- Magnetic horn
-
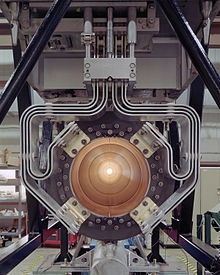 End-on view of one of the NuMI horns.
End-on view of one of the NuMI horns.
A magnetic horn or neutrino horn is a device used in the production of neutrino beams. It focuses charged particles that will decay into neutrinos so that the resulting neutrino beam is as narrow as possible.
Description
Production of a neutrino beam generally involves directing protons onto a fixed target of solid material. The protons interact strongly with the nuclei in the target, producing a variety of secondary hadrons. The proton beam energy and target material are chosen so that these hadrons are mostly pions and kaons. Both of these particles' decays produce neutrinos. However, without a neutrino horn, the resulting neutrino beam is very wide, both geometrically and in energy spread. This is because the secondary particles are produced at a variety of angles and energies and then when they decay, the neutrinos are again produced at a variety of angles and energies.
The neutrinos themselves cannot be focused with electric or magnetic fields because they are electrically neutral. Instead, one or more magnetic horns can be used to focus the secondary particles. The shape of the horn and strength of the magnetic field can be tuned to select a range of particle energies that are to be best focused. In this way, the resulting neutrino beam is both geometrically focused and given a chosen range of energies. Note however that the decays of the secondary hadrons still impart some random direction to the neutrinos, so the beam will always spread to some degree no matter how well the horn works.
Notable uses
- The NuMI beam, used by the MINOS experiment, uses 2 magnetic horns to produce a 3GeV muon neutrino beam.
- The Gargamelle bubble chamber, in which the first neutral current reactions were observed, used a 20GeV muon anti-neutrino beam focused by a single horn.
References
- The CERN magnetic horn (1971) and its remote-handling system. J.C Dusseux, J.B M. Pattison, G. Ziebarth . CERN-72-11, Jun 1972.
- Status of a magnetic horn for a neutrino factory. Simone S. Gilardoni, G. Grawer, G. Maire, J.M. Maugain, S. Rangod, F. Voelker (CERN & Geneva U.). 2003. Prepared for NuFact02: 4th International Workshop on Neutrino Factories, London, England, 1-6 Jul 2002.
- Experimental Study of the High-energy Reactions Anti-muon-neutrino e → Antu-muon-neutrino e-, Anti-muon-neutrino N → mu + X in the Gargamelle Bubble Chamber. (In French) Farhad Rahimi (Strasbourg, CRN) . CRN-HE-84-13, Dec 1982.
Categories:- Particle accelerators
- Types of magnets
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
