on a ring mounting. Bomb load: unknown.pecifications
aircraft specifications
plane or copter?=plane
jet or prop?=prop
ref=Glass, A. (1977)
crew=2, pilot and observer
capacity=
length main= 8.21 m
length alt=
span main=11.31 m
span alt=
height main=3.07 m
height alt=
area main=33.2 m²
area alt= ft²
airfoil=
empty weight main= 1246 kg
empty weight alt=
loaded weight main= 1915 kg
loaded weight alt=
useful load main= 669 kg
useful load alt=
max takeoff weight main= 1240 kg
max takeoff weight alt=
engine (prop)=Lorraine-Dietrich 12 Eb
type of prop= water-cooled 12-cylinder inlineW engine
number of props=1
power main=478 hp / 450 hp nominal power
power alt=
max speed main=205 km/h
max speed alt=
cruise speed main= 180 km/h
cruise speed alt=
stall speed main=
stall speed alt=
range main=800 km
range alt=
ceiling main=6325 m
ceiling alt=
climb rate main= 5.5 m/s
climb rate alt=
loading main= 57.7 kg/m²
loading alt=
power/mass main=
power/mass alt=
armament=
*2 fixed front-firing 7.7 mm Vickers machineguns
*2 movable 7.7 mm Lewis machineguns
*light bombsee also
aircontent
related=
similar aircraft=Breguet 19 -Potez 15 -Potez 25 -Aero A.32
lists=
see also=*WZ-III - WZ-IV -CWL WZ-VIII -CWL WZ-IX References
*Andrzej Glass: "Polskie konstrukcje lotnicze 1893-1939" ("Polish aviation constructions 1893-1939"), WKiŁ, Warsaw 1977, p. 122-123 pl icon
External links
* [http://www.airwar.ru/enc/fww1/wzx.html Photos and drawings ] at [http://www.airwar.ru Ugolok Neba] site
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
