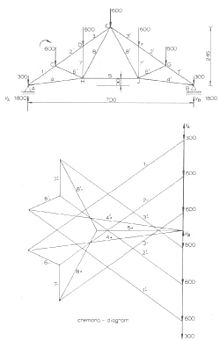
- Cremona diagram
-
The Cremona diagram is a graphical method used in statics of trusses to determine the forces in members (graphic statics). The method was created by the Italian mathematician Luigi Cremona.
In the Cremona method, first the external forces and reactions are drawn (to scale) forming a vertical line in the lower right side of the picture. This is the sum of all the force vectors and is equal to zero as there is mechanical equilibrium.
Since the equilibrium holds for the external forces on the entire truss construction, it also holds for the internal forces acting on each joint. For a joint to be at rest the sum of the forces on a joint must also be equal to zero. Starting at joint Aorda, the internal forces can be found by drawing lines in the Cremona diagram representing the forces in the members 1 and 4, going clockwise; VA (going up) load at A (going down), force in member 1 (going down/left), member 4 (going up/right) and closing with VA. As the force in member 1 is towards the joint, the member is under compression, the force in member 4 is away from the joint so the member 4 is under tension. The length of the lines for members 1 and 4 in the diagram, multiplied with the chosen scale factor is the magnitude of the force in members 1 and 4.
Now, in the same way the forces in members 2 and 6 can be found for joint C; force in member 1 (going up/right), force in C going down, force in 2 (going down/left), force in 6 (going up/left) and closing with the force in member 1.
The same steps can be taken for joints D, H and E resulting in the complete Cremona diagram where the internal forces in all members are known.
In a next phase the forces caused by wind must be considered. Wind will cause pressure on the upwind side of a roof (and truss) and suction on the downwind side. This will translate to asymmetrical loads but the Cremona method is the same. Wind force may introduce larger forces in the individual truss members than the static vertical loads.
Categories:- Mechanics
- Structural system
- Diagrams
- Classical mechanics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.