- Alta California
-
This article is about a historical territory. For the locale in Placer County, California, see Alta, California.
Coordinates: 38°N 115°W / 38°N 115°W
Alta California
Territorio de Alta California— Territory — Country  Mexico
MexicoCapital Monterey, California Division of the Californias 1804 Mexican Independence 1821 Government - First Spanish Governor José Joaquín de Arrillaga (1804–1814) - Last Spanish Governor Pablo Vicente de Solá (1815–1822) - First Mexican Governor Luís Antonio Argüello (1822–1825) - Last Mexican Governor Pío de Jesus Pico IV (1845–1846) Population (1847) - Total ~85,000 Alta California (English: Upper California) was a province and territory in the Viceroyalty of New Spain and later a territory and department in independent Mexico. The territory was created in 1769 out of the northern part of the former province of Las Californias, and consisted of the modern American states of California, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, western Colorado and southwestern Wyoming. The territory passed to American control after the Mexican–American War and ceased to exist with the creation of the State of California in 1850.
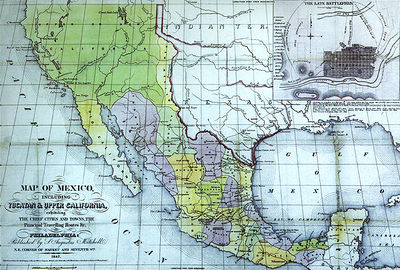 Map of Mexico. S. Augustus Mitchell, Philadelphia, 1847. New California is depicted with a north-eastern border at the meridian leading north of the Rio Grande headwaters.
Map of Mexico. S. Augustus Mitchell, Philadelphia, 1847. New California is depicted with a north-eastern border at the meridian leading north of the Rio Grande headwaters.
Contents
Spanish colonization
Further information: Spanish missions in CaliforniaAlthough the Spanish had explored the coastal area of Alta California as early as the sixteenth century and considered the area as the domain of the Spanish monarchy, they made no efforts to settle the area until the eighteenth century, when other European powers—in particular Russia—began exploring the area. In preparation for settlement, the northern, mainland region of Las Californias was granted to Franciscan missionaries to convert the Native population to Catholicism, following a model that had been used for over a century in Baja California. The Spanish Crown funded the construction and subsidized the operation of the missions, with the goal that the relocation, conversion and enforced labor of Native people would enforce Spanish rule. The first mission was established in San Diego in 1769. In 1773 a boundary between the Baja California missions, controlled by the Dominicans, and those of Alta California was set by Francisco Palóu. The missionary effort was followed by the construction of presidios and pueblos, which were to be manned and populated by Hispanic people. The first pueblo founded was San José in 1777, followed by Los Ángeles in 1781.
Spanish rule
By law mission land and property were to pass to the resident Native Americans of California after a period of about ten years, when the natives would become Spanish subjects. In the interim period, the Franciscans were to act as mission administrators who held the land in trust for the Native residents. The Franciscans, however, prolonged their control over the missions and ran them for more than sixty years. The transfer of property never occurred.[1][2]
As Spanish settlers grew in Alta California, the boundaries and natural resources of the mission properties became disputed. Conflicts between the Crown and the Church and between Natives and settlers arose. State and ecclesiastical bureaucrats debated over authority of the missions.[3] The Franciscan priests of Mission Santa Clara de Asís sent a petition to the governor in 1782 which stated that the Mission Indians owned both the land and cattle and represented the Ohlone against the Spanish settlers in nearby San José.[4] The priests reported that Indians' crops were being damaged by the pueblo settlers' livestock and that the settlers' livestock was also "getting mixed up with the livestock belonging to the Indians from the mission" causing losses. They advocated that the Natives owned property and had the right to defend it.[5]
Due to the growth of the Hispanic population in the Alta California by 1804, the Province of Las Californias, then a part of the Commandancy General of the Internal Provinces, was divided into two separate territorial administrations following Palóu's division between the Dominican and Franciscan missions. Diego de Borica is credited with defining Alta California and Baja California's official borders.[6] The Baja California peninsula became the territory of Baja California ("Lower California"), also referred to at times as Vieja California ("Old California"). The northern part became Alta California, also alternatively called Nueva California ("New California"). Because the eastern boundaries of the Las Californias Province were not defined, many maps from the period show its borders including parts of today's Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, western Colorado and southwestern Wyoming. The province would have bordered on the east with the Spanish settlements in Arizona and the Nuevo México Province.[7]
Ranchos
Main article: Ranchos of CaliforniaThe Spanish and later Mexican governments encouraged the establishment of large land grants, known as ranchos, for the raising of cattle and sheep. Hides and tallow from the livestock were the primary exports of California until the mid-19th century. The construction, ranching and domestic workers on these estates primarily consisted of Native Americans, who often learned to speak Spanish and ride horses. Unfortunately a large percentage of the population of Native Californians died from the Indian Reductions and European diseases. Under Spanish and Mexican rule the ranchos prospered and grew with the missions. Cattle ranchers and townspeople evolved into a unique Californio society.
Independent Mexico
Mexico gained independence from Spain in 1821 upon conclusion of the decade-long Mexican War of Independence. As the successor state to the Viceroyalty of New Spain, Mexico automatically included the provinces of Alta California and Baja California as territories. With the establishment of a republican government in 1823, Alta California, like many northern territories, was not recognized as one of the constituent States of Mexico because of its small population. The 1824 Constitution of Mexico refers to Alta California as a "territory". The capital of Alta California was Monterey. After a revolt led by Juan Bautista Alvarado in 1836, the territory was transformed into a department, which granted it more autonomy. The last Mexican governor of California was Pío Pico, who served until 1846.
Mexican-American War
Main article: Mexican-American WarIn the final decades of Mexican rule, American and European immigrants arrived and settled in Alta California. Those in Southern California mainly settled in and around the established coastal settlements and tended to intermarry with the Californios. In Northern California, they mainly formed new settlements further inland, especially in the Sacramento Valley, and these immigrants focused on fur-trapping and farming and kept apart from the Californios.
In 1846, following reports of the annexation of Texas to the United States, American settlers in inland Northern California formed an army, captured the Mexican garrison town of Sonoma, and declared independence there as the California Republic. At the same time, the United States and Mexico had gone to war, and forces of the United States Army and Navy entered into Alta California and overpowered the Mexican garrison and Californio militia units. The forces of the California Republic abandoned their independence and assisted the United States forces after their arrival. The California Republic was never recognized by any nation, and existed for less than one month, but its flag (the "Bear Flag") survives as the flag of the State of California.
In southern California, the Californios formed defensive units, which were victorious in the Siege of Los Angeles, the Battle of San Pasqual and the Battle of Domínguez Rancho. But subsequent encounters, the battles of Río San Gabriel and La Mesa, were indecisive. The southern Californios formally surrendered with the signing of the Treaty of Cahuenga on January 13, 1847. After twenty-seven years in independent Mexico, California was ceded to the United States in 1848 with the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. United States paid Mexico fifteen million dollars for the total lands ceded.
Spanish governors
- 1804 – 25 July 1814 José Joaquín de Arrillaga
- 25 July 1814 – 15 August 1815 José Darío Argüello (acting)
- 15 August 1815 – 11 April 1822 Pablo Vicente de Solá
For Mexican governors see List of pre-statehood governors of California
Flags that have passed over California

Spanish Empire, first by Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo in 1542, upon entering the bay of San Diego, then sailing north to the Russian River. Claim validated and area mapped in 1602 during the sea voyage of the San Agustín under Sebastián Vizcaíno. 
St. George Cross of England, June 1579, voyage of the Golden Hind under Captain Francis Drake at Bodega Bay, Tomales Bay, Drakes Bay or Bolinas Bay (exact location disputed).[8][9][10] 
October 1775, the Sonora at Bodega Bay, under Lt. Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra until 1821, when New Spain gained independence from the Spanish Empire. 
Russian-American Company, by Ivan Alexandrovich Kuskov, the founder of Fort Ross and, from 1812 to 1821, its colonial administrator. Note: There is an overlap of rule with the Mexican Empire (second item below), until the Russians sold Fort Ross in 1841 to John Sutter, and subsequently left the area in 1842. 
Argentina, by Hippolyte de Bouchard, a French corsair who occupied Monterey from November 24 to November 29, 1818, raising the Argentine flag there and claiming Alta California for that country. 
First Mexican Empire, August 24, 1821, Mexico under Emperor Agustín de Iturbide (October 1822, probable time new flag raised in California) until 1823. 
United Mexican States, 1823, until January 13, 1847 at Los Angeles. 
Bear Flag of the California Republic, June 14, 1846, at Sonoma until July 9, 1846. 
United States of America, July 9, 1846; see History of California. for even more Californian flags see: Flags over California, A History and Guide. Sacramento: State of California, Military Department. 2002. http://www.militarymuseum.org/Flags_Over_Ca.pdf.
In popular culture
- In the second half of the nineteenth century, there was a San Francisco-based newspaper called The Daily Alta California (or The Alta Californian). Mark Twain's first widely successful book, The Innocents Abroad, was an edited collection of letters written for this publication.
- In the 1998 film, The Mask of Zorro, fictional former Governor Don Rafael Montero plans to purchase the area from Mexico to set up an independent republic, roughly corresponding to historical Alta California.
- The Carl Barks comic book Donald Duck in Old California! provided a glimpse into the lives of the Californios.
See also
- Spanish and Mexican control
- Russian colonies
- United States control
- List of pre-statehood governors of California
- Bear Flag Revolt and the California Republic
Notes
- ^ Beebe, 2001, page 71
- ^ Fink, 1972, pages 63–64.
- ^ Milliken, 1995, page 2 footnote.
- ^ Milliken, 1995, page 72–73
- ^ Milliken, 1995, page 73, quoting Murguia and Pena [1782] 1955:400.
- ^ Field, Maria Antonia (1914). "California Under Spanish Rule". Chimes of Mission Bells. San Francisco, Calif.: Philopolis Press. http://www.books-about-california.com/Pages/Chimes_of_Mission_Bells/Chimes_of_Mission_Chap_04.html.
- ^ José Bandini, in a note to either Governor Echeandía or to his son, Juan Bandini, a member of the Territorial Deputation (legislature), noted that California was bounded "on the east, where the Government has not yet established the border line, by either the Colorado River or the great Sierra (Sierra Nevadas)." A Description of California in 1828 by José Bandini (Berkeley, Friends of the Bancroft Library, 1951), 3. Reprinted in Mexican California (New York, Arno Press, 1976). ISBN 0-405-09538-4
- ^ "Biographical Notes: Sir Francis Drake" Wandering Lizard. Consulted on 2008-08-07.
- ^ Sterling, Richard and Tom Downs. San Francisco: City Guide. (Lonely Planet, 2004), 233–234. ISBN 978-1-74104-154-5
- ^ Starr, Kevin. California: A History. (New York: Modern Library, 2005), 25. ISBN 0-679-64240-4
References
- Beebe, Rose Marie (2001). Lands of Promise and Despair: Chronicles of Early California, 1535–1846. Berkeley: Heyday Books. ISBN 1-890771-48-1.
- Fink, Augusta (1972). Monterey, The Presence of the Past. San Francisco, CA: Chronicle Books. ISBN 0877010723.
- Milliken, Randall (1995). A Time of Little Choice: The Disintegration of Tribal Culture in the San Francisco Bay Area 1769–1910. Menlo Park, CA: Ballena Press Publication. ISBN 0-87919-132-5
External links
- Alta California grants in UC Library System Calisphere
- Mexican Land Grants of Santa Clara County at the UC Berkeley Library
History of California to 1899 Precontact · First explorations · Later explorations · Spanish colonization · Russian colonization · Mexican rule · California Trail · Mexican-American War · U.S. rule · Gold Rush · Civil War
since 1900 By topic By city Los Angeles · Riverside · Sacramento · San Bernardino · San Diego · San Francisco · San Jose
Categories:- Pre-state history of California
- New Spain
- Colonial Mexico
- Colonial United States (Spanish)
- Mexican California
- Independent Mexico
- 1804 in Mexico
- Former political entities in North America
- Former Spanish colonies
- Former states of Mexico
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

