- Lipocalin
Pfam_box
Symbol = Lipocalin
Name =
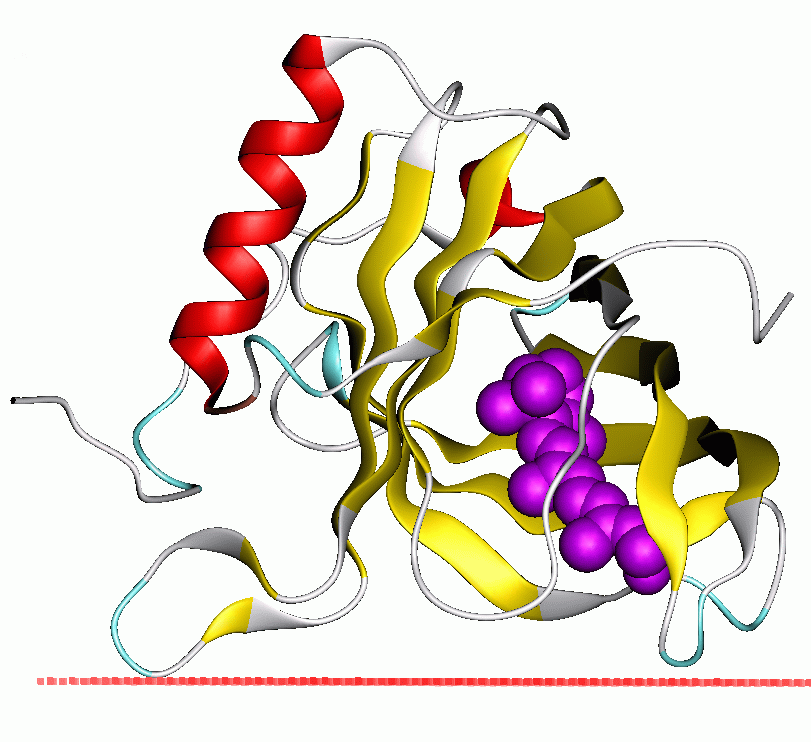
width =250
caption =Retinol -binding protein in a calculated membrane-bound state of the protein PDB3|1kt6
Pfam= PF00061
InterPro= IPR000566
SMART=
PROSITE = PDOC00187
SCOP = 1hms
TCDB =
OPM family=52
OPM protein= 1kt6
PDB=PDB3|1qy0A:34-173 PDB3|1qy1A:34-173 PDB3|1yp6A:34-173PDB3|1znkA:34-173 PDB3|1zneA:34-173 PDB3|2a2uD:35-174PDB3|1bj7 :29-168 PDB3|1e5pD:23-163 PDB3|1e06B:13-153PDB3|1gt4A:14-153 PDB3|1cj5A:32-173 PDB3|2akqB:32-173PDB3|2blg :32-173 PDB3|1b0o :32-173 PDB3|1exsA:34-171PDB3|1lf7A:48-186 PDB3|1iw2A:48-186 PDB3|1jzuA:31-171PDB3|1dfvA:48-193 PDB3|1x89C:48-193 PDB3|1x71A:48-193PDB3|1x8uB:48-193 PDB3|1epaA:34-174 PDB3|1epbA:34-174PDB3|1fen :21-171 PDB3|1erb :21-171 PDB3|1kt5A:21-171PDB3|1hbp :21-171 PDB3|1fel :21-171 PDB3|1fem :21-171PDB3|1kt3A:21-171 PDB3|1kt4A:21-171 PDB3|1hbq :21-171PDB3|1kt6A:21-171 PDB3|1kt7A:21-171 PDB3|1aqb :39-159PDB3|1brp :39-189 PDB3|1jyjA:39-189 PDB3|1brq :39-189PDB3|1jydA:39-189 PDB3|1rbp :39-189 PDB3|1iiuA:42-188PDB3|1lkeA:38-182PDB3|1z24A:24-172 PDB3|1gkaB:27-168 PDB3|1s44B:32-171PDB3|1obqB:32-171 PDB3|1i4uB:32-171 PDB3|1obuA:32-171PDB3|1s2pA:32-171 PDB3|1h91B:32-171 PDB3|1opbA:6-133PDB3|1eiiA:6-133 PDB3|1b4m :6-133 PDB3|1opaA:6-133PDB3|1kqwA:6-134 PDB3|1kqxA:6-134 PDB3|1lpjA:6-134PDB3|1crb :6-134 PDB3|1mx8A:6-134 PDB3|1gglA:6-133PDB3|1xcaB:5-137 PDB3|3cbsA:5-137 PDB3|1blr :5-137PDB3|2cbsA:5-137 PDB3|1bm5 :5-137 PDB3|1cbs :5-137PDB3|1cbq :5-137 PDB3|2cbrA:5-136 PDB3|1cbiA:5-136PDB3|1cbrA:5-136 PDB3|1ftpA:6-133 PDB3|1g5wA:6-132PDB3|2hmb :6-131 PDB3|1hmr :6-131 PDB3|1hms :6-131PDB3|1bwyA:6-132 PDB3|1fdqA:6-131 PDB3|1fe3A:6-131PDB3|1b56 :8-134 PDB3|1jjjA:8-134 PDB3|1mf9A:5-132PDB3|1o8vA:5-132 PDB3|1vyfA:5-132 PDB3|1vygA:5-132PDB3|1sa8A:36-131 PDB3|1ifb :4-131 PDB3|1ael :4-131PDB3|1dc9A:4-131 PDB3|2ifb :4-131 PDB3|1icm :4-131 PDB3|3ifbA:4-131PDB3|1kzwA:4-131 PDB3|1kzxA:4-131 PDB3|1mdc :4-131PDB3|1tvqA:4-125 PDB3|1mvgA:4-125 PDB3|1tw4A:4-125PDB3|1zryA:4-125 PDB3|1p6pA:4-125 PDB3|2f73E:4-127Pfam_box
Symbol = Lipocalin_2
Name = Lipocalin-like domain
width =
caption =
Pfam= PF08212
InterPro= IPR013208
SMART=
Prosite =
SCOP =
TCDB =
OPM family=52
OPM protein= 1qwd
PDB=PDB3|1qwdA:34-174 PDB3|2apd :37-182The lipocalins are a family of proteins which transport small hydrophobic molecules such as
steroid s, bilins,retinoid s, andlipids . They share limited regions of sequence homology and a common tertiary structure architecturecite journal |author=Pervaiz S, Brew K |title=Homology and structure-function correlations between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and serum retinol-binding protein and its relatives |journal=FASEB J. |volume=1 |issue=3 |pages=209–214 |year=1987 |pmid=3622999] cite journal |author=Nagata A, Igarashi M, Toh H, Urade Y, Hayaishi O |title=Structural organization of the gene for prostaglandin D synthase in the rat brain |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=89 |issue=12 |pages=5376–5380 |year=1992 |pmid=1608945 |doi=10.1073/pnas.89.12.5376] cite journal |author=Cowan SW, Jones TA, Newcomer ME |title=Crystallographic refinement of human serum retinol binding protein at 2A resolution |journal=Proteins |volume=8 |issue=1 |pages=44–61 |year=1990 |pmid=2217163 |doi=10.1002/prot.340080108] cite journal |author=Flower DR, Attwood TK, North AC |title=Structure and sequence relationships in the lipocalins and related proteins |journal=Protein Sci. |volume=2 |issue=5 |pages=753–761 |year=1993 |pmid=7684291] cite journal |author=Godovac-Zimmermann J |title=The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? |journal=Trends Biochem. Sci. |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=64–66 |year=1988 |pmid=3238752 |doi=10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-X] . This is an eight stranded antiparallel beta-barrel with a repeated + 1 topology enclosing an internal ligand binding site.These proteins are found in
gram negative bacteria,vertebrate cells, andinvertebrate cells, and in plants. Lipocalins have been associated with many biological processes, among themimmune response,pheromone transport, biologicalprostaglandin synthesis,retinoid binding, andcancer cell interactions.Function
Immune Response
Lipocalin proteins are involved in
inflammation anddetoxification processes caused by immune system activation in mammals. They are known respiratoryallergen s of mice, cats, dogs, horses, and other animals. Examples of lipocalin proteins involved in immune system responses include alpha-1-microglobulin, alpha-1-acid glycoprotein, and c8gamma. Structural information for many immune system influencing lipocalin proteins is available, while their exact role in biological systems is still somewhat unclear. Human allergenic reactions to lipocalins have not been extensively investigated.Pheromone Transport
The lipocalin family has been connected with the transport of mammalian
pheromones due to easily observable protein-pheromone interactions. Lipocalins are comparatively small in size, and are thus less complicated to study as opposed to large, bulky proteins. They can also bind to variousligands for different biological purposes. Lipocalins have been detected as carrier proteins of important pheromones in thenasal mucus of rodents, as well as mouse and rat urine.Prostaglandin Synthesis
This family of proteins plays a part in the biological system of terminal prostaglandin synthesis.
Retinoid Binding
Retinol , (vitamin A), is an importantmicronutrient that affects eyesight,cell differentiation , immune system function, bone growth, andtumor suppression. Retinol absorption and metabolism depends on lipocalins that act as binding proteins. Retinylesters (present in meats) andbeta-carotene (present in plants) are the two main sources of retinoids in the diet. After intake, they are converted to retinol, successively metabolized, and finally bound to retinol binding proteins (lipocalins) in theblood plasma .Cancer Cell Interactions
Because lipocalins are
extracellular proteins, theirintracellular effects are not obvious, and demand further study. However,lipophilic ligands, present assubstituent s to the lipocalins, have the ability to enter the cell, where they can act astumor protease inhibitors. This research suggests another possible route of protein-tumor investigations.Allergens
Some of the proteins in this family are allergens. Allergies are hypersensitivity reactions of the immune system to specific substances called allergens (such as pollen, stings, drugs, or food) that, in most people, result in no symptoms. A nomenclature system has been established for antigens (allergens) that cause IgE-mediated atopic allergies in humans [ [WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Subcommittee King T.P., Hoffmann D., Loewenstein H., Marsh D.G., Platts-Mills T.A.E., Thomas W. Bull. World Health Organ. 72:797-806(1994)] ] . This nomenclature system is defined by a designation that is composed of the first threeletters of the genus; a space; the first letter of the species name; a space and an Arabic number. In the event that two species names have identical designations, they are discriminated from one another by adding one or more letters (as necessary) to each species designation.
The allergens in this family include allergens with the following designations: Bla g 4, Bos d 2, Bos d 5, Can f 1, Can f 2, Equ c 1 and Equ c 2.
tructure
Although lipocalins are a broad family of greatly varied proteins, their three-dimensional structure is a unifying characteristic. Lipocalins have an eight-stranded, antiparallel, symmetrical β-barrel fold, which is in essence a
beta sheet which has been rolled into a cylindrical shape. Inside this barrel is located a ligand binding site, which plays an important role in the lipocalin classification as a transport protein. Lipocalins have desirable properties in terms ofcrystallization ability, molecular size, and commercial availability. Structure determination involves such processes as crystallization and multi-dimensional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy (NMR). Specifically, this NMR technique is known asNOESY (Nuclear Overhauser Effect Spectroscopy), and is used to determine structures of otherwise complex macromolecules such as proteins.If lipocalins are genetically engineered in the attempt to modify their binding properties, they are calledAnticalin s.Proteins included in the family
The name 'lipocalin' has been proposed for this protein family, but
cytosolic fatty acid binding protein s are also included. The sequences of most members of the family, the core or kernel lipocalins, are characterised by three short conserved stretches of residues, while others, the outlier lipocalin group, share only one or two of thesecite journal |author=Flower DR, Attwood TK, North AC |title=Mouse oncogeneprotein 24p3 is a member of the lipocalin protein family |journal=Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. |volume=180 |issue=1 |pages=69–74 |year=1991 |pmid=1834059 |doi=10.1016/S0006-291X(05)81256-2] cite journal |author=Flower DR, Attwood TK, North AC |title=Structure and sequence relationships in the lipocalins and related proteins |journal=Protein Sci. |volume=2 |issue=5 |pages=753–761 |year=1993 |pmid=7684291] . Proteins known to belong to this family include alpha-1-microglobulin (protein HC); alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid)cite journal |author=Wilting J, Kremer JM, Janssen LH |title=Drug binding to human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in health and disease |journal=Pharmacol. Rev. |volume=40 |issue=1 |pages=1–47 |year=1988 |pmid=3064105] ; aphrodisin;apolipoprotein D ;beta-lactoglobulin ;complement component C8 gamma chaincite journal |author=Peitsch MC, Tschopp J, Jenne DE, Haefliger JA |title=Structural and functional characterization of complement C8 gamma, a member of the lipocalin protein family |journal=Mol. Immunol. |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=123–131 |year=1991 |pmid=1707134 |doi=10.1016/0161-5890(91)90095-2] ; crustacyanincite journal |author=Keen JN, Caceres I, Eliopoulos EE, Zagalsky PF, Findlay JB |title=Complete sequence and model for the A2 subunit of the carotenoid pigment complex, crustacyanin |journal=Eur. J. Biochem. |volume=197 |issue=2 |pages=407–417 |year=1991 |pmid=2026162 |doi=10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15925.x] ; epididymal-retinoic acid binding protein (E-RABP)cite journal |author=Newcomer ME |title=Structure of the epididymal retinoic acid binding protein at 2.1 A resolution |journal=Structure |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=7–18 |year=1993 |pmid=8069623 |doi=10.1016/0969-2126(93)90004-Z] ; insectacyanin;odorant-binding protein (OBP); human pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2 globulin; probasin (PB), a prostatic protein;prostaglandin D synthase (EC number|5.3.99.2)cite journal |author=Boguski MS, Peitsch MC |title=The first lipocalin with enzymatic activity |journal=Trends Biochem. Sci. |volume=16 |issue=10 |pages=363–363 |year=1991 |pmid=1723819 |doi=10.1016/0968-0004(91)90149-P] ; purpurin; Von Ebner's gland protein (VEGP)cite journal |author=Kock K, Ahlers C, Schmale H |title=Structural organization of the genes for rat von Ebner's gland proteins 1 and 2 reveals their close relationship to lipocalins |journal=Eur. J. Biochem. |volume=221 |issue=3 |pages=905–916 |year=1994 |pmid=7514123 |doi=10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18806.x] ; and lizard epididymal secretory protein IV (LESP IV)cite journal |author=Morel L, Depeiges A, Dufaure JP |title=LESP, an androgen-regulated lizard epididymal secretory protein family identified as a new member of the lipocalin superfamily |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=268 |issue=14 |pages=10274–10281 |year=1993 |pmid=8486691] .Human proteins that contain lipocalin domain
AMBP ;APOD ;C8G ;CRABP1 ;CRABP2 ;FABP1 ;FABP2 ;FABP3 ;FABP4 ;FABP5 ;FABP6 ;FABP7 ;LCN1 ;LCN10 ;LCN12 ;LCN2 ;LCN8 ;LCN9 ;OBP2A ;OBP2B ;ORM1 ;ORM2 ;PAEP ;PERF15 ;PMP2 ;PTGDS ;RBP1 ;RBP2 ;RBP4 ;RBP5 ;RBP7 ;UNQ2541 ;References
Further reading
* The Lipocalins: A Review. The Edward Jenner Institute for Vaccine Research.
* Virtanen, Tuomas et al. "Important Animal Allergens Are Lipocalin Proteins: Why Are They Allergenic?" Department of Clinical Microbiology; University of Kuopio. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 1999.
* Bratt, T. "Lipocalins and Cancer". M&E Biotech. PubMed; 10/18/2000.
* Charron, Jean-Benoit Frenette et al. "Identification, Expression, and Evolutionary Analyses of Plant Lipocalins" Département des Sciences Biologiques, Université du Québec à Montréal. 10/04/2005.
* Novotny, M.V. et al. "Pheromones, binding proteins and receptor responses in rodents" Institute for Pheromone Research, University of Indiana, Bloomington. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2003.
* Diwan, J. "Review: Protein Structure". Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. 2003.ee also
Retinol binding protein External links
* [http://www.jenner.ac.uk/Lipocalin/crystalstructures/experiment.htm Experimentally Determined Lipocalin Structures]
* [http://www.jenner.ac.uk/Lipocalin/ The Lipocalin Website]
* [http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop/data/scop.b.c.je.b.html Lipocalins in SCOP database]
* - Calculated spatial positions of some Lipocalins in membranes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
