- T-84
-
Not to be confused with M-84, a Yugoslav main battle tank.
T-84 
An early model T-84 tank—later versions have reactive armour integrated more smoothly with the hull.Type Main battle tank Place of origin  Ukraine
UkraineService history In service 1999–present Used by Ukraine Production history Designer KMDB Designed 1993–94 Manufacturer Malyshev Factory Produced 1994–present Specifications (T-80[1]) Weight 46 tonnes Length 7.086 m (23 ft 3 in) Width 3.775 m (12 ft 5 in) Height 2.215 m (7 ft 3 in) Crew 3 Elevation +13°, -6° Armour Steel, composite, ERA Main
armamentKBA-3 125 mm smoothbore gun (43 rds) Secondary
armament7.62 mm KT-7.62 coaxial machine gun
12.7 mm KT-12.7 anti-aircraft machine gunEngine KMDB 6TD-2 6-cylinder diesel
1,200 hp (890 kW)Power/weight 26 hp/tonne Suspension Torsion-bars, hydraulic dampers Ground clearance 0.515 m (1 ft 8.3 in) Fuel capacity 1,300 l (290 imp gal; 340 US gal) Operational
range540 km (340 mi) Speed 65 km/h (40 mph) - 70 km/h (43 mph) Post-Cold War tanks- List
- Category
Under 120 mm gun
Under 50 tonnes
- Al-Zarrar
- Al-Khalid
- P'okpoong-Ho
- PT-91 Twardy
- T-84
- T-90
- Type 96
- Zulfiqar
Not in service
- Altay
- Black Eagle
- EE-T1 Osório
- K2 Black Panther
- M60-2000
- M-95 Degman
- M-84AS
- T-95
- Tank EX
- Type 10
- Type 99KM
The T-84 is a Ukrainian main battle tank, a development of the Soviet T-80 main battle tank. It was first built in 1994 and entered service in the Ukrainian Armed Forces in 1999. The T-84 is based on the diesel-engined T-80 version, the T-80UD. Its high-performance engine makes it one of the fastest MBTs in the world, with a power-to-weight ratio of about 26 horsepower per tonne (19 kW/t). The T-84 Oplot is an advanced version incorporating an armoured ammunition compartment in a new turret bustle; ten of these entered Ukrainian service in 2001. The T-84-120 Yatagan is a prototype model intended for export, mounting a 120 mm gun capable of firing standard NATO ammunition and guided missiles.
Contents
Production history
 BM Oplot guided onto a tank transporter.
BM Oplot guided onto a tank transporter.
The T-84 is the latest Ukrainian development of the T-80 series, designed by KMDB in Kharkiv (while the Russian T-90 is an advanced version of the T-72BM, with some T-80 features). A main design objective was to make Ukraine's arms industry independent of Russia's, after resulting difficulties in fulfilling a contract to supply T-80UD tanks to Pakistan.[2][3] An external difference from earlier models is the new Ukrainian welded turret, replacing the T-80's Russian-built cast turret (some T-80s shipped to Pakistan were fitted with the T-84 welded turret, but lack other T-84 improvements).[4]
The T-84's outstanding feature is the 26 hp/t power-to-weight ratio (compared to 18 hp/t of the contemporary Russian T-90, or 22 hp/t of the newer T-90S). It has inherited the nickname Flying Tank from the T-80. The tank is also designed to perform well in hot climates, and even includes an air-conditioned crew compartment (operating temperature range is claimed to be −40 °C to 55 °C).
Due to the collapse of Soviet Union, Malshev Factory was no longer able to obtain ceremic armour modules from Russia and only the initial batch of T-84 were produced with such. Instead, later batches of T-84's composite armour is composed of special purpose rubber sandwiched between steel and alloy plates. The exclusion of ceremic plate from the tank's armour may indicate downgraded protection compared to older models.
Ukraine has demonstrated several upgraded prototypes of this tank, intended for both domestic employment and international sale.
Variants
- T-84: Ukrainian upgrade of the T-80UD. New welded turret and Shtora-1 countermeasures suite, 1,200 hp (895 kW) 6TD-2 diesel engine.
- T-84U: Ukrainian upgrade of the T-84. New armoured side skirts, turret-conformal Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armour, auxiliary power unit, thermal imaging sight, satellite navigation, commander's laser range-finder, muzzle reference system, and other improvements.
- T-84 Oplot: T-84U with new western-style turret, but retaining the 125 mm gun. The Oplot tank features a new welded turret with separate crew and ammunition compartments with blowout panels on the ammunition compartment, a new bustle-mounted autoloader. A small number are in service with the Ukrainian Army.
- T-84-120 Yatagan: a prototype version of Oplot tailored for evaluation by the Turkish Army (prototype designation, KERN2-120). Mounts a 120 mm main gun which fires both NATO 120 mm rounds (like the M829 DU series) and a special 120 mm version of the AT-11 Sniper ATGM. It also has automated gear shifting in place of mechanical gear selector, driver's T-bar control replacing tiller bars, air conditioning, and projectile muzzle velocity sensor, as well as differences in the fire control system, communications, etc.
- T-84 Oplot-M (Modernized), or BM Oplot: The newest and most sophisticated version of the T-84 is an upgraded version of the "T-84 Oplot" mounting more advanced armor and new electronic countermeasure systems. One visible feature is the new PNK-6 panoramic tank sight.[5]
- BREM-84: armoured recovery vehicle
- BMU-84: bridgelayer tank
- BTMP-84: Heavy infantry fighting vehicle prototype based on the T-84 Oplot tank, with lengthened hull, an extra pair of road wheels, and a rear compartment for five infantrymen.
Users
 Bangladesh: In 2007 the Bangladesh Army began negotiations for the procurement of 76 T-84 Yatagan tanks in the first batch. The Bangladesh Army intends to induct a substantial number of Yatagans (200 to 300) over the next several years as part of its third generation main battle tank procurement program[6]
Bangladesh: In 2007 the Bangladesh Army began negotiations for the procurement of 76 T-84 Yatagan tanks in the first batch. The Bangladesh Army intends to induct a substantial number of Yatagans (200 to 300) over the next several years as part of its third generation main battle tank procurement program[6] Azerbaijan: January 2011, Azerbaijan showed interest in the Oplot main battle tank and the Defense Ministry of Ukraine has long been holding negotiations on this issue.[7]
Azerbaijan: January 2011, Azerbaijan showed interest in the Oplot main battle tank and the Defense Ministry of Ukraine has long been holding negotiations on this issue.[7]
 Thailand: March 2011, Royal Thai Army placed an order for 49 T-84s to replace existing U.S made M41A3. Up to 200 may be acquired. Although, no officially announcement is released from the Royal Thai Army yet.[8][9] So far, the government has just approved 7.155 billion Baht to purchase the first 49 T-84 Oplot main battle tanks to be assigned to the 2nd Cavalry battalion (Royal Guard at Fort Chakkraphongse, Prachinburi), the 4th Cavalry Battalion (Royal Guard at Kiakkai, Bangkok), the 8th Cavalry battalion (Fort Suranari, Nakhon Ratchasima), and the 9th Cavalry Battalion (Fort Ekathotsarot, Phitsanuloke). [10][11][12]
Thailand: March 2011, Royal Thai Army placed an order for 49 T-84s to replace existing U.S made M41A3. Up to 200 may be acquired. Although, no officially announcement is released from the Royal Thai Army yet.[8][9] So far, the government has just approved 7.155 billion Baht to purchase the first 49 T-84 Oplot main battle tanks to be assigned to the 2nd Cavalry battalion (Royal Guard at Fort Chakkraphongse, Prachinburi), the 4th Cavalry Battalion (Royal Guard at Kiakkai, Bangkok), the 8th Cavalry battalion (Fort Suranari, Nakhon Ratchasima), and the 9th Cavalry Battalion (Fort Ekathotsarot, Phitsanuloke). [10][11][12]
See also
- List of tanks
- List of Soviet tanks
- M-84AS
- M-95 Degman
References
- ^ Jane's Armour and Artillery, 2005–2006
- ^ T-84 MBT globalsecurity.com
- ^ Zaloga 2000, p 3.
- ^ Zaloga 2000, p 4.
- ^ http://photopribor.ck.ua/en/products/defense/btt/pnk-6/
- ^ Yatagan Main Battle Tank bdmilitary.com
- ^ Azerbaijan to purchase new Oplot tank from Ukraine
- ^ "New Ukraine tanks leave soldiers riled". Bangkok Post. http://www.bangkokpost.com/news/local/228666/new-ukraine-tanks-leave-soldiers-riled. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ^ Украина выиграла тендер на поставку 200 танков «Оплот» в Таиланд Segodnya.ua
- ^ "วาระแทรกซื้อรถถังยูเครน ครม.อนุมัติ 7.2 พันล้าน". The Nation (Thailand). http://breakingnews.nationchannel.com/read.php?newsid=508154&lang=T&cat=. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ^ "รถถัง7พันล้าน ครม.สั่งลา เอาใจกองทัพ". Thai Rath. http://www.thairath.co.th/content/pol/169018. Retrieved 5 May 2011.
- ^ "สำนึกในการซื้อ “อาวุธ” ของกองทัพ กรรมวิธีในการสร้างฉันทามติจากสังคม". มติชน. http://www.matichon.co.th/news_detail.php?newsid=1304570454&grpid=&catid=02&subcatid=0200. Retrieved 5 May 2011.
- Steven Zaloga and David Markov (2000). Russia's T-80U Main Battle Tank. Hong Kong: Concord. ISBN 962-361-656-2.
External links
 External images
External imagesThe T-84 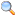
Photo of T-84 
T-84 and improved T-72 
Gunner's station from inside - T-84 Oplot Data Sheet and pictures
- Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau—Ukrainian producer of the T-80. KMDB's pages for T-80UD, T-84, Oplot, and BTMP-84.
- T-84 MBT at globalsecurity.org
Russian, Ukrainian, and former Soviet armoured fighting vehicles after World War II Tanks Armoured personnel carriers TrackedWheeledInfantry fighting vehicles Self-propelled artillery Guns- 2S1 Gvozdika
- 2S3 Akatsiya
- 2S4 Tyulpan
- 2S5 Giatsint
- 2S7 Pion
- 2S9 Nona
- 2S19 Msta
- 2S23 Nona-SVK
- 2S25 Sprut-SD
- 2S30 Iset
- 2S31 Vena
- ASU-57
- ASU-85
- A-222 Bereg
- 2K6 Luna (FROG-3/5)
- 9K52 Luna-M (FROG-7)
- 9K79 Tochka (SS-21 Scarab)
- R-400 Oka (SS-23 Spider)
- Iskander (SS-26 Stone)
- K-300P Bastion-P
Self-propelled anti-aircraft weapons GunsCategories:- Main battle tanks of the post–Cold War period
- Main battle tanks of Ukraine
- Tanks with autoloaders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
