- Chromocene
-
Chromocene 
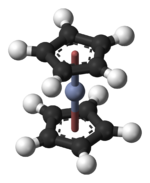 chromocene, bis(η5-cyclopentadienyl)chromiumOther namesCrCp2
chromocene, bis(η5-cyclopentadienyl)chromiumOther namesCrCp2Identifiers CAS number 1271-24-5 ChemSpider 71485 ChEBI CHEBI:30677 RTECS number GB7600000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Cr+2].[c-]1cccc1.c1[c-]ccc1
- InChI=1/2C5H5.Cr/c2*1-2-4-5-3-1;/h2*1-5H;/q2*-1;+2
Key: TYYBBNOTQFVVKN-UHFFFAOYAS
Properties Molecular formula C10H10Cr Molar mass 182.18 g/mol Appearance dark red crystals Density 1.43 g/cm3, solid Melting point 168-170 °C
Boiling point sublimes (under vacuum)
Solubility in water decomposes in water Structure Coordination
geometrypseudooctahedral
see FerroceneDipole moment 0 D Hazards EU classification  Xi
XiR-phrases R20/21/22, R36/37/38 S-phrases S26, S37/39, S45 Main hazards pyrophoric NFPA 704 Related compounds Related compounds Fe(C5H5)2
Ni(C5H5)2
Chromium(II) acetateExcept where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Chromocene is an organochromium compound with the formula Cr(C5H5)2, often abbreviated Cp2Cr. This sandwich compound is structurally similar to ferrocene but does not follow the 18-electron rule because it only has 16 electrons.[1] It also paramagnetic and highly reducing. Also like structurally related metallocenes, chromocene sublimes readily in a vacuum and is soluble in non-polar organic solvents.
It is prepared from chromium(II) chloride and cyclopentadienylsodium:
- CrCl2 + 2 NaC5H5 → Cr(C5H5)2 + 2 NaCl
Such syntheses are typically conducted in THF solution. The structure of the compound has been verified by X-ray crystallography; the average Cr-C bond length is 215.1(13) pm.[2]
The strongly reducing analogue decamethylchromocene, Cr[C5(CH3)5]2, is prepared analogously from LiC5(CH3)5.
Like some other metallocenes, the C5H5 ligands are displaceable in chromacene. Thus, chromocene in combination with silica gel gives the Union Carbide catalyst for the polymerization of ethylene, although other preparations exist for this important catalyst. The chromocene decomposes on the silica surface to generate high reactive organometallic centers that are responsible for the catalysis.
Safety
Chromium compounds are toxic, although Cr(VI) species are usually considered more dangerous than reduced chromium compounds. Chromocene is highly reactive toward air and could inflame upon exposure to the atmosphere.
References
- ^ C. Elschenbroich, A. Salzer ”Organometallics : A Concise Introduction” (2nd Ed) (1992) from Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. ISBN 3-527-28165-7
- ^ Kevin R. Flower, Peter B. Hitchcock "Crystal and molecular structure of chromocene (η5-C5H5)2Cr" Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 1996, volume 507, p. 275-277. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(95)05747-D.
Categories:- Organochromium compounds
- Metallocenes
- Cyclopentadienyl complexes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

